

新疆石油地质 ›› 2022, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (6): 640-653.doi: 10.7657/XJPG20220602
何海清1( ), 唐勇2, 邹志文3(
), 唐勇2, 邹志文3( ), 郭华军3, 徐洋3, 李亚哲3
), 郭华军3, 徐洋3, 李亚哲3
收稿日期:2022-07-27
修回日期:2022-08-30
出版日期:2022-12-01
发布日期:2022-11-22
通讯作者:
邹志文
E-mail:hehq@petrochina.com.cn;zouzw_hz@petrochina.com.cn
作者简介:何海清(1966-),男,甘肃临洮人,教授,油气勘探,(E-mail)基金资助:
HE Haiqing1( ), TANG Yong2, ZOU Zhiwen3(
), TANG Yong2, ZOU Zhiwen3( ), GUO Huajun3, XU Yang3, LI Yazhe3
), GUO Huajun3, XU Yang3, LI Yazhe3
Received:2022-07-27
Revised:2022-08-30
Online:2022-12-01
Published:2022-11-22
Contact:
ZOU Zhiwen
E-mail:hehq@petrochina.com.cn;zouzw_hz@petrochina.com.cn
摘要:
为评估准噶尔盆地中央坳陷西部风城组油气勘探前景,利用微量元素、岩心、岩石薄片、古地貌、测井相、地震相等的综合分析,开展了研究区风城组岩性组合和沉积相研究。结果表明,研究区风城组是在前陆构造背景、干旱—半干旱气候、水体盐度与水深呈周期性变化的环境下的扇三角洲—碱湖沉积。从坳陷边缘至中心,依次形成盆缘扇三角洲碎屑岩类、斜坡外前缘白云质岩类、斜坡高地火山岩类、低隆带白云质灰质滩坝混积岩类和中心湖盆碱层岩类。根据沉积特征,建立了风城组扇三角洲—碱湖沉积及演化模式。结合沉积相、岩相和油气勘探现状,研究区风城组可划分为盆缘超削带常规油气区、斜坡外前缘致密油气区、湖盆页岩油气区、低凸起周缘常规油气区和高地火山岩常规油气区,7 000 m以浅的勘探有利面积达1.2×104 km2,油气储量达十亿吨级,展现了研究区风城组全油气系统内巨大的勘探潜力。
中图分类号:
何海清, 唐勇, 邹志文, 郭华军, 徐洋, 李亚哲. 准噶尔盆地中央坳陷西部风城组岩相古地理及油气勘探[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2022, 43(6): 640-653.
HE Haiqing, TANG Yong, ZOU Zhiwen, GUO Huajun, XU Yang, LI Yazhe. Lithofacies Paleogeography and Petroleum Exploration of Fengcheng Formation in Western Central Depression of Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2022, 43(6): 640-653.
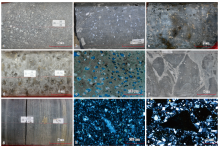
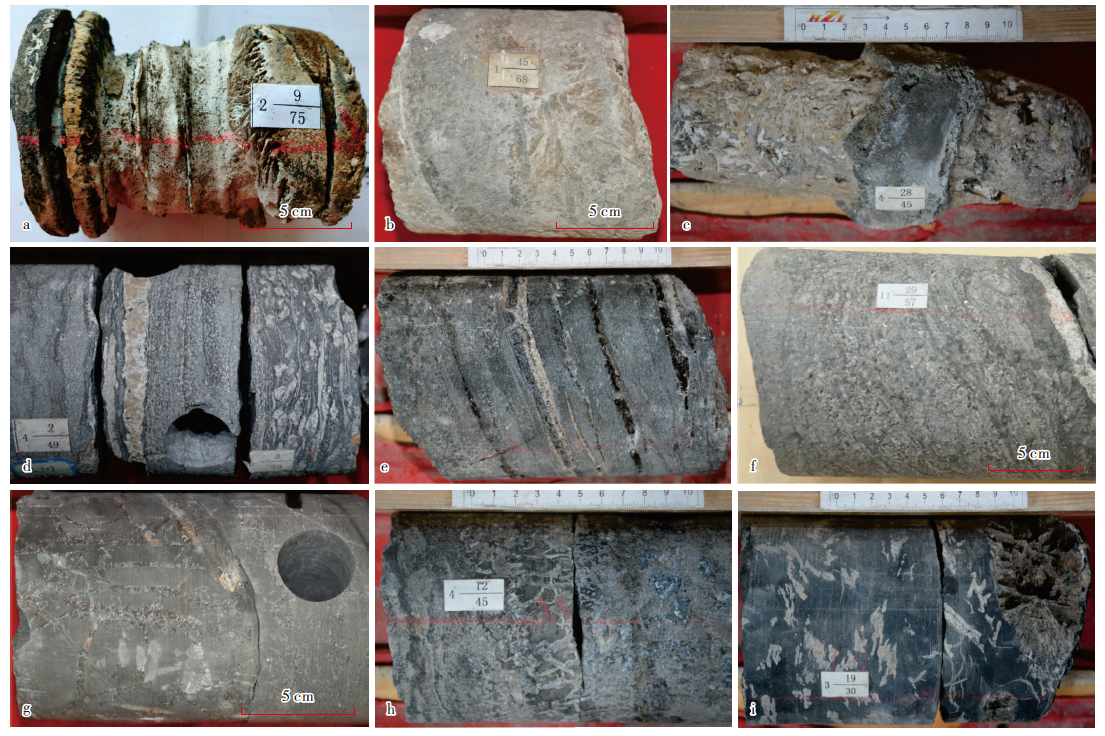
图2
中央坳陷西部风城组高地火山岩类组合主要岩性特征 a—灰色安山岩,玛页1井,5 028.10 m,风一段;b—灰色气孔杏仁状玄武岩,玛页1井,4 973.10 m,风一段;c—黑灰色气孔状油斑玄武岩,克207井,4 728.90 m,风二段;d—灰褐色油斑熔结凝灰岩,玛页1井,4 952.30 m,风一段;e—多孔熔结凝灰岩,夏72井,4 809.22 m,风一段,单偏光;f—沉火山角砾岩,玛页1井,4 994.50 m,风一段;g—灰色沉凝灰岩,玛页1井,4 940.00 m,风一段;h—沉凝灰岩,风南1井,4 195.88 m,风一段,正交偏光;i—含火山角砾凝灰质中砂岩,玛湖025井,4 254.10 m,风二段,正交偏光"
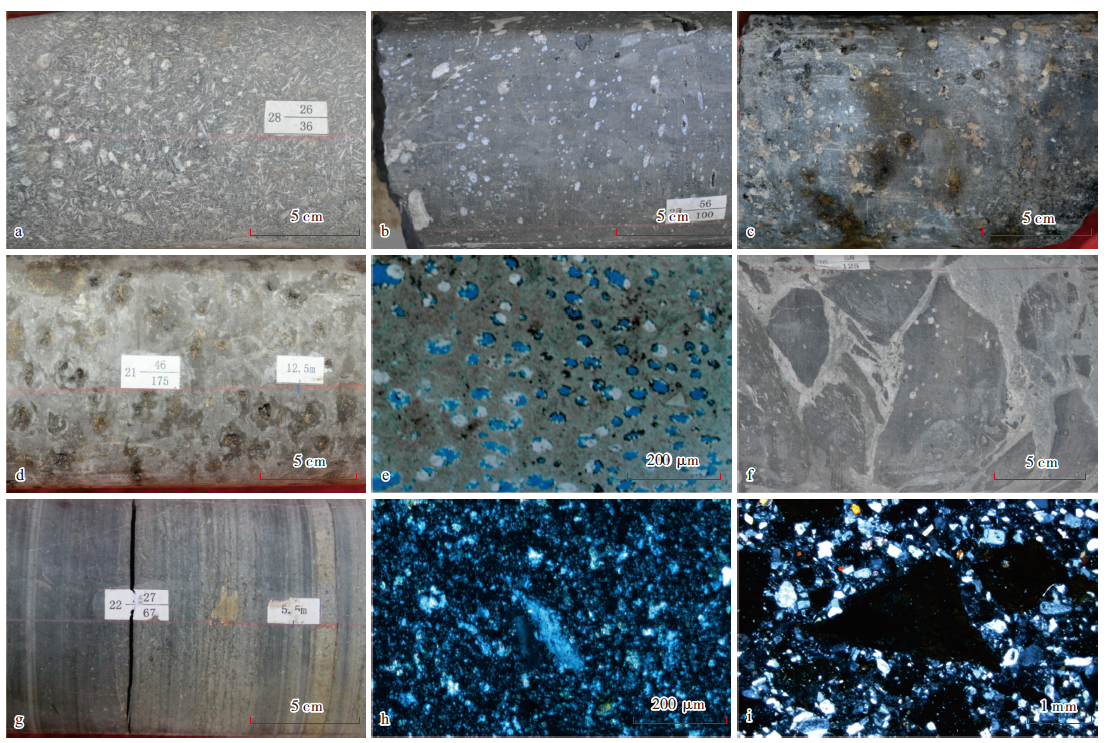
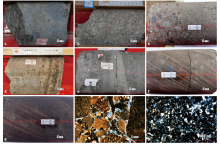
图3
