

新疆石油地质 ›› 2025, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (6): 659-667.doi: 10.7657/XJPG20250602
毛新军a( ), 王然b(
), 王然b( ), 郑孟林b, 李菁b, 潘进b, 王韬b, 黄立良b, 常秋生b
), 郑孟林b, 李菁b, 潘进b, 王韬b, 黄立良b, 常秋生b
收稿日期:2025-04-30
修回日期:2025-07-17
出版日期:2025-12-01
发布日期:2025-12-05
通讯作者:
王然
E-mail:mxj7341n@petrochina.com.cn;nuture@petrochina.com.cn
作者简介:毛新军(1973-),男,浙江温岭人,教授级高级工程师,硕士,油气勘探,(Email)基金资助:
MAO Xinjuna( ), WANG Ranb(
), WANG Ranb( ), ZHENG Menglinb, LI Jingb, PAN Jinb, WANG Taob, HUANG Liliangb, CHANG Qiushengb
), ZHENG Menglinb, LI Jingb, PAN Jinb, WANG Taob, HUANG Liliangb, CHANG Qiushengb
Received:2025-04-30
Revised:2025-07-17
Online:2025-12-01
Published:2025-12-05
Contact:
WANG Ran
E-mail:mxj7341n@petrochina.com.cn;nuture@petrochina.com.cn
摘要: 准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷二叠系芦草沟组页岩油甜点储集层岩性复杂、物性变化快,成岩作用对页岩油甜点储集层孔隙演化具有重要影响。利用岩石薄片、铸体薄片、扫描电镜、X射线衍射等研究储集层孔隙微观特征,旨在揭示孔隙成因、物性变化规律及控制因素。结果表明:吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组甜点主要发育砂岩类和白云岩类储集层,2类储集层孔隙类型均以粒间溶孔、粒内溶孔、铸模孔、溶蚀缝等次生孔隙为主,孔隙直径大于50 μm的宏孔占50%以上;砂岩类和白云岩类储集层物性相当,属于中—低孔低—特低渗储集层,砂岩类储集层平均孔隙度为13.51%,平均渗透率为0.81 mD,白云岩类储集层平均孔隙度为12.86%,平均渗透率为2.38 mD;2类储集层均经历压实作用—风化淋滤溶蚀作用—胶结作用—有机酸溶蚀作用,整体处于中成岩阶段A期;表生成岩阶段的风化淋滤溶蚀作用促进了毛细管孔隙、超毛细管孔隙等大孔隙的形成,该孔隙为主要储集空间,中成岩阶段的有机酸溶蚀作用促进了纳米级微毛细管孔隙的形成,对储集层物性改善有限。
中图分类号:
毛新军, 王然, 郑孟林, 李菁, 潘进, 王韬, 黄立良, 常秋生. 吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组页岩油甜点储集层孔隙成因及成岩演化[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(6): 659-667.
MAO Xinjun, WANG Ran, ZHENG Menglin, LI Jing, PAN Jin, WANG Tao, HUANG Liliang, CHANG Qiusheng. Pore Genesis and Diagenetic Evolution of Shale Oil Sweet Spot Reservoirs in Lucaogou Formation, Jimsar Sag[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2025, 46(6): 659-667.
