

新疆石油地质 ›› 2025, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (3): 296-307.doi: 10.7657/XJPG20250306
曹江骏a,b( ), 张道锋a,b, 王继平a,b, 周游b,c, 李笑天a,b, 李娅a,b, 范倩倩a,b, 董倩云a,b
), 张道锋a,b, 王继平a,b, 周游b,c, 李笑天a,b, 李娅a,b, 范倩倩a,b, 董倩云a,b
收稿日期:2024-12-04
修回日期:2024-12-17
出版日期:2025-06-01
发布日期:2025-06-13
作者简介:曹江骏(1993-),男,陕西西安人,工程师,博士,沉积与储层地质学,(Tel)029-86978132(Email)基金资助:
CAO Jiangjuna,b( ), ZHANG Daofenga,b, WANG Jipinga,b, ZHOU Youb,c, LI Xiaotiana,b, LI Yaa,b, FAN Qianqiana,b, DONG Qianyuna,b
), ZHANG Daofenga,b, WANG Jipinga,b, ZHOU Youb,c, LI Xiaotiana,b, LI Yaa,b, FAN Qianqiana,b, DONG Qianyuna,b
Received:2024-12-04
Revised:2024-12-17
Online:2025-06-01
Published:2025-06-13
摘要:
庆阳气田二叠系山1段埋藏深度大,成岩作用复杂,成岩-孔隙演化差异大,对有利储集层认识不清晰。利用铸体薄片、扫描电镜、高压压汞、阴极发光、自生黏土矿物X射线衍射等资料,结合前人研究成果,对庆阳气田山1段成岩作用进行研究。结果表明:庆阳气田山1段从西南至东北依次发育曲流河三角洲平原亚相及前缘亚相,前缘亚相储集层较平原亚相储集层而言,填隙物含量低,孔隙发育,孔喉结构好,物性较高;沉积作用控制了储集层的初始孔隙度,差异性成岩-孔隙演化影响了储集层的致密化程度,前缘亚相储集层初始孔隙度较高,压实-胶结作用降低了36.34%的孔隙度,溶蚀作用升高了4.28%的孔隙度,现今平均孔隙度为7.13%,平原亚相储集层初始孔隙度较低,压实-胶结作用降低了37.72%的孔隙度,溶蚀作用升高了3.65%的孔隙度,现今平均孔隙度为4.43%;前缘亚相储集层经历了中等压实作用降低孔隙度—中等胶结作用降低孔隙度—中等溶蚀作用升高孔隙度的致密化过程,储集层质量较好;平原亚相储集层经历了强压实作用降低孔隙度—中等胶结作用降低孔隙度—弱溶蚀作用升高孔隙度的致密化过程,储集层质量较差。
中图分类号:
曹江骏, 张道锋, 王继平, 周游, 李笑天, 李娅, 范倩倩, 董倩云. 庆阳气田山1段差异性成岩作用及其对储集层的影响[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(3): 296-307.
CAO Jiangjun, ZHANG Daofeng, WANG Jiping, ZHOU You, LI Xiaotian, LI Ya, FAN Qianqian, DONG Qianyun. Differential Diagenesis of Shan-1 Member and Its Impact on Reservoirs in Qingyang Gas Field[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2025, 46(3): 296-307.
