

Xinjiang Petroleum Geology ›› 2024, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (2): 189-198.doi: 10.7657/XJPG20240207
• RESERVOIR ENGINEERING • Previous Articles Next Articles
TU Yi( ), DAI Jianwen, YANG Jiao, WANG Yahui, WANG Hua, TANG Zhonghao, LI Qi
), DAI Jianwen, YANG Jiao, WANG Yahui, WANG Hua, TANG Zhonghao, LI Qi
Received:2023-04-27
Revised:2023-07-17
Online:2024-04-01
Published:2024-03-26
CLC Number:
TU Yi, DAI Jianwen, YANG Jiao, WANG Yahui, WANG Hua, TANG Zhonghao, LI Qi. Architectures of and Remaining Oil Potential Tapping in Heavy Oil Reservoirs of Panyu Oilfield Group[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2024, 45(2): 189-198.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Table 2.
Architecture characteristics of the heavy oil reservoirs in Panyu oilfield group"
| 分类 | 测井特征 | 构型界面 级次 | 构型界面模式 | 成因 | 沉积相 | 厚度 | 分布规模 | 物性 | 典型油藏 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 岩性分类 | 成因分类 | |||||||||
| 泥岩 隔夹层 | 洪泛 泥岩 | 自然伽马回返率大于40%,分布稳定,基本全区可对比,多为隔层 | 5级 | 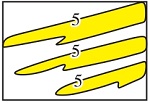 | 洪水间歇期形成的细粒沉积物或海泛面沉积 | 前三角洲 | 多大于2.0 m | 多大于1.0 km,全区分布 | 孔隙度小于5%,渗透率小于5 mD,封隔性强 | Z20、Z40、Z60、Z80、Z20、Z35、R10、R20 |
| 间湾 泥岩 | 自然伽马回返率为20%~40%,分布稳定,侧向与分流河道砂体对接,仅局部可对比 | 4级居多 | 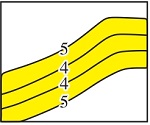 | 由于水动力减弱,水中沉积物沉积下来,多为相变成因 | 水下分流间湾、河口坝侧缘 | 主要为0.8~2.5 m,平均为1.5 m | 多为0.6~1.0 km,宽厚比约为500 | 孔隙度为3%~8%,渗透率小于20 mD,封隔性强 | Z40、Z60、Z35、Z46、R60、R10、R20、R30、R60、R80 | |
| 落淤 泥岩 | 自然伽马回返率小于20%,厚度差异大,分布在河口坝反韵律砂体顶部,仅局部分布物性夹层 | 3级居多, 4级较少 | 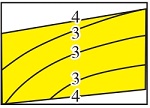 | 短时间内水下分流河道间水动力弱,水中沉积物沉积下来可形成物性夹层 | 河口坝侧缘、水下分流河道侧缘、浪成砂坝主体 | 主要为0.2~1.0 m,平均为0.5 m | 多小于0.2 km,平均宽厚比为350 | 孔隙度为5%~10%,渗透率小于40 mD,局部有一点渗透性 | Z20、Z80、Z05、R60、R20 | |
| 钙质 隔夹层 | 顶部钙质夹层 | 自然伽马曲线不回返,密度剧增,分布在砂岩顶部,可对比 | 4级 | 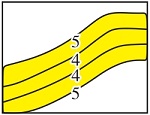 | 生物碎屑及先前的碳酸盐胶结物提供钙质来源,形成可能与有机酸和黏土矿物转化有关 | 河口坝主体、水下分流河道主体、浪成砂坝主体 | 主要为0.2~1.0 m,平均为0.5 m | 多为全区分布,也见局部发育,多大于0.6 km | 孔隙度为2%~8%,渗透率小于5 mD,封隔性强 | Z16.01、Z16.10、Z16.20、Z17.20、Z17.42、R15.60、R15.70、R16.01、R16.10、R16.30、R16.60 |
| 层内钙质夹层 | 自然伽马曲线不回返,密度剧增,随机分布在砂岩内部和底部,不可对比 | 3级居多,4级较少 | 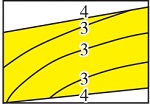 | 生物碎屑提供主要钙质来源,形成于海平面相对下降时期 | 河口坝主体、水下分流河道主体、浪成砂坝主体 | 主要为0.2~1.1 m,平均为0.7 m | 多小于0.2 km,平均宽厚比为300 | 孔隙度为6%~12%,渗透率小于100 mD,局部有一定的渗透性 | Z10、Z20、Z60、Z80、Z20、Z25、Z46、R70、R01、R40、R60 | |
Table 3.