中央坳陷西部风城组盆缘碎屑岩组合主要岩性特征 a—深灰色油迹砂砾岩,百泉1井(玛湖凹陷),4 101.10 m,风三段;b—浅灰色细砾岩,石西18井(盆1井西凹陷),5 000.10 m,风三段;c—褐色砂质中砾岩—中砂岩,沸石胶结,沙排3井(沙湾凹陷),4 723.90 m,风二段;d—褐灰色油斑白云质砂岩,风南409井,4 524.00 m,风二段;e—灰色荧光砂岩—砂砾岩,风南4井,4 582.50 m,风二段;f—灰褐色泥质粉砂岩,沙排3井,4 725.00 m,风二段;g—褐色泥岩,沙排3井,4 720.00 m,风二段;h—方沸石溶孔砂砾岩,含沥青,白261井,3 069.00 m,风二段,单偏光;i—白云质中砂岩,克891井,3 657.36 m,风二段,正交偏光"
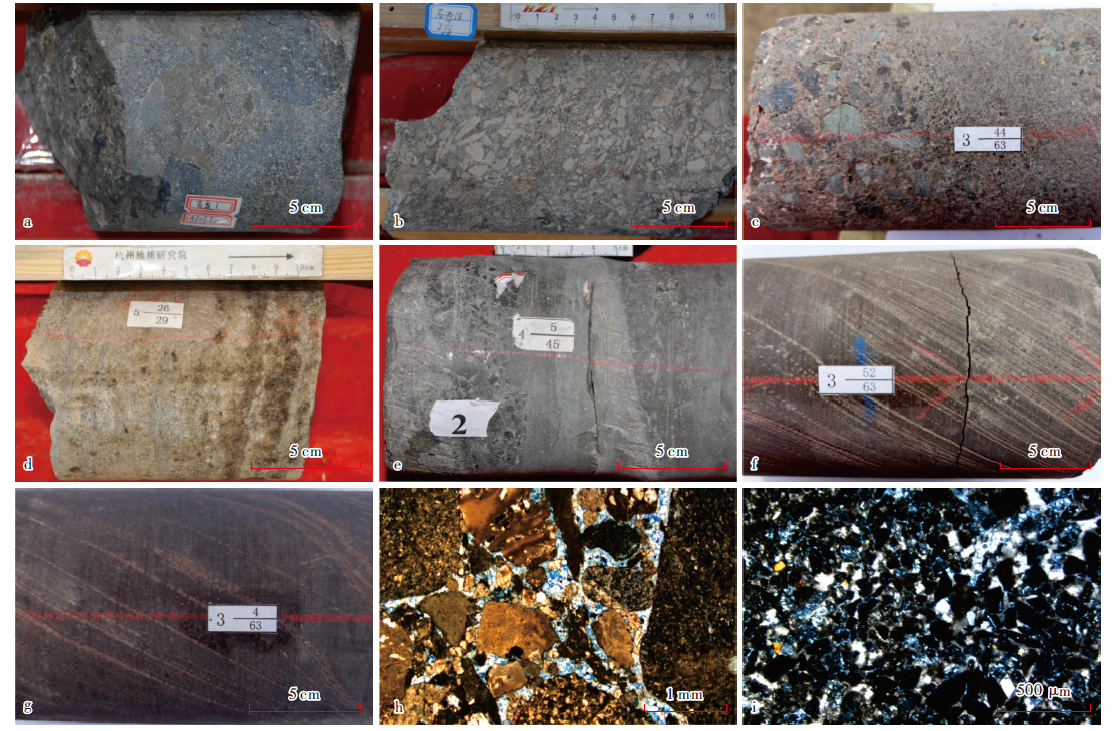

图4
中央坳陷西部风城组斜坡白云质岩类组合主要岩性特征 a—绿灰色灰质白云岩,见缝合线,下部为深灰色灰质泥岩,夏云1井,5 108.0 m,风二段;b—灰白色细晶白云岩,风南14井,4 034.6 m,风二段;c—凝灰质细晶白云岩,风南14井,白云石呈粉细晶粒状,4 034.6 m,风二段,正交偏光;d—灰色灰质泥粉晶白云岩,风南14井,4 059.7 m,风二段;e—泥粉晶白云岩,风南14井,4 059.7 m,风二段,单偏光;f—浅灰色含碱泥质白云岩,含凝灰质条带及碳钠钙石,风南14井,4 172.1 m,风二段;g—泥质粉晶白云岩,风南14井,见碳钠钙石,4 172.1 m,风二段;h—灰色白云质粉砂岩,风南14井,4 061.5 m,风二段;i—灰色斜层理白云质细砂岩,克207井,4 748.5 m,风二段"
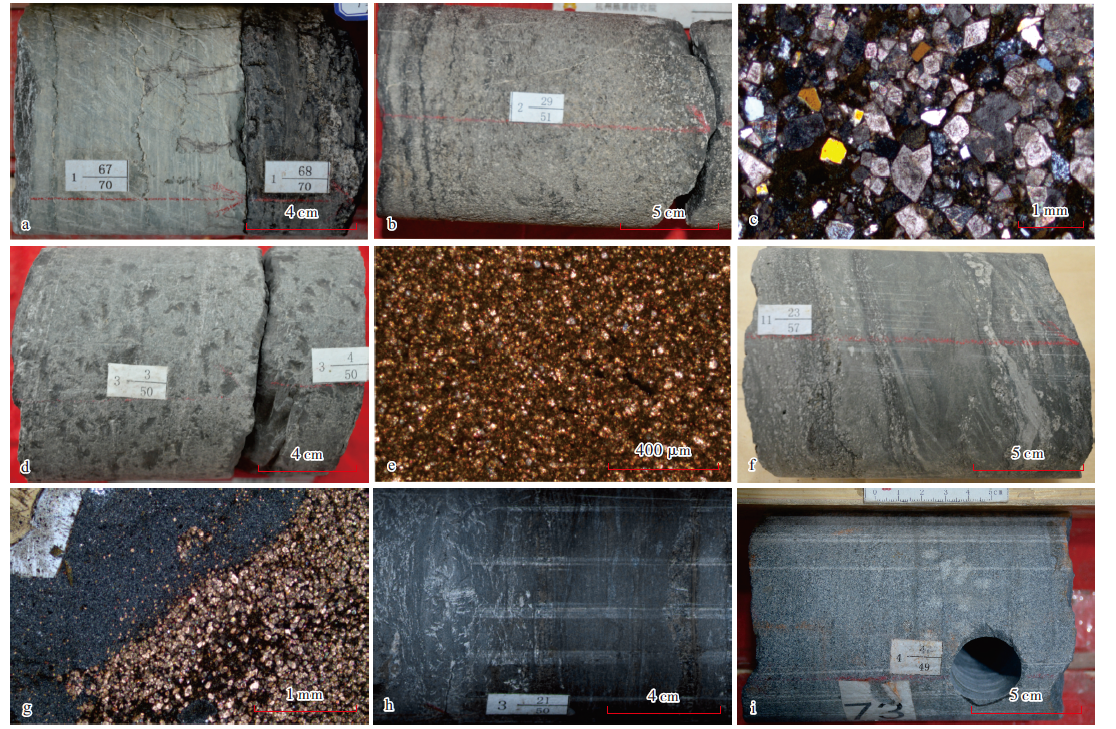


图5
中央坳陷西部风城组中心碱层岩类组合主要岩性特征 a—灰白色天然碱、碳氢钠石与深灰色泥岩互层,风云1井,5 229.1 m,风二段;b—灰白色放射状(玫瑰状)天然碱、碳氢钠石,风南5井,4 070.5 m,风二段;c—灰白色粗晶天然碱与灰色泥岩(竹节状),玛页2井,4 436.2 m,风二段;d—浅灰色含碱含白云质粉砂岩,中间碱层为天然碱与碳氢钠石,白色团块状、条带状为碳钠钙石等碱性矿物,克207井,4 854.4 m,风二段;e—灰色含顺层碱矿粉—细砂岩(部分碱矿被钻井液溶蚀),玛页2井,4 154.7 m,风二段;f—灰色含硅硼钠石泥岩,风南14井,4 173.0 m,风二段;g—灰色含碱矿凝灰质粉砂岩,网状裂缝中充填硅硼钠石、碳钠钙石,风城1井,4 275.0 m,风二段;h—灰色含碱矿凝灰质粉—细砂岩,玛页2井,4 435.1 m,风二段;i—灰色含撕裂状碱矿泥岩(硅硼钠石、碳钠钙石),底部有放射状碳氢钠石被钻井液溶蚀,玛湖52井,5 286.4 m,风二段"

| [1] | 秦志军, 陈丽华, 李玉文, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷下二叠统风城组碱湖古沉积背景[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2016, 37(1):1-6. |
| QIN Zhijun, CHEN Lihua, LI Yuwen, et al. Paleo-sedimentary setting of the Lower Permian Fengcheng alkali lake in Mahu sag,Junggar basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2016, 37(1):1-6. | |
| [2] |
曹剑, 雷德文, 李玉文, 等. 古老碱湖优质烃源岩:准噶尔盆地下二叠统风城组[J]. 石油学报, 2015, 36(7):781-790.
doi: 10.7623/syxb201507002 |
|
CAO Jian, LEI Dewen, LI Yuwen, et al. Ancient high-quality alkaline lacustrine source rocks discovered in the Lower Permian Fengcheng formation,Junggar basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2015, 36(7):781-790.
doi: 10.7623/syxb201507002 |
|