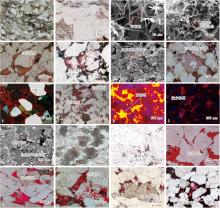
图7
庆阳气田山1段储集层成岩作用 a—塑性岩屑颗粒被挤压变形,呈假杂基充填孔隙,H4井,平原亚相,4 241.2 m,单偏光;b—刚性石英颗粒被挤压破碎,L43井,前缘亚相,4 156.1 m,单偏光;c—丝发状伊利石胶结,L46井,平原亚相,4 269.5 m,扫描电镜;d—蜂窝状伊蒙混层胶结,L46井,前缘亚相,4 269.5 m,扫描电镜;e—绿泥石以薄膜状附着于孔隙表面,Q2井,前缘亚相,3 975.8 m,单偏光;f—针叶状绿泥石胶结,L2-45井,平原亚相,3 835.4 m,单偏光;g—六方板状高岭石胶结,L20井,前缘亚相,3 848.5 m,扫描电镜;h—高岭石晶间微孔,L47井,平原亚相,4 000.2 m,单偏光;i—早期方解石基底式胶结,L5井,前缘亚相,4 028.0 m,正交偏光;j—晚期铁方解石胶结,L3井,前缘亚相,4 079.8 m,单偏光;k—早期方解石发橙黄色光,L1井,平原亚相,4 258.0 m,阴极发光;l—晚期铁方解石发橘红色光,L27井,平原亚相,4 392.1 m,阴极发光;m—马鞍状铁白云石,L20井,前缘亚相,4 018.5 m,扫描电镜;n—块状菱铁矿胶结,Q5井,平原亚相,4 298.1 m,单偏光;o—Ⅲ级石英加大边,H1井,前缘亚相,3 699.6 m,单偏光;p—石英单晶胶结,L38井,前缘亚相,4 386.3 m,单偏光;q—粒间溶孔,L38井,前缘亚相,4 385.5 m,单偏光;r—长石溶孔,C3-4井,平原亚相,3 826.9 m,单偏光;s—岩屑溶孔,H30井,平原亚相,3 937.9 m,单偏光;t—杂基溶孔,L6-7井,平原亚相,4 602.2 m,单偏光。"

| [1] | HUANG Yanqing, WANG Ai, XIAO Kaihua, et al. Types and genesis of sweet spots in the tight sandstone gas reservoirs:Insights from the Xujiahe formation,northern Sichuan Basin,China[J]. Energy Geoscience, 2022, 3(3):270-281. |
| [2] | 郭绪杰, 支东明, 毛新军, 等. 准噶尔盆地煤岩气的勘探发现及意义[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2021, 26(6):38-49. |
|
GUO Xujie, ZHI Dongming, MAO Xinjun, et al. Discovery and significance of coal measure gas in Junggar Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2021, 26(6):38-49.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2021.06.003 |
|
| [3] | ZHANG Jinchuan, LI Zhen, WANG Dongsheng, et al. Shale gas accumulation patterns in China[J]. Natural Gas Industry B, 2023, 10(1):14-31. |
| [4] | 李妍蓉, 李靖, 苏文杰, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地伊陕斜坡太原组碳酸盐岩气藏富集规律[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2023, 44(5):509-516. |
| LI Yanrong, LI Jing, SU Wenjie, et al. Natural gas enrichment in carbonate gas reservoirs of Taiyuan formation in Yishaan slope,Ordos Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2023, 44(5):509-516. | |
| [5] | 付金华, 李明瑞, 张雷, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地陇东地区铝土岩天然气勘探突破与油气地质意义探索[J]. 天然气工业, 2021, 41(11):1-11. |
| FU Jinhua, LI Mingrui, ZHANG Lei, et al. Breakthrough in the exploration of bauxite gas reservoir in Longdong area of the Ordos Basin and its petroleum geological implications[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2021, 41(11):1-11. | |
| [6] | CUI Gaixia, XU Shouyu, WEI Qinlian, et al. The influence of diagenesis on the quality of tight sandstone reservoirs in Longdong,Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Petroleum Exploration and Production Technology, 2024, 14:3331-3348. |
| [7] | 周港, 程甜, 李杰, 等. 胜北洼陷三间房组致密储集层成岩作用及孔隙演化[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2023, 44(3):289-298. |
| ZHOU Gang, CHENG Tian, LI Jie, et al. Diagenesis and pore evolution of tight reservoirs of Sanjianfang formation in Shengbei subsag[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2023, 44(3):289-298. | |
| [8] | NAGTEGAL P J C. Relationship of facies and reservoir quality in Rotliegendes desert sandstones,southern North Sea region[J]. Journal of Petroleum Geology, 1979, 2(10):145-158. |
| [9] | 李杪, 侯云东, 罗静兰, 等. 致密砂岩储层埋藏-成岩-油气充注演化过程与孔隙演化定量分析:以鄂尔多斯盆地东部上古生界盒8 段天然气储层为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2016, 37(6):882-892. |
| LI Miao, HOU Yundong, LUO Jinglan, et al. Burial,diagenesis,hydrocarbon charging evolution process and quantitative analysis of porosity evolution:A case study from He 8 tight sand gas reservoir of the Upper Paleozoic in eastern Ordos Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2016, 37(6):882-892. | |
| [10] | FU Yong, LUO Jinglan, SHI Xiaofan, et al. Implications of lithofacies and diagenetic evolution for reservoir quality:A case study of the Upper Triassic Chang 6 tight sandstone,southeastern Ordos Basin,China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2022, 218(11):1-23. |
| [11] |
范彩伟, 曹江骏, 罗静兰, 等. 异常高压下海相重力流致密砂岩非均质性特征及其影响因素:以莺歌海盆地LD10区中新统黄流组储集层为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2021, 48(5):903-915.