Targets and countermeasures for potential tapping in the heavy oil reservoirs in Panyu oilfield group"
| 油田名称 | 油藏名称 | 油藏 类型 | 潜力井个数 | 油柱 高度/m | 富集部位 | 剩余油 赋存模式 | 层内夹层构型界面 主控因素 | 挖潜策略 (低产低效井侧钻) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 番禺B油田 | Z40 | 底水 | 2 | 3.0 | 西南部 | 脊间型 | 层内4级界面 | 小井距、短井段 |
| Z60 | 底水 | 2 | 3.5 | 西南部 | 郊区型 | 层内3级界面 | 侧钻 | |
| 6.0 | 北部 | 遮挡型 | 层内3级界面 | 侧钻 | ||||
| Z80 | 底水 | 2 | 1.5 | 西南部 | 脊间型 | 层内4级界面 | 定向井 | |
| 5.0 | 北部 | 遮挡型 | 层内4级界面 | 侧钻 | ||||
| Z20 | 边水 | 1 | 2.0 | 北部高点 | 脊间型 | 层底4级界面 | 小井距、短井段 | |
| Z25 | 底水 | 1 | 4.0 | 中部 | 遮挡型 | 层内3级界面 | 侧钻 | |
| 番禺A油田 | R60 | 底水 | 2 | 5.0~6.0 | A09-2井与B05-1井 之间、B10井以北 | 遮挡型 | 层内4级界面 | 侧钻 |
| R01 | 底水 | 2 | 4.0~5.0 | A09-2井以南、B18井与B15-1井之间 | 脊间型 | 层内3级界面 | 侧钻 | |
| R20 | 底水 | 6 | 6.0~10.0 | 井间加密 | 脊间型 | 层内3级界面 | 小井距、短井段 | |
| R40 | 底水 | 1 | 3.2 | A07井—A09-3井与A03井—A11井之间 | 郊区型 | 层内4级界面 | 侧钻 | |
| R80 | 底水 | 1 | 6.0 | A09-2井与A18-1井之间 | 遮挡型 | 层内4级界面 | 小井距、短井段 | |
| 番禺B油田 | Z20 | 底水 | 2 | 2.5~4.0 | 北部高点 | 遮挡型 | 层底3级界面 | 侧钻 |
| 3.0~4.0 | 南部 | 未动用 | 层内3级界面 | 侧钻 | ||||
| Z05 | 底水 | 1 | 2.5~3.0 | 北部高点 | 脊间型 | 层底3级界面 | 侧钻 | |
| 番禺A油田 | Z40 | 边水 | 2 | 3.0~4.0 | 中—高部位 | 未动用 | 无夹层 | 侧钻 |
| Z50 | 底水 | 1 | 4.0 | 高部位 | 未动用 | 层内4级界面 | 侧钻 | |
| Z90 | 底水 | 1 | 3.5 | 高部位 | 未动用 | 无夹层 | 侧钻 | |
| H68 | 底水 | 1 | 6.8 | 高部位 | 未动用 | 层内4级界面 | 侧钻 |
| [1] | 汤婧. 海相砂岩稠油油藏储层精细表征研究:以番禺5-1油田为例[J]. 中国石油和化工标准与质量, 2021, 41(24):134-136. |
| TANG Jing. Study on fine reservoir characterization of marine sandstone heavy oil reservoirs:A case study of Panyu 5-1 oilfield[J]. China Petroleum and Chemical Standard and Quality, 2021, 41(24):134-136. | |
| [2] |
ALLEN J R L. The plan shape of current ripples in relation to flow conditions[J]. Sedimentology, 1977, 24(1):53-62.
doi: 10.1111/sed.1977.24.issue-1 |
| [3] |
MIALL A D. Architectural-element analysis:A new method of facies analysis applied to fluvial deposits[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 1985, 22:261-308.
doi: 10.1016/0012-8252(85)90001-7 |
| [4] | MIALL A D. Reservoir heterogeneities in fluvial sandstones:Lessons from outcrop studies[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1988, 72(6):682-697. |
| [5] |
WYNN R B, CRONIN B T, PEAKALL J. Sinuous deep-water channels:Genesis,geometry and architecture[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2007, 24:341-387.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2007.06.001 |
| [6] |
岳大力, 吴胜和, 刘建民. 曲流河点坝地下储层构型精细解剖方法[J]. 石油学报, 2007, 28(4):99-103.
doi: 10.7623/syxb200704020 |
|
YUE Dali, WU Shenghe, LIU Jianmin. An accurate method for anatomizing architecture of subsurface reservoir in point bar of meandering river[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2007, 28(4):99-103.
doi: 10.7623/syxb200704020 |
|
| [7] | 蒋平, 赵应成, 李顺明, 等. 不同沉积体系储集层构型研究与展望[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2013, 34(1):111-115. |
| JIANG Ping, ZHAO Yingcheng, LI Shunming, et al. Reservoir configuration research and prospect of different deposit systems[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2013, 34(1):111-115. | |
| [8] | 闫百泉, 张鑫磊, 于利民, 等. 基于岩心及密井网的点坝构型与剩余油分析[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2014, 41(5):597-604. |
| YAN Baiquan, ZHANG Xinlei, YU Limin, et al. Point bar configuration and residual oil analysis based on core and dense well pattern[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2014, 41(5):597-604. | |
| [9] | 印森林, 刘忠保, 陈燕辉, 等. 冲积扇研究现状及沉积模拟实验:以碎屑流和辫状河共同控制的冲积扇为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2017, 35(1):10-23. |
| YIN Senlin, LIU Zhongbao, CHEN Yanhui, et al. Research progress and sedimentation experiment simulation about alluvial fan:A case study on alluvial fan controlled by debris flow and braided river[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2017, 35(1):10-23. | |
| [10] |
冯文杰, 吴胜和, 刘忠保, 等. 逆断层正牵引构造对冲积扇沉积过程与沉积构型的控制作用:水槽沉积模拟实验研究[J]. 地学前缘, 2017, 24(6):370-380.