| [3] | 张志杰, 袁选俊, 汪梦诗, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷二叠系风城组碱湖沉积特征与古环境演化[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2018, 45(6):972-984. |
| ZHANG Zhijie, YUAN Xuanjun, WANG Mengshi, et al. Alkaline-lacustrine deposition and paleoenvironmental evolution in Permian Fengcheng formation at the Mahu sag,Junggar basin,NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2018, 45(6):972-984. | |
| [4] | 李威, 张元元, 倪敏婕, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷下二叠统古老碱湖成因探究:来自全球碱湖沉积的启示[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(6):1839-1 852. |
| LI Wei, ZHANG Yuanyuan, NI Minjie, et al. Genesis of alkaline lacustrine deposits in the Lower Permian Fengcheng formation of the Mahu sag,northwestern Junggar basin:insights from a comparison with the worldwide alkaline lacustrine deposits[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(6):1839-1 852. | |
| [5] | 王力宝, 厚刚福, 卞保力, 等. 现代碱湖对玛湖凹陷风城组沉积环境的启示[J]. 沉积学报, 2020, 38(5):911-922. |
| WANG Libao, HOU Gangfu, BIAN Baoli, et al. The role of modern alkaline lakes in explaining the sedimentary environment of the Fengcheng formation,Mahu depression[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2020, 38(5):911-922. | |
| [6] |
支东明, 唐勇, 郑孟林, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷风城组页岩油藏地质特征与成藏控制因素[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2019, 24(5):615-623.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2019.05.008 |
|
ZHI Dongming, TANG Yong, ZHENG Menglin, et al. Geological characteristics and accumulation controlling factors of shale reservoirs in Fengcheng formation,Mahu sag,Junggar basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2019, 24(5):615-623.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2019.05.008 |
|
| [7] | 陈磊, 杨镱婷, 汪飞, 等. 准噶尔盆地勘探历程与启示[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2020, 41(5):505-518. |
| CHEN Lei, YANG Yiting, WANG Fei, et al. Exploration history and enlightenment in Junggar basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2020, 41(5):505-518. | |