图3
吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组页岩油甜点储集层孔隙特征 a—粒内溶孔、粒间溶孔和晶模孔,石灰质粉—细砂岩,J31井,2 725.36 m,铸体薄片;b—粒内溶孔,石灰质粉砂岩,J174井,3 141.04 m,铸体薄片;c—粒间溶孔和粒内溶孔,石灰质粉砂岩,J174井,3 262.59 m,铸体薄片;d—半充填缝和粒内溶孔,泥质粉砂岩,J31井,4 081.87 m,铸体薄片;e—粒内溶孔和晶间孔,微晶白云岩,J174井,3 182.43 m,铸体薄片;f—晶内溶孔,砂质粉晶白云岩,J174井,3 301.93 m,铸体薄片;g—体腔溶孔,示底构造,泥晶白云岩,J25井,3 411.05 m,铸体薄片;h—溶蚀缝,泥晶白云岩,J31井,3 896.02 m,铸体薄片。"
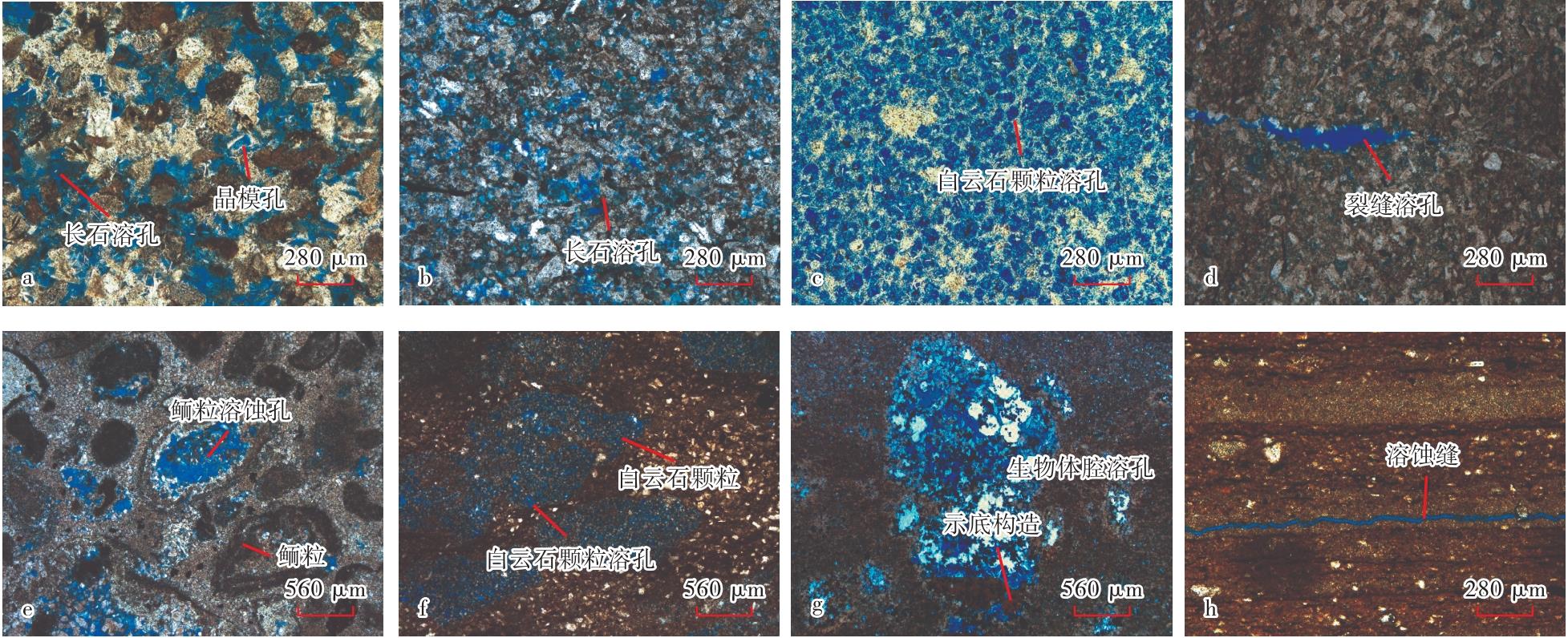
表1
吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组页岩油甜点储集层孔隙结构数据"
| 岩性 | 压汞分析 | 铸体薄片 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 孔隙度/ % | 渗透率/ mD | 排驱压力/ MPa | 最大孔喉 半径/μm | 孔喉 体积比 | 平均毛细管 半径/μm | 最大孔隙直径/ μm | 最小孔隙 直径/μm | 平均孔隙 直径/μm | |
| 砂岩类 | 4.90~25.50 (13.51) | 0.01~14.00 (0.81) | 0.14~25.42 (2.53) | 0.03~5.29 (0.95) | 1.36~19.27 (3.87) | 0.01~1.35 (0.27) | 4.56~133.32 (29.03) | 2.10~16.58 (2.84) | 3.48~102.29 (13.71) |
| 白云岩类 | 5.20~27.80 (12.86) | 0.01~23.30 (2.38) | 0.02~5.13 (1.38) | 0.14~30.13 (2.70) | 1.58~22.90 (4.25) | 0.07~3.84 (0.49) | 9.37~2 039.18 (146.24) | 2.10~21.59 (6.24) | 4.78~1 449.22 (86.62) |
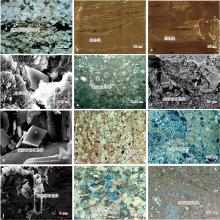
图4
吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组页岩油甜点储集层成岩作用 a—部分小碎屑颗粒定向排列,含石炭质细砂岩,J174井,3 125.70 m,岩石薄片;b—沿层理面不均匀溶蚀形成缝合线,泥质白云岩,J174井,3 275.74—3 278.01 m,岩心;c—层理缝,泥质粉砂岩,J174井,3 227.00—3 229.23 m,岩心;d—准同生期形成的半自形白云石晶体,泥晶白云岩,J174井,3 255.10 m,扫描电镜;e—与菌藻类生物有关白云石化作用,微—亮晶鲕粒白云岩,J174井,3 177.40 m,岩石薄片;f—埋藏白云石化作用形成的自形铁白云石,泥质粉砂岩,J10025井,3 555.08 m,场发射扫描电镜;g—颗粒之间充填菱形方解石晶体,泥质白云岩,J174井,3 217.98 m,扫描电镜;h—黄铁矿充填孔隙,零星分布,泥晶白云岩,J174井,3 291.24 m,铸体薄片;i—颗粒之间充填长条状钠长石,泥质粉砂岩,J174井,3 121.38 m,岩石薄片;j—颗粒之间充填板状沸石晶体,含砂屑泥—微晶白云岩,J174井,3 247.44 m,扫描电镜;k—风化淋滤溶蚀作用形成的成片分布的粒间大溶孔,泥质粉砂岩,J174井,3 141.04 m,铸体薄片;l—有机酸溶蚀作用形成的分散分布的粒内或晶间小溶孔,微晶白云岩,J174井,3 138.76 m,铸体薄片。"

| [1] | 王剑, 刘金, 潘晓慧, 等. 吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组页岩油生烃母质及其生烃机理[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2024, 45(3):253-261. |
| WANG Jian, LIU Jin, PAN Xiaohui, et al. Precursor and mechanism of hydrocarbon generation for shale oil in Lucaogou formation,Jimsar sag[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2024, 45(3):253-261. | |
| [2] | 李国欣, 雷征东, 董伟宏, 等. 中国石油非常规油气开发进展、挑战与展望[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2022, 27(1):1-11. |
| LI Guoxin, LEI Zhengdong, DONG Weihong, et al. Progress,challenges and prospects of unconventional oil and gas development of CNPC[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2022, 27(1):1-11. | |
| [3] | 贾承造, 王祖纲, 姜林, 等. 中国页岩油勘探开发研究进展与科学技术问题[J]. 世界石油工业, 2024, 31(4):1-11. |
| JIA Chengzao, WANG Zugang, JIANG Lin, et al. Progress and key scientific and technological problems of shale oil exploration and development in China[J]. World Petroleum Industry, 2024, 31(4):1-11. | |
| [4] | SU Yang, ZHA Ming, DING Xiujian, et al. Petrographic, palynologic and geochemical characteristics of source rocks of the Permian Lucaogou formation in Jimsar sag,Junggar Basin,NW China:Origin of organic matter input and depositional environments[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2019,183:106364. |
