

新疆石油地质 ›› 2026, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (1): 20-30.doi: 10.7657/XJPG20260103
吕厚宽1( ), 张磊2, 安志渊2, 况昊1(
), 张磊2, 安志渊2, 况昊1( ), 豆方鹏2, 李存1, 潘浪1
), 豆方鹏2, 李存1, 潘浪1
收稿日期:2025-07-28
出版日期:2026-02-01
发布日期:2026-01-23
通讯作者:
况昊
E-mail:a2605320739@foxmail.com;kwanghow@foxmail.com
作者简介:吕厚宽(1999-),男,贵州贵阳人,硕士研究生,沉积储层,(Email)基金资助:
LYU Houkuan1( ), ZHANG Lei2, AN Zhiyuan2, KUANG Hao1(
), ZHANG Lei2, AN Zhiyuan2, KUANG Hao1( ), DOU Fangpeng2, LI Cun1, PAN Lang1
), DOU Fangpeng2, LI Cun1, PAN Lang1
Received:2025-07-28
Online:2026-02-01
Published:2026-01-23
Contact:
KUANG Hao
E-mail:a2605320739@foxmail.com;kwanghow@foxmail.com
摘要:
沸石胶结物的成因差异造成了储层储集空间类型多样、成分复杂且非均质性强。为探究其对储集空间产生的影响,综合运用岩心观察、薄片鉴定、电镜扫描、全岩X射线衍射分析及能谱分析等手段,宏观、微观相结合对玛湖凹陷—沙湾凹陷中—下二叠统沸石胶结物类型、形成机制及储集空间类型进行了系统对比分析与研究,结果表明:碎屑成分差异控制着沸石胶结物类型及成因,玛湖凹陷和沙湾凹陷风城组和夏子街组沸石胶结物成因是凝灰岩火山玻璃水化作用;中拐凸起和车排子凸起佳木河组沸石胶结物由斜长石钠长石化形成。而沸石胶结物成因差异又造成了储集空间类型分异,玛湖凹陷和沙湾凹陷风城组和夏子街组沸石胶结物演化过程伴随胶结物密度改变和结晶水释放,易形成粒缘缝;中拐凸起和车排子凸起佳木河组由于浊沸石与方解石的溶蚀,储集空间以溶孔为主。
中图分类号:
吕厚宽, 张磊, 安志渊, 况昊, 豆方鹏, 李存, 潘浪. 玛湖凹陷—沙湾凹陷中—下二叠统富火山碎屑砂砾岩储层成因[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2026, 47(1): 20-30.
LYU Houkuan, ZHANG Lei, AN Zhiyuan, KUANG Hao, DOU Fangpeng, LI Cun, PAN Lang. Genesis of Pyroclastic-Rich Sandy Conglomerate Reservoirs in the Lower-Middle Permian of Mahu-Shawan Sags[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2026, 47(1): 20-30.