| [8] | 薛晶晶, 孙靖, 朱筱敏, 等. 准噶尔盆地二叠系风城组白云岩储集层特征及成因分析[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(4):755-761. |
| XUE Jingjing, SUN Jing, ZHU Xiaomin, et al. Characteristics andformation mechanism for dolomite reservoir of Permian Fengchengformation in Junggar basin[J]. Geoscience, 2012, 26(4):755-761. | |
| [9] | 朱世发, 朱筱敏, 陶文芳, 等. 准噶尔盆地乌—夏地区二叠系风城组云质岩类成因研究[J]. 高校地质学报, 2013, 19(1):38-45. |
| ZHU Shifa, ZHU Xiaomin, TAO Wenfang, et al. Origin of dolomitic reservoir rock in the Permian Fengcheng formation in Wu-Xia area of the Junggar basin[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2013, 19(1):38-45. | |
| [10] | 余宽宏, 操应长, 邱隆伟, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷早二叠世风城组沉积时期古湖盆卤水演化及碳酸盐矿物形成机理[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2016, 27(7):1248-1 263. |
| YU Kuanhong, CAO Yingchang, QIU Longwei, et al. Brine evolution of ancient lake and mechanism of carbonate minerals during the sedimentation of Early Permian Fengcheng formation in Mahu depression,Junggar basin,China[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2016, 27(7):1248-1 263. | |
| [11] | 唐勇, 郑孟林, 王霞田, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷风城组烃源岩沉积古环境[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2022, 33(5):677-692. |
| TANG Yong, ZHENG Menglin, WANG Xiatian, et al. Sedimentary paleoenvironment of source rocks of Fengcheng formation in Mahu sag,Junggar basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2022, 33(5):677-692. | |
| [12] | 尤兴弟. 准噶尔盆地西北缘风城组沉积相探讨[J]. 新疆石油地质, 1986, 7(1):47-52. |
| YOU Xingdi. Discuss on the Lower Permian Fengcheng formation in the northwest margin of Junggar basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 1986, 7(1):47-52. | |
| [13] | 鲁新川, 孙东, 夏维民, 等. 准噶尔盆地西北缘二叠系风城组白云岩化作用及其对储层影响[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2015, 26(2):52-61. |