| [5] | 李二庭, 潘越扬, 杨光庆, 等. 准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷二叠系芦草沟组不同源储结构页岩生排油实验研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(4):705-713. |
| LI Erting, PAN Yueyang, YANG Guangqing, et al. Experimental study on hydrocarbon generation and expulsion characteristics of shale with different source-reservoir structures in Lucaogou formation,Jimsar sag,Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(4):705-713. | |
| [6] | 郭海平, 吴承美, 张金风, 等. 吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组混积型页岩油可动性实验[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2023, 44(1):76-83. |
| GUO Haiping, WU Chengmei, ZHANG Jinfeng, et al. Experiments on mobility of mixed shale oil in Lucaogou formation in Jimsar sag[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2023, 44(1):76-83. | |
| [7] | WANG Jian, CAO Yingchang, LIU Keyu, et al. Fractal characteristics of the pore structures of fine-grained,mixed sedimentary rocks from the Jimsar sag,Junggar Basin:Implications for lacustrine tight oil accumulations[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science & Engineering, 2019,182:106363. |
| [8] | 金之钧, 张谦, 朱如凯, 等. 中国陆相页岩油分类及其意义[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2023, 44(4):801-819. |
| JIN Zhijun, ZHANG Qian, ZHU Rukai, et al. Classification of lacustrine shale oil reservoirs in China and its significance[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2023, 44(4):801-819. | |
| [9] | YANG Yongqiang, QIU Longwei, WAN Ming, et al. Depositional model for a salinized lacustrine basin:The Permian Lucaogou formation,Jimsar sag,Junggar Basin,NW China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2019,178:81-95. |
| [10] | WANG Ran, CHEN Xuan, CHANG Qiusheng, et al. Identification of Milankovitch sedimentary cycle in Fengcheng formation,Mahu depression:A case study of Well Maye 1[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 2024,12:1390929. |
| [11] | 况军, 齐雪峰. 准噶尔前陆盆地构造特征与油气勘探方向[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2006, 27(1):5-9. |
| KUANG Jun, QI Xuefeng. The structural characteristics and oil-gas explorative direction in Junggar foreland basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2006, 27(1):5-9. | |
| [12] | 何登发, 尹成, 杜社宽, 等. 前陆冲断带构造分段特征:以准噶尔盆地西北缘断裂构造带为例[J]. 地学前缘, 2004, 11(4):91-101. |
| HE Dengfa, YIN Cheng, DU Shekuan, et al. Characteristics of structural segmentation of foreland thrust belts:A case study of the fault belts in the northwestern margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2004, 11(4):91-101. | |
| [13] | 刘金, 王剑, 马啸, 等. 陆相咸化湖盆页岩油甜点孔隙特征与成因:以准噶尔盆地芦草沟组为例[J]. 地质学报, 2023, 97(3):864-878. |
| LIU Jin, WANG Jian, MA Xiao, et al. Pore characteristics and genesis of shale oil sweet spots in saline lacustrine basins:A case study from the Lucaogou formation in the Junggar Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2023, 97(3):864-878. | |