图5
玛湖凹陷和沙湾凹陷中—下二叠统沸石胶结物类型 a—凝灰岩岩屑粒间充填浊沸石,MH39井,5 088.88 m,单偏光;b—自生柱状浊沸石集合体产于颗粒边缘,ST2井,5 720.71 m,扫描电镜;c—柱状浊沸石与片沸石共生,SP5井,4 658.68 m,扫描电镜;d—砖红色片沸石与不规则粒状方沸石充填粒间孔隙,方沸石呈异常消光,SP3井,4 693.30 m,正交偏光;e—粒间发育板状浊沸石,少量片沸石发育,SP4井,4 354.57 m,扫描电镜;f—浊沸石能谱(图5e),Si/Al为2.35;g—褐红色块状片沸石沿碎屑颗粒的边缘垂直生长,硅质胶结物充填粒间孔隙,B56井,2 439.28 m,单偏光;h—连片状片沸石,SP5井,4 781.07 m,扫描电镜;i—片沸石能谱(图5h),Si/Al为3.18。"

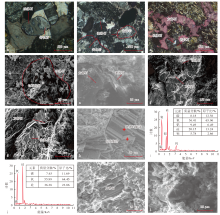
图6
中拐凸起和车排子凸起中—下二叠统沸石胶结物类型 a—不规则状浊沸石沿解理缝交代安山岩岩屑中的钙长石,ZJ4井,4 436.98 m,正交偏光;b—浊沸石以不规则状交代安山岩岩屑中的钙长石,ZJ4井,4 436.98 m,正交偏光;c—不规则状浊沸石交代钙长石,粒间充填方解石与浊沸石,ZJ4井,4 411.16 m,正交偏光;d—长石颗粒受溶解,颗粒内含少量柱状浊沸石,CP2井,2 836.63 m,扫描电镜;e—粒间充填柱状浊沸石与方解石,ZJ14井,4 298.60 m,扫描电镜;f—柱板状浊沸石产于颗粒边缘,方解石充填粒间孔隙,CP5井,4 732.71 m,扫描电镜;g—粒间充填柱板状浊沸石,方解石产于粒间浊沸石内,CP5井,4 672.01 m,扫描电镜;h—粒间充填浊沸石与石英,ZJ903X井,4 729.98 m,扫描电镜;i—浊沸石能谱(图6h),Si/Al为2.47;j—石英能谱(图6h);k—粒间充填条状片沸石,片沸石晶体间发育晶间孔,ZJ903X井,4 730.80 m,扫描电镜;l—球粒状方沸石赋存于颗粒表面,并伴生伊蒙混层,ZJ903X井,4 730.80 m,扫描电镜。"

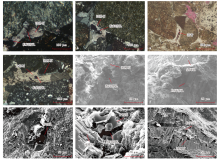
图9
中拐凸起和车排子凸起中—下二叠统储集空间类型 a—粒间浊沸石溶蚀形成粒间溶孔,ZJ4井,4 628.39 m,正交偏光;b—浊沸石粒间溶孔,ZJ4井,4 437.51 m,正交偏光;c—沥青充填粒间溶孔,ZJ4井,4 436.98 m,单偏光;d—颗粒间发育浊沸石与方解石,方解石粒间溶蚀,ZJ4井,4 634.19 m,正交偏光;e—粒间板状浊沸石发育粒间溶蚀,ZJ141井,4 410.66 m,扫描电镜;f—粒间板柱状浊沸石发育晶间孔与粒间溶孔,ZJ15井,4 048.99 m,扫描电镜;g—颗粒间方解石发生溶蚀,CP3井,3 602.87 m,扫描电镜;h—颗粒间发育板状浊沸石与方解石,方解石部分溶蚀,CP5井,4 672.01 m,扫描电镜;i—粒间柱板状浊沸石溶蚀,CP7井,3 419.19 m,扫描电镜。"

| [1] | 张义杰, 柳广弟. 准噶尔盆地复合油气系统特征,演化与油气勘探方向[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2002, 29(1):36-39. |
| ZHANG Yijie, LIU Guangdi. Characteristics and evolution of composite petroleum systems and the exploration strategy in Junggar Basin,northwest China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2002, 29(1):36-39. | |
| [2] | 张枝焕, 秦黎明, 李伟, 等. 准噶尔盆地腹部车莫古隆起南北两侧含油构造油源及烃源灶转移[J]. 中国地质, 2009, 36(4):826-836. |
| ZHANG Zhihuan, QIN Liming, LI Wei, et al. The distribution of oil sources and the transformation of hydrocarbon kitchens in oil-bearing structural belts on northern and southern sides of the Chemo plaeo-uplift within central Junggar Basin[J]. Geology in China, 2009, 36(4):826-836. | |
| [3] | 张义杰, 王绪龙, 刘得光. 准噶尔盆地天然气资源勘探战略与对策[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2001, 22(5):386-389. |
| ZHANG Yijie, WANG Xulong, LIU Deguang. The measures and strategy for exploration of natural gas resources in Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2001, 22(5):386-389. | |
| [4] | 邓高山. 准噶尔盆地沙湾凹陷原油地球化学特征与油源分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2024, 54(2):389-412. |
| DENG Gaoshan. Geochemical characteristics and source of crude oil in Shawan depression,Junggar Basin[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 2024, 54(2):389-412. | |
| [5] | 左如斯, 曾翔, 曹忠祥, 等. 沉积岩中沸石类矿物成岩演化特征及其意义[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2023, 44(5):543-553. |