| LU Xinchuan, SUN Dong, XIA Weimin, et al. The dolomitization of Permian Fengcheng formation and its effect on reservoir in northwestern Junggar basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2015, 26(2):52-61. | |
| [14] | 冯有良, 张义杰, 王瑞菊, 等. 准噶尔盆地西北缘风城组白云岩成因及油气富集因素[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2011, 38(6):685-692. |
| FENG Youliang, ZHANG Yijie, WANG Ruiju, et al. Dolomites genesis and hydrocarbon enrichment of the Fengcheng formation in the northwestern margin of Junggar basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2011, 38(6):685-692. | |
| [15] | 蒋宜勤, 文华国, 祁利祺, 等. 准噶尔盆地乌尔禾地区二叠系风城组盐类矿物和成因分析[J]. 矿物岩石, 2012, 32(2):105-114. |
| JIANG Yiqin, WEN Huaguo, QI Liqi, et al. Salt minerals and their genesis of the Permian Fengcheng formation in Urho area,Junggar basin[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 2012, 32(2):105-114. | |
| [16] | 潘晓添. 准噶尔盆地西北缘风城组湖相热液白云岩形成机理[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2013. |
| PAN Xiaotian. Forming mechanism of Fengcheng formation of lacusteine hydrothermal dolomite in the Junggar basin in northwestern margin[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2013. | |
| [17] | 王启宇, 牟传龙, 陈小炜, 等. 准噶尔盆地及周缘地区石炭系岩相古地理特征及油气基本地质条件[J]. 古地理学报, 2014, 16(5):655-671. |
| WANG Qiyu, MOU Chuanlong, CHEN Xiaowei, et al. Palaeogeographic characteristics and basic geological conditions of petroleum of the Carboniferous in Junggar basin and its adjacent areas[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2014, 16(5):655-671. | |
| [18] | 周进高, 席胜利, 邓红婴, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地寒武系—奥陶系深层海相碳酸盐岩构造-岩相古地理特征[J]. 天然气工业, 2020, 40(2):41-53. |
| ZHOU Jingao, XI Shengli, DENG Hongying, et al. Tectonic-lithofacies paleogeographic characteristics of Cambrian-Ordovician deep marine carbonate rocks in the Ordos basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2020, 40(2):41-53. | |
| [19] | 马慧, 苏中堂, 梁茹, 等. 川西地区栖霞组白云岩成因新证据:稀土元素地球化学特征[J]. 天然气工业, 2021, 41(12):49-59. |