| [14] | 王林生, 叶义平, 覃建华, 等. 陆相页岩油储层微观孔喉结构表征与含油性分级评价:以准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷二叠系芦草沟组为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2022, 43(1):149-160. |
| WANG Linsheng, YE Yiping, QIN Jianhua, et al. Microscopic pore structure characterization and oil-bearing property evaluation of lacustrine shale reservoir:A case study of the Permian Lucaogou formation in Jimsar sag,Junggar Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2022, 43(1):149-160. | |
| [15] | 王然, 何文军, 赵辛楣, 等. 准噶尔盆地吉174井芦草沟组页岩油地质剖面分析[J]. 油气藏评价与开发, 2022, 12(1):192-203. |
| WANG Ran, HE Wenjun, ZHAO Xinmei, et al. Geological section analysis of shale oil in Lucaogou formation of Well-Ji-174,Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 2022, 12(1):192-203. | |
| [16] |
葸克来, 张媛媛, 操应长, 等. 孔喉微观润湿性对页岩油赋存的控制作用:以准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷二叠系芦草沟组纹层状页岩为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2023, 50(2):297-308.
doi: 10.11698/PED.20220525 |
| XI Kelai, ZHANG Yuanyuan, CAO Yingchang, et al. Control of micro-wettability of pore-throat on shale oil occurrence:A case study of laminated shale of Permian Lucaogou formation in Jimusar sag,Junggar Basin,NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2023, 50(2):297-308. | |
| [17] | 李志明, 刘雅慧, 等.何晋译, 陆相页岩油“甜点”段评价关键参数界限探讨[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2023, 44(6):1453-1467. |
| LI Zhiming, LIU Yahui, HE Jinyi, et al. Limits of critical parameters for sweet-spot interval evaluation of lacustrine shale oil[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2023, 44(6):1453-1467. | |
| [18] | 匡立春, 唐勇, 雷德文, 等. 准噶尔盆地二叠系咸化湖相云质岩致密油形成条件与勘探潜力[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2012, 39(6):657-667. |
| KUANG Lichun, TANG Yong, LEI Dewen, et al. Formation conditions and exploration potential of tight oil in the Permian saline lacustrine dolomitic rock,Junggar Basin,NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2012, 39(6):657-667. | |
| [19] | 宋永, 周路, 郭旭光, 等. 准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组湖相云质致密油储集层特征与分布规律[J]. 岩石学报, 2017, 33(4):1160-1170. |
| SONG Yong, ZHOU Lu, GUO Xuguang, et al. Characteristics and occurrence of lacustrine dolomitic tight-oil reservoir in the Middle Permian Lucaogou formation,Jimusaer sag,southeastern Junggar Basin[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2017, 33(4):1160-1170. | |
| [20] | 马克, 刘钰铭, 侯加根, 等. 陆相咸化湖混合沉积致密储集层致密化机理:以吉木萨尔凹陷二叠系芦草沟组为例[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2019, 40(3):253-261. |
| MA Ke, LIU Yuming, HOU Jiagen, et al. Densification mechanism of tight reservoirs from mixed sedimentation in saline lacustrine environment:A case study of Permian Lucaogou formation,Jimsar sag[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2019, 40(3):253-261. | |
| [21] | 斯春松, 陈能贵, 余朝丰, 等. 吉木萨尔凹陷二叠系芦草沟组致密油储层沉积特征[J]. 石油实验地质, 2013, 35(5):528-533. |