doi: 10.11698/PED.2021.05.03 |
| FAN Caiwei, CAO Jiangjun, LUO Jinglan, et al. Heterogeneity and influencing factors of marine gravity flow tight sandstone under abnormally high pressure:A case study from the Miocene Huangliu formation reservoirs in LD10 area,Yinggehai Basin,South China Sea[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2021, 48(5):903-915. | |
| [12] | 曹江骏, 罗静兰, 范彩伟, 等. 深部热流体活动对储层成岩作用及孔隙演化的影响:以莺歌海盆地LDX区中新统黄流组为例[J]. 地学前缘(中国地质大学(北京);北京大学), 2022, 29(4):412-429. |
| CAO Jiangjun, LUO Jinglan, FAN Caiwei, et al. Deep thermal fluid activity and its influence on the diagenesis and pore evolution of reservoir:A case study from the Miocene Huangliu formation reservoir in LDX area,Yinggehai Basin,the northern South China Sea[J]. Earth Science Frontiers(China University of Geosciences(Beijing);Peking University), 2022, 29(4):412-429. | |
| [13] | 李弛, 罗静兰, 胡海燕, 等. 热动力条件对白云凹陷深水区珠海组砂岩成岩演化过程的影响[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(2):572-587. |
| LI Chi, LUO Jinglan, HU Haiyan, et al. Thermodynamic impact on deepwater sandstone diagenetic evolution of Zhuhai formation in Baiyun sag,Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Earth Science, 2019, 44(2):572-587. | |
| [14] | 段志强, 夏辉, 王龙, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地庆阳气田山1段储集层特征及控制因素[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2022, 43(3):285-293. |
| DUAN Zhiqiang, XIA Hui, WANG Long, et al. Reservoir characteristics and controlling factors of Shan 1 member in Qingyang gas field,Ordos Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2022, 43(3):285-293. | |
| [15] | 夏辉, 王龙, 张道锋, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地庆阳气田二叠系山西组1段层序结构与沉积演化及其控制因素[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2022, 43(6):1397-1412. |
| XIA Hui, WANG Long, ZHANG Daofeng, et al. Sequence architecture,sedimentary evolution and controlling factors of the Permian Shan-1 member,Qingyang gas field,southwestern Ordos Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2022, 43(6):1397-1412. | |
| [16] | 李进步, 王继平, 王龙, 等. 古地貌恢复及其对三角洲前缘沉积砂体的控制作用:以鄂尔多斯盆地庆阳气田二叠系山西组13亚段为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2021, 42(5):1136-1145. |
| LI Jinbu, WANG Jiping, WANG Long, et al. Paleogeomorphologic restoration and its controlling effect on deposition of delta-front sand bodies:A case study of Shan 13 sub-member of the Permian Shanxi formation,Qingyang gas field,Ordos Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2021, 42(5):1136-1145. | |
| [17] |
曹江骏, 陈朝兵, 罗静兰, 等. 自生黏土矿物对深水致密砂岩储层微观非均质性的影响:以鄂尔多斯盆地西南部合水地区长6油层组为例[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2020, 32(6):36-49.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20200604 |
|
CAO Jiangjun, CHEN Chaobing, LUO Jinglan, et al. Impact of authigenic clay minerals on micro-heterogeneity of deep water tight sandstone reservoirs:A case study of Triassic Chang 6 oil reservoir in Heshui area,southwestern Ordos Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2020, 32(6):36-49.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20200604 |
|
| [18] |
付金华, 魏新善, 罗顺社, 等. 庆阳深层煤成气大气田发现与地质认识[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2019, 46(6):1047-1061.