| MA Hui, SU Zhongtang, LIANG Ru, et al. New evidence for the genesis of Qixia formation dolomites in the western Sichuan basin:geochemical characteristics of rare earth elements[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2021, 41(12): 49-59. | |
| [20] | 刘俊英, 曹励明, 李兆麟, 等. 元素地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1984:422-428. |
| LIU Junying, CAO Liming, LI Zhaolin, et al. Elemental geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1984:422-428. | |
| [21] | MCCULLOCH M, CAPPOM, AUMEND J, et al. Tracing the life history of individual barramundi using laser ablation MC-ICP-MS Sr-isotopic and Sr/Ba ratios in otoliths[J]. Marine & Freshwater Research, 2005, 56(5):637-644. |
| [22] |
LEVENTHAL J S. Relationship between inferred redox potential of the depositional environment and geochemistry of the Upper Pennsylvanian(Missourian) stark shale member of the Dennis limestone,Wabaunsee County,Kansas,USA[J]. Chemical Geology, 1992, 99(1/2/3):65-82.
doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(92)90031-Y |
| [23] | 谢继容, 李亚, 杨跃明, 等. 川西地区二叠系火山碎屑岩规模储层发育主控因素与天然气勘探潜力[J]. 天然气工业, 2021, 41(3):48-57. |
| XIE Jirong, LI Ya, YANG Yueming, et al. Main controlling factors and natural gas exploration potential of Permian scale volcanoclastic reservoirs in the western Sichuan basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2021, 41(3):48-57. | |
| [24] | 黄芸, 梁舒艺, 贾春明, 等. 准噶尔盆地改造残留古火山机构判识与油气勘探实践[J]. 天然气工业, 2020, 40(3):30-37. |
| HUANG Yun, LIANG Shuyi, JIA Chunming, et al. Identification and oil and gas exploration practices of reworked residual paleovolcanic edifice in the Junggar basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2020, 40(3):30-37. | |
| [25] | 夏茂龙, 文龙, 李亚, 等. 四川盆地简阳地区二叠系火山喷发旋回、环境与模式[J]. 天然气工业, 2020, 40(9):11-22. |
| XIA Maolong, WEN Long, LI Ya, et al. Permian volcanic eruption cycle,environment and model in the Jianyang area of the Sichuan basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2020, 40(9):11-22. | |