| SI Chunsong, CHEN Nenggui, YU Chaofeng, et al. Sedimentary characteristics of tight oil reservoir in Permian Lucaogou formation,Jimsar sag[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2013, 35(5):528-533. | |
| [22] | 马铨峥, 杨胜来, 杨龙, 等. 准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组致密储层微观孔隙特征[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 2020, 39(6):13-20. |
| MA Quanzheng, YANG Shenglai, YANG Long, et al. Characteristics of the micro-pore in Lucaogou formation tight reservoir of Jimsar sag,Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing, 2020, 39(6):13-20. | |
| [23] |
葸克来, 操应长, 朱如凯, 等. 吉木萨尔凹陷二叠系芦草沟组致密油储集层岩石类型及特征[J]. 石油学报, 2015, 36(12):1495-1507.
doi: 10.7623/syxb201512004 |
|
XI Kelai, CAO Yingchang, ZHU Rukai, et al. Rock types and characteristics of tight oil reservoir in Permian Lucaogou formation,Jimsar sag[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2015, 36(12):1495-1507.
doi: 10.7623/syxb201512004 |
|
| [24] | 王然, 常秋生, 钱永新, 等. 准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组页岩油“甜点体”储集特征及成因机理[J]. 石油实验地质, 2020, 42(4):604-611. |
| WANG Ran, CHANG Qiusheng, QIAN Yongxin, et al. Reservoir characteristics and genesis of shale oil “sweet spots” in Lucaogou formation,Jimsar sag,Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2020, 42(4):604-611. | |
| [25] |
李哲萱, 柳益群, 焦鑫, 等. 湖相细粒沉积岩中的“斑状”深源碎屑:以准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组为例[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2020, 31(2):220-234.
doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2019.11.008 |
|
LI Zhexuan, LIU Yiqun, JIAO Xin, et al. Deep-derived clastics with porphyroclastic structure in lacustrine fine-grained sediments:Case study of the Permian Lucaogou formation in Jimsar sag,Junggar Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2020, 31(2):220-234.
doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2019.11.008 |
|
| [26] | 方世虎, 宋岩, 徐怀民, 等. 构造演化与含油气系统的形成:以准噶尔盆地东部吉木萨尔凹陷为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2007, 29(2):149-153. |
| FANG Shihu, SONG Yan, XU Huaimin, et al. Relationship between tectonic evolution and petroleum system formation:Taking the Jimsar sag of eastern Junggar Basin as example[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2007, 29(2):149-153. | |
| [27] | 王剑, 李二庭, 陈俊, 等. 准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷二叠系芦草沟组优质烃源岩特征及其生烃机制研究[J]. 地质论评, 2020, 66(3):755-764. |
| WANG Jian, LI Erting, CHEN Jun, et al. Characteristics and hydrocarbon generation mechanism of high-quality source rocks in Permian Lucaogou formation,Jimsar sag,Junggar Basin[J]. Geological Review, 2020, 66(3):755-764. | |
| [28] | 王剑, 周路, 刘金, 等. 准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷二叠系芦草沟组酸碱交替成岩作用特征及对页岩储集层的影响[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2020, 47(5):1-15. |
|
WANG Jian, ZHOU Lu, LIU Jin, et al. Acid-base alternation diagenesis and its influence on shale reservoirs in the Permian Lucaogou formation,Jimusar sag,Junggar Basin,NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2020, 47(5):1-15.
doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(20)60001-5 |
|
| [29] | KACHEL H G, KROUSE H R. Products and distinguishing criteria of bacterial and thermochemical sulfate reduction[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 1995,10:373-389. |
| [30] | 张义杰, 齐雪峰, 程显胜, 等. 准噶尔盆地晚石炭世和二叠纪沉积环境[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2007, 28(6):673-675. |
| ZHANG Yijie, QI Xuefeng, CHENG Xiansheng, et al. Approach to sedimentary environment of Late Carboniferous-Permian in Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2007, 28(6):673-675. | |
| [31] |
王卓卓, 粱江平, 李国会, 等. 成岩作用对储集层物性的影响及与沉积环境的关系:以鄂尔多斯盆地劳山地区为例[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2008, 19(2):171-177.
doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2008.02.171 |
|
WANG Zhuozhuo, LIANG Jiangping, LI Guohui, et al. Affection of diagenesis on reservoir properties and its relationship with depositional setting:A case from Upper Triassic Yanchang formation sandstones,Laoshan[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2008, 19(2):171-177.
doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2008.02.171 |
| [1] | 金之钧, 曹琰, 张虹, 唐勇, 秦志军, 刘扣其, 梁成钢, 李关访, 何文军. 吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组页岩油甜点主控因素研究与实践[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(6): 647-658. |
| [2] | 曹剑, 秦志军, 魏超, 向宝力, 刘金. 陆相纹层型页岩油源储耦合与甜点形成机理——以准噶尔盆地风城组为例[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(6): 668-683. |
| [3] | 刘金, 白雷, 张宝真, 魏超, 雷海艳, 邓远, 曹剑. 吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组页岩油微观赋存特征与开采动态响应[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(6): 684-692. |
| [4] | 邹阳, 陈文顺, 罗刚, 陈绍蓉, 陈方文, 何文军, 刘新龙, 朱涛. 玛湖凹陷风城组碱湖页岩油富集和高产主控因素[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(6): 693-702. |
| [5] | 魏兆胜, 齐洪岩, 赵建飞, 何吉祥, 刘可成, 王俊超. 准噶尔盆地页岩油开发进展及效益建产关键技术[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(6): 703-711. |
| [6] | 李庆, 罗刚, 李映艳, 邓远, 肖佃师, 谢潇权. 吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组页岩油接替区开发潜力[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(6): 712-722. |
| [7] | 刘向君, 甘仁忠, 熊健, 汤诗棋, 万有维, 周鑫, 梁利喜, 张淼. 吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组页岩油储层体积改造主控地质力学因素[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(6): 723-733. |
| [8] | 齐洪岩, 王振林, 郑国庆, 余佩蓉, 杨旺旺. 页岩油储集层水平井密切割压裂裂缝非均衡扩展机理[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(6): 734-741. |
| [9] | 李映艳, 丁艺, 罗刚, 丁怀宇, 唐慧莹, 贺戈. 基于地质工程一体化的井网-缝网协同优化——以准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷页岩油为例[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(6): 742-753. |
| [10] | 吝佳莹, 齐洪岩, 常婷, 张韵洁, 张浩, 陈刚, 梁成钢, 魏晓琛. 走滑断裂滑移诱发套管变形数值模拟及压裂方案优化——以吉木萨尔凹陷页岩油为例[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(6): 754-761. |
| [11] | 杜雪彪, 张金风, 肖佃师, 冉阳, 刘英杰, 秦嘉敏, 王良哲. 基于ReliefF和LSBoost集成树核磁有效孔隙度频谱预测及分辨率匹配研究[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(6): 762-772. |
| [12] | 姚菊琴, 陈刚, 唐廷明, 赵春雪, 李维, 余雪峰, 于江龙. 点复数谱提频方法在吉木萨尔页岩油甜点预测中的应用[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(6): 773-778. |
| [13] | 毛锐, 尉珈敏, 王盼, 李晴晴, 赵磊. 玛湖凹陷风城组页岩油储集层关键参数测井评价方法[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(6): 779-789. |
| [14] | 李杨虎, 王振林, 邵欢欢, 陈山河, 汤富康, 刘财广, 王伟, 张浩. 基于黏土矿物含量的页岩油水平井声波各向异性校正方法及应用[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(6): 790-799. |
| [15] | 李聚豪, 何金先, 杨兆彪, 张晓丽, 吴蒙, 马丽, 袁媛, 闻明忠. 黔西地区龙潭组煤系泥页岩储集层孔隙结构及控制因素[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(5): 521-530. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||