| ZUO Rusi, ZENG Xiang, CAO Zhongxiang, et al. Diagenetic evolution and its significance of zeolites in sedimentary rocks[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2023, 44(5):543-553. | |
| [6] | 朱世发, 朱筱敏, 王绪龙, 等. 准噶尔盆地西北缘二叠系沸石矿物成岩作用及对油气的意义[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2011, 41(11):1602-1612. |
| ZHU Shifa, ZHU Xiaomin, WANG Xulong, et al. Zeolite diagenesis and its control on petroleum reservoir quality of Permian in northwestern margin of Junggar Basin,China[J]. Science China:Earth Sciences, 2011, 41(11):1602-1612. | |
| [7] |
王涛, 张生银, 魏璞, 等. 沸石类矿物成因及其对储层储集性能的影响[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2022, 34(1):175-186.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20220118 |
|
WANG Tao, ZHANG Shengyin, WEI Pu, et al. Genesis of zeolite minerals and its influences on reservoir properties[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2022, 34(1):175-186.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20220118 |
|
| [8] | 李振华, 邱隆伟, 师政, 等. 准噶尔盆地中拐地区佳二段沸石类矿物成岩作用及其对油气成藏的意义[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 38(1):1-7. |
| LI Zhenhua, QIU Longwei, SHI Zheng, et al. Diagenesis of zeolite minerals and its significance for hydrocarbon accumulation in the second member of Jiamuhe formation of Zhongguai area,Junggar Basin[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum(Edition of Natural Science), 2014, 38(1):1-7. | |
| [9] | 韩波, 李新, 罗燕颖, 等. 玛湖地区二叠系含沸石砂砾岩岩石物理实验[J]. 测井技术, 2022, 46(4):397-403. |
| HAN Bo, LI Xin, LUO Yanying, et al. Petrophysical experiment of Permian zeolite glutenite in Mahu area[J]. Well Logging Technology, 2022, 46(4):397-403. | |
| [10] | 白清华, 柳益群, 樊婷婷. 鄂尔多斯盆地上三叠统延长组浊沸石分布及其成因分析[J]. 西北地质, 2009, 42(2):100-107. |
| BAI Qinghua, LIU Yiqun, FAN Tingting. Genesis and distribution of laumontite in Yanchang formation of Upper Triassic in Ordos Basin[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2009, 42(2):100-107. | |
| [11] |
孙靖, 尤新才, 郑孟林, 等. 准噶尔盆地深层—超深层二叠系碎屑岩储层特征及控制因素[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2024, 29(5):120-135.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2024.05.010 |
|
SUN Jing, YOU Xincai, ZHENG Menglin, et al. Characteristics and controlling factors for the Permian clastic reservoirs in deep to ultra-deep formations in Junggar Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2024, 29(5):120-135.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2024.05.010 |
|
| [12] | WOPFNER H, MARKWORT S, SEMKIWA P M. Early diagenetic laumontite in the Lower Triassic Manda beds of the Ruhuhu Basin,southern Tanzania[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1991, 61(1):65-72. |
| [13] |
KRALJ P, RYCHAGOV S, KRALJ P. Zeolites in volcanic-igneous hydrothermal systems:A case study of Pauzhetka geothermal field (Kamchatka) and Oligocene Smrekovec volcanic complex(Slovenia)[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2010, 59(5):951-956.