| [26] | 朱世发, 朱筱敏, 刘继山, 等. 富孔熔结凝灰岩成因及油气意义:以准噶尔盆地乌—夏地区风城组为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2012, 39(2):162-171. |
| ZHU Shifa, ZHU Xiaomin, LIU Jishan, et al. Genesis and hydrocarbon significance of vesicular ignimbrite:a case study from Fengcheng formation,Wu-Xia area,Junggar basin,NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2012, 39(2):162-171. | |
| [27] | 杨智峰, 唐勇, 郭旭光, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷二叠系风城组页岩油赋存特征与影响因素[J]. 石油实验地质, 2021, 43(5):784-796. |
| YANG Zhifeng, TANG Yong, GUO Xuguang, et al. Occurrence states and potential influencing factors of shale oil in the Permian Fengcheng formation of Mahu sag,Junggar basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2021, 43(5):784-796. | |
| [28] | 刘英辉. 准噶尔盆地乌—夏地区风城组云质岩类沉积环境及成因探讨[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2022, 52(1):80-93. |
| LIU Yinghui. Origin of dolomitic tuff in Permian Fengcheng formation in Wu-Xia area of Junggar basin[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2022, 52(1):80-93. | |
| [29] | 支东明, 唐勇, 何文军, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷风城组常规—非常规油气有序共生与全油气系统成藏模式[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2021, 48(1):38-51. |
| ZHI Dongming, TANG Yong, HE Wenjun, et al. Orderly coexistence and accumulation models of conventional and unconventional hydrocarbons in Lower Permian Fengcheng formation,Mahu sag,Junggar basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2021, 48(1):38-51. | |
| [30] | 何文军, 钱永新, 赵毅, 等. 玛湖凹陷风城组全油气系统勘探启示[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2021, 42(6):641-655. |
| HE Wenjun, QIAN Yongxin, ZHAO Yi, et al. Exploration implications of total petroleum system in Fengcheng formation,Mahu sag,Junggar basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2021, 42(6):641-655. |
| [1] | 阿力甫江·热合木吐力, 潘龙, 李献民, 林娟, 马晶晶, 窦强峰. 基于双平方根算子的速度建模方法及应用[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2023, 44(1): 119-124. |