doi: 10.11698/PED.2019.06.04 |
| FU Jinhua, WEI Xinshan, LUO Shunshe, et al. Discovery and geological knowledge of the large deep coal-formed Qingyang gas field,Ordos Basin,NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2019, 46(6):1047-1061. | |
| [19] |
JIANG Fujie, JIA Chengzao, PANG Xiongqi, et al. Upper Paleozoic total petroleum system and geological model of natural gas enrichment in Ordos Basin,NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2023, 50(2):281-292.
doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(23)60387-8 |
| [20] | FOLK R L. Petrology of sedimentary rocks:Austin[M]. Texas,USA: Hemphill Publishing Company, 1968. |
| [21] | 中华人民共和国石油天然气行业标准. 油气储层评价方法:SY/T 6285—1997[S]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1998. |
| Petroleum and Natural Gas Industry Standard of the People’s Republic of China. Evaluating methods of oil and gas reservoirs:SY/T 6285—1997[S]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 1998. | |
| [22] | BEARD D C, WEYL P K. Influence of texture on porosity and permeability of unconsolidated sand[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1973, 57(2):349-369. |
| [23] | 任大忠, 孙卫, 屈雪峰, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长组长6储层成岩作用特征及孔隙度致密演化[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 47(8):2706-2714. |
| REN Dazhong, SUN Wei, QU Xuefeng, et al. Characteristic of diagenesis and pore dense evolution of Chang 6 reservoir of Triassic Yanchang formation,Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Central South University(Science and Technology), 2016, 47(8):2706-2714. | |
| [24] | 周晓峰, 李书恒, 于均民, 等. 砂岩中绿泥石膜形貌和组成的成岩过程响应:以鄂尔多斯盆地陇东地区长8砂岩为例[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(2):110-116. |
| ZHOU Xiaofeng, LI Shuheng, YU Junming, et al. Diagenetic process responses of morphologies and chemical compositions of chlorite rims in sandstones:A case from Chang 8 sandstone,Longdong area,Ordos Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(2):110-116. | |
| [25] |
吴家洋, 吕正祥, 卿元华, 等. 致密油储层中自生绿泥石成因及其对物性的影响:以川中东北部沙溪庙组为例[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2020, 32(1):76-85.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20200108 |
|
WU Jiayang, LYU Zhengxiang, QING Yuanhua, et al. Genesis of authigenic chlorite in tight oil reservoirs and its influence on physical properties:A case study of Shaximiao formation in NE of central Sichuan Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2020, 32(1):76-85.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20200108 |
|
| [26] | 田建锋, 喻建, 张志国. 砂岩中碱性溶蚀研究进展[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(5):83-93. |
| TIAN Jianfeng, YU Jian, ZHANG Zhiguo. Advance in alkaline dissolution of sandstone[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(5):83-93. | |
| [27] | 罗静兰, 罗晓容, 白玉彬, 等. 差异性成岩演化过程对储层致密化时序与孔隙演化的影响:以鄂尔多斯盆地西南部长7致密浊积砂岩储层为例[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2016, 38(1):79-92. |
| LUO Jinglan, LUO Xiaorong, BAI Yubin, et al. Impact of differential diagenetic evolution on the chronological tightening and pore evolution of tight sandstone reservoirs:A case study from the Chang-7 tight turbidite sandstone reservoir in the southwestern Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2016, 38(1):79-92. | |