doi: 10.1007/s12665-009-0249-4 |
| [14] | IIJIMA A. Zeolites in petroleum and natural gas reservoirs[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 2001, 45(1):347-402. |
| [15] |
ZHANG Y, MA B, JIANG S, et al. Formation mechanisms of anomalously high reservoir quality in deep-buried volcaniclastic sandstones,central Junggar Basin,northwestern China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2024, 163:106772.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2024.106772 |
| [16] | 王继远, 王斌, 胡宗全, 等. 深层—超深层碎屑岩优质储层成因机理:以准噶尔盆地腹部二叠系—三叠系为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2025, 46(1):151-166. |
| WANG Jiyuan, WANG Bin, HU Zongquan, et al. Genetic mechanisms of high-quality deep to ultra-deep clastic reservoirs:A case study of the Permian-Triassic strata in the hinterland of the Junggar Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2025, 46(1):151-166. | |
| [17] | 杨川, 吴涛, 李啸, 等. 准噶尔盆地中拐凸起佳木河组储集层物性实测值校正[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2021, 42(6):749-755. |
| YANG Chuan, WU Tao, LI Xiao, et al. Correction of measured reservoir physical properties of Jiamuhe formation in Zhongguai uplift of Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2021, 42(6):749-755. | |
| [18] | 况昊, 周元东, 刘豪, 等. 沙湾凹陷砂砾岩沸石胶结物与碎屑颗粒粘结差异成因分析[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2024, 45(2):163-171. |
| KUANG Hao, ZHOU Yuandong, LIU Hao, et al. Genesis of differential bonding between zeolite cements and clastic particles in sandy conglomerates in Shawan sag,Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2024, 45(2):163-171. | |
| [19] | 吴和源, 唐勇, 常秋生. 准噶尔盆地中拐凸起佳木河组沸石类胶结砂砾岩储集层成因机理[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2017, 38(3):281-288. |
| WU Heyuan, TANG Yong, CHANG Qiusheng. Genesis of sandy conglomerate reservoirs cemented by zeolites in Jiamuhe formation of Zhongguai swell,Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2017, 38(3):281-288. | |
| [20] |
郭沫贞, 寿建峰, 徐洋, 等. 准噶尔盆地中拐—西北缘地区二叠系沸石胶结物分布与控制因素[J]. 石油学报, 2016, 37(6):695-705.
doi: 10.7623/syxb201606001 |
|
GUO Mozhen, SHOU Jianfeng, XU Yang, et al. Distribution and controlling factors of Permian zeolite cements in Zhongguai-northwest margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2016, 37(6):695-705.
doi: 10.7623/syxb201606001 |
|
| [21] | HAY R L. Zeolites and zeolitic reactions in sedimentary rocks[M]. Geological Society of America, 1966. |
| [22] |
CHIPERA S J, GOFF F, GOFF C J, et al. Zeolitization of intracaldera sediments and rhyolitic rocks in the 1.25 Ma lake of Valles caldera,New Mexico,USA[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 2008, 178(2):317-330.
doi: 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2008.06.032 |
| [23] | NOH J H, BOLES J R. Origin of zeolite cements in the Miocene sandstones,north Tejon oil fields,California[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 1993, 63(2):248-260. |
| [24] | CHAO S, YANG Y, WANG X, et al. Genesis mechanism of laumontite cement and its impact on the reservoir of siliciclastic rock:A case study of Jurassic Shaximiao formation in central Sichuan Basin,China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2024,165:106 873. |
| [25] |
BROXTON D E, BISH D L, WARREN R G. Distribution and chemistry of diagenetic minerals at Yucca mountain,Nye County,Nevada[J]. Clays and Clay Minerals, 1987, 35(2):89-110.
doi: 10.1346/CCMN.1987.0350202 |
| [26] |
AOYAGI K, KAZAMA T. Transformational changes of clay minerals,zeolites and silica minerals during diagenesis[J]. Sedimentology, 1980, 27(2):179-188.