| [2] | 况昊, 周润驰, 王钧民, 刘豪, 谭先锋, 蔡鑫勇, 肖振兴. 玛湖凹陷与沙湾凹陷上乌尔禾组储集层差异及成因[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2023, 44(1): 18-24. |
| [3] | 金之钧, 梁新平, 王小军, 朱如凯, 张元元, 刘国平, 高嘉洪. 玛湖凹陷风城组页岩油富集机制与甜点段优选[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2022, 43(6): 631-639. |
| [4] | 唐勇, 雷德文, 曹剑, 刘寅, 黄立良, 李卉. 准噶尔盆地二叠系全油气系统与源内天然气勘探新领域[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2022, 43(6): 654-662. |
| [5] | 何文军, 宋永, 汤诗棋, 尤新才, 白雨, 赵毅. 玛湖凹陷二叠系风城组全油气系统成藏机理[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2022, 43(6): 663-673. |
| [6] | 龚德瑜, 刘海磊, 杨海波, 李宗浩, 王瑞菊, 吴卫安. 准噶尔盆地风城组烃源岩生气潜力与天然气勘探领域[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2022, 43(6): 674-683. |
| [7] | 蒋文龙, 阿布力米提·依明, 卞保力, 王韬, 任海姣, 韩杨. 准噶尔盆地西北缘风城组烃源岩热演化生物标志化合物变化及意义[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2022, 43(6): 684-692. |
| [8] | 钱门辉, 王绪龙, 黎茂稳, 李志明, 冷筠莹, 孙中良. 玛页1井风城组页岩含油性与烃类赋存状态[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2022, 43(6): 693-703. |
| [9] | 单祥, 窦洋, 晏奇, 陈希光, 彭博, 易俊峰. 玛南斜坡区风城组致密油藏储集层特征及控制因素[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2022, 43(6): 704-713. |
| [10] | 邹阳, 戚艳平, 宋栋, 陈文顺, 韦盼云. 玛页1井风城组页岩油藏地质特征及甜点评价[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2022, 43(6): 714-723. |
| [11] | 雷海艳, 齐婧, 周妮, 陈俊, 孟颖, 张锡新, 陈锐兵. 玛湖凹陷玛页1井风城组富硅页岩成因及其油气意义[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2022, 43(6): 724-732. |
| [12] | 刘财广, 季瑞雪, 王伟, 张融. 玛湖凹陷风城组页岩油产量影响因素及甜点评价[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2022, 43(6): 733-742. |
| [13] | 毛锐, 申子明, 张浩, 陈山河, 樊海涛. 基于岩性扫描测井的混积岩岩性识别——以玛湖凹陷风城组为例[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2022, 43(6): 743-749. |
| [14] | 余佩蓉, 郑国庆, 孙福泰, 王振林. 玛湖凹陷风城组页岩油藏水平井压裂裂缝扩展模拟[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2022, 43(6): 750-756. |
| [15] | 于江龙, 陈刚, 吴俊军, 李维, 杨森, 唐廷明. 玛湖凹陷风城组页岩油地质工程甜点地震预测方法及应用[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2022, 43(6): 757-766. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||