| [28] | 朱瑞静, 李荣西, 刘新社, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南部上古生界致密砂岩气储层成岩演化特征及物性演化[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 57(5):637-649. |
| ZHU Ruijing, LI Rongxi, LIU Xinshe, et al. Characteristics of the diagenetic evolution of tight sandstone gas reservoir and its property in the Upper Paleozoic erathem in southwestern Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University(Natural Sciences), 2021, 57(5):637-649. | |
| [29] |
刘金库, 邓明杰, 张泽, 等. 歧北斜坡沙二段储层碱性环境成岩演化及其对储集性能的影响[J]. 特种油气藏, 2023, 30(3):38-46.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2023.03.005 |
| LIU Jinku, DENG Mingjie, ZHANG Ze, et al. Influence of alkaline environment diagenetic evolution on reservoir performance in the second member of Shahejie formation of Qibei slope[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2023, 30(3):38-46. | |
| [30] | 刘伟, 窦齐丰, 黄述旺, 等. 成岩作用的定量表征与成岩储集相研究:以科尔沁油田交2断块区九佛堂组(J3jf)下段为例[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2002, 31(5):62-66. |
| LIU Wei, DOU Qifeng, HUANG Shuwang, et al. Quantitative characterization of diagenesis and diagenesis reservoir facies:The case study of lower member of J3jf of Jiao 2 block in Kerqin oilfield[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2002, 31(5):62-66. |
| [1] | 黄有根, 郑小鹏, 张道锋, 胡薇薇, 何梦卿, 王冰. 鄂尔多斯盆地本溪组煤岩微观特征及气体赋存状态[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(3): 253-262. |
| [2] | 张正涛, 费世祥, 罗文琴, 钟广浩, 兰天君, 王晔, 崔越华, 汪淑洁, 张芳. 鄂尔多斯盆地东部本溪组煤岩气储集层评价及甜点区优选[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(3): 263-272. |
| [3] | 赵玉华, 王雅婷, 黄研, 赵德勇, 曹永亮. 鄂尔多斯盆地马家滩地区乌拉力克组页岩气藏甜点预测[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(3): 273-279. |
| [4] | 马志欣, 李进步, 付斌, 白慧, 李浮萍, 马生晖, 贾金娥. 苏里格气田二叠系山西组曲流河储集层岩相与构型[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(3): 280-287. |
| [5] | 杨龙, 朱玉双, 康永梅, 刘一婷, 包琛龙, 何辉. 演武油田延安组储集层特征及敏感性主控因素[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(3): 288-295. |
| [6] | 罗丽荣, 李剑锋, 朱静, 孔令印, 白嫦娥, 居迎军, 侯云超. 平凉北地区长8段油藏油源及其成藏模式[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(3): 318-328. |
| [7] | 龙盛芳, 侯云超, 赵玉华, 张杰, 郝金鑫, 谷兆兴. 鄂尔多斯盆地演武地区断裂特征及其对侏罗系油藏的影响[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(3): 329-337. |
| [8] | 宋鹏, 张心罡, 杨卫国, 王楠, 石坚, 谢启超, 段文豪. 低渗透底水油藏底部注水方法及应用[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(3): 375-381. |
| [9] | 王雯清, 彭磊, 石华强, 侯瑞, 高辉, 王琛, 李腾. 鄂尔多斯盆地北部与西南部地区二叠系山1段可动流体差异分析[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(2): 172-180. |
| [10] | 慕倩, 李高仁, 张文静, 迟瑞强. 基于核磁共振测井的致密砂岩储集层有效性评价[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(1): 121-126. |
| [11] | 向鹏飞, 季汉成, 汪新伟, 史燕青, 黄芸, 孙予舒. 冀中坳陷奥陶系深层白云岩储集层成因机制[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2024, 45(6): 659-670. |
| [12] | 陈军军, 杨兴利, 辛毅超, 柳朝阳, 仝波文. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长油田双河西区块长6油藏开发参数[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2024, 45(5): 552-559. |
| [13] | 宋海强, 刘慧卿, 王敬, 斯尚华, 杨潇. 鄂尔多斯盆地东南部长7段页岩油气富集主控因素[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2024, 45(1): 27-34. |
| [14] | 孔令印, 李剑锋, 吴凯, 马军. 鄂尔多斯盆地黄陵—铜川地区延安组煤矿原油成因[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2024, 45(1): 35-46. |
| [15] | 石雪峰, 游利军, 葛岩, 胡云亭, 马立涛, 王艺钧, 郭飒飒. 临兴气田致密砂岩气藏压裂后产水机理[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2024, 45(1): 81-87. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||