doi: 10.1111/sed.1980.27.issue-2 |
| [27] | 刘超威, 吕正祥, 陈梦娜, 等. 准噶尔盆地阜康凹陷中—上二叠统砂砾岩中自生沸石成因及对储层发育的影响[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2024, 44(4):826-839. |
| LIU Chaowei, LYU Zhengxiang, CHEN Mengna, et al. Origin of authigenic zeolite and its influence on reservoir development in glutenites of the Middle-Upper Permian in Fukang sag,Junggar Basin [J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2024, 44(4):826-839. | |
| [28] | 史燕青, 季汉成, 张国一, 等. 准噶尔盆地阜东斜坡梧桐沟组储层沸石分布特征及成因机制[J]. 石油科学通报, 2021, 6(1):1-15. |
| SHI Yanqing, JI Hancheng, ZHANG Guoyi, et al. Characteristics and genetic mechanisms of widely distributed zeolites in the Wutonggou formation reservoir in the southern Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Science Bulletin, 2021, 6(1):1-15. | |
| [29] | 黄思静, 刘洁, 沈立成, 等. 碎屑岩成岩过程中浊沸石形成条件的热力学解释[J]. 地质论评, 2001, 47(3):301-308. |
| HUANG Sijing, LIU Jie, SHEN Licheng, et al. Thermodynamic interpretation for the conditions of the formation of laumonite related to clastic diagenesis[J]. Geological Review, 2001, 47(3):301-308. | |
| [30] | 张立飞. 陕北三叠系延长统浊沸石的成因及形成条件的理论计算[J]. 岩石学报, 1992, 8(2):145-152. |
| ZHANG Lifei. Origin of laumontite and condition for its formation in Trassic Yanchang series,north Shaanxi[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 1992, 8(2):145-152. | |
| [31] | 杨跃明, 王茂云, 吴长江, 等. 川中地区侏罗系沙溪庙组二段富钙地层水成因及其对天然气运聚的指示意义[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2025, 46(1):178-191. |
| YANG Yueming, WANG Maoyun, WU Changjiang, et al. Origin of calcium-rich formation water and its implications for natural gas migration and accumulation in the 2nd member of the Jurassic Shaximiao formation,central Sichuan Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2025, 46(1):178-191. | |
| [32] | 杨晓萍, 裘怿楠. 鄂尔多斯盆地上三叠统延长组浊沸石的形成机理、分布规律与油气关系[J]. 沉积学报, 2002, 20(4):628-632. |
| YANG Xiaoping, QIU Yinan. Formation process and distribution of laumontite in Yanchang formation (Upper Triassic) of Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2002, 20(4):628-632. | |
| [33] |
陈少云, 杨勇强, 邱隆伟, 等. 川中地区侏罗系沙溪庙组储层特征及控制因素[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2022, 33(10):1597-1610.
doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2022.06.007 |
|
CHEN Shaoyun, YANG Yongqiang, QIU Longwei, et al. Reservoir characteristics and controlling factors of Jurassic Shaximiao formation in central Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2022, 33(10):1597-1610.
doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2022.06.007 |
|
| [34] | 牛君, 王聪, 梁飞. 绿泥石与浊沸石矿物特征及其对储集层物性的影响:以准噶尔盆地陆梁隆起西部下乌尔禾组为例[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(1):13-21. |
| NIU Jun, WANG Cong, LIANG Fei. Mineral features of chlorite and laumontite and their impacts on reservoir physical properties:A case study of lower Wuerhe formation in western Luliang uplift,Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2025, 46(1):13-21. | |
| [35] | 石油地质勘探专业标准化技术委员会. [S]. 北京: 国家能源局, 2011. |
| Technical Committee for Standardization of Petroleum Geology and Exploration. [S]. Beijing: National Energy Administration, 2011. | |
| [36] | 王继远, 王斌, 邱岐, 等. 沸石成因及其控储机制研究进展[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2025, 32(1):29-39. |
| WANG Jiyuan, WANG Bin, QIU Qi, et al. Progress in zeolite origin and its control for reservoir development[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2025, 32(1):29-39. | |
| [37] | 袁珍, 郑艳忠, 袁海莉, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东南缘延长组浊沸石胶结物特征及其成岩模式[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 50(1):124-134. |
| YUAN Zhen, ZHENG Yanzhong, YUAN Haili, et al. Study on the characteristics and diagenesis model of laumontite cement in Yanchang formation in the southeastern margin of Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Northwest University(Natural Science Edition), 2020, 50(1):124-134. |
| [1] | 陈旋, 林霖, 刘俊田, 龚德瑜, 杨润泽, 王波, 谢安. 吉木萨尔凹陷二叠系全油气系统成藏机理与勘探潜力[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2026, 47(1): 1-10. |
| [2] | 黄立良, 邹阳, 杨勇强, 李广兴, 吴俊军, 姜振学, 刘新龙. 玛湖凹陷风城组二段页岩油层系伴生碱矿特征及沉积发育模式[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2026, 47(1): 11-19. |
| [3] | 陈绍蓉, 赵毅, 邹阳, 任海姣, 陈方文, 吴俊军. 玛湖凹陷风城组古沉积环境特征及其对页岩油甜点的影响[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2026, 47(1): 46-56. |
| [4] | 芦慧, 汪飞, 张译丹, 汪俊伟, 张金龙, 陈磊, 肖贝, 杨皝, 李臣. 准噶尔盆地西部隆起现今地温场分布及地热资源评价[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2026, 47(1): 92-102. |
| [5] | 金之钧, 曹琰, 张虹, 唐勇, 秦志军, 刘扣其, 梁成钢, 李关访, 何文军. 吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组页岩油甜点主控因素研究与实践[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(6): 647-658. |
| [6] | 曹剑, 秦志军, 魏超, 向宝力, 刘金. 陆相纹层型页岩油源储耦合与甜点形成机理——以准噶尔盆地风城组为例[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(6): 668-683. |
| [7] | 刘金, 白雷, 张宝真, 魏超, 雷海艳, 邓远, 曹剑. 吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组页岩油微观赋存特征与开采动态响应[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(6): 684-692. |
| [8] | 邹阳, 陈文顺, 罗刚, 陈绍蓉, 陈方文, 何文军, 刘新龙, 朱涛. 玛湖凹陷风城组碱湖页岩油富集和高产主控因素[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(6): 693-702. |
| [9] | 魏兆胜, 齐洪岩, 赵建飞, 何吉祥, 刘可成, 王俊超. 准噶尔盆地页岩油开发进展及效益建产关键技术[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(6): 703-711. |
| [10] | 刘向君, 甘仁忠, 熊健, 汤诗棋, 万有维, 周鑫, 梁利喜, 张淼. 吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组页岩油储层体积改造主控地质力学因素[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(6): 723-733. |
| [11] | 李映艳, 丁艺, 罗刚, 丁怀宇, 唐慧莹, 贺戈. 基于地质工程一体化的井网-缝网协同优化——以准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷页岩油为例[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(6): 742-753. |
| [12] | 杜雪彪, 张金风, 肖佃师, 冉阳, 刘英杰, 秦嘉敏, 王良哲. 基于ReliefF和LSBoost集成树核磁有效孔隙度频谱预测及分辨率匹配研究[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(6): 762-772. |
| [13] | 姚菊琴, 陈刚, 唐廷明, 赵春雪, 李维, 余雪峰, 于江龙. 点复数谱提频方法在吉木萨尔页岩油甜点预测中的应用[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(6): 773-778. |
| [14] | 毛锐, 尉珈敏, 王盼, 李晴晴, 赵磊. 玛湖凹陷风城组页岩油储集层关键参数测井评价方法[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(6): 779-789. |
| [15] | 李素华, 卢齐军, 胡昊, 李蓉, 苏成鹏, 蒋能春. 四川盆地西南部井研地区二叠系茅口组断溶体识别[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(5): 544-552. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||