doi: 10.13745/j.esf.yx.2016-11-63 |
| FENG Wenjie, WU Shenghe, LIU Zhongbao, et al. The controlling effects on depositional process and sedimentary architecture of alluvial fan by normal drag structure caused by thrust fault:Insights from flume tank experiments[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2017, 24(6):370-380. | |
| [11] | 刘金库, 胡杨, 伍燚. 苏里格气田盒8 段辫状河储集层构型空间展布[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2023, 44(2):144-150. |
| LIU Jinku, HU Yang, WU Yi. Spatial distribution of architectures of braided river reservoirs in He 8 member,Sulige gas field[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2023, 44(2):144-150. | |
| [12] | 吴胜和, 岳大力, 冯文杰, 等. 碎屑岩沉积构型研究若干进展[J]. 古地理学报, 2021, 23(2):245-262. |
| WU Shenghe, YUE Dali, FENG Wenjie, et al. Research progress of depositional architecture of clastic systems[J]. Journal of Paleogeography, 2021, 23(2):245-262. | |
| [13] | 郑昕, 束青林, 苏朝光, 等. 基于模拟退火的曲流河复合点坝建模新方法[J]. 断块油气田, 2023, 30(1):114-119. |
| ZHENG Xin, SHU Qinglin, SU Chaoguang, et al. A new modeling method of meandering river complex point bars based on simulated annealing[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2023, 30(1):114-119. | |
| [14] | 马世忠, 杨清彦. 曲流点坝沉积模式、三维构形及其非均质模型[J]. 沉积学报, 2000, 18(2):241-247. |
| MA Shizhong, YANG Qingyan. The depositional model,3-D architecture and heterogeneous model of point bar in meandering channels[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2000, 18(2):241-247. | |
| [15] | 胡光义, 肖大坤, 范廷恩, 等. 河流相储层构型研究新理论、新方法:海上油田河流相复合砂体构型概念、内容及表征方法[J]. 古地理学报, 2019, 21(1):143-159. |
| HU Guangyi, XIAO Dakun, FAN Tingen, et al. New theory and method of fluvial reservoir architecture study:Concepts,contents and characterization of offshore oilfield fluvial compound sand-body architecture[J]. Journal of Paleogeography, 2019, 21(1):143-159. | |
| [16] | 叶小明, 刘小鸿, 张岚, 等. 曲流河储层构型建模方法研究进展[J]. 中国海上油气, 2022, 34(1):84-93. |
| YE Xiaoming, LIU Xiaohong, ZHANG Lan, et al. Research progress on the architecture modeling methods of meandering river reservoirs[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2022, 34(1):84-93. | |
| [17] | 毛平. 砂质辫状河储集层构型表征研究现状及展望[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2018, 39(4):492-500. |
| MAO Ping. The status and prospects of research on characterization for sandy braided river reservoir architecture[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2018, 39(4):492-500. | |
| [18] | 刘伟新, 王华, 万琼华, 等. 基于分频RGB融合技术的辫状河三角洲储层构型精细解剖[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2022, 44(5):765-774. |
| LIU Weixin, WANG Hua, WAN Qionghua, et al. Fine analysis of braided river delta resevoir architecture based on frequency division RGB fusion technology[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2022, 44(5):765-774. | |
| [19] | 涂乙, 刘伟新, 戴宗, 等. 珠江口盆地A油田储集层参数概率分布有效性检验及油气储量评估[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2017, 38(3):302-308. |
| TU Yi, LIU Weixin, DAI Zong, et al. Validity test of reservoir parameter probability distribution and estimation of petroleum reserves in Oilfield A,Pearl River Mouth basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2017, 38(3):302-308. | |
| [20] | 涂乙, 闫正和, 戴建文, 等. 中国南海珠江口盆地西江油田运聚再生油藏模式创新认识与挖潜效果[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2021, 42(2):522-532. |
| TU Yi, YAN Zhenghe, DAI Jianwen, et al. New understanding and tapping effect of remaining oil reservoirs in Xijiang oilfield,PRMB,South China sea[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2021, 42(2):522-532. | |
| [21] | 戴建文, 张伟, 王华, 等. 海上稀井网油田碎屑岩储集层构型特征及储集层预测:以珠江口盆地陆丰凹陷L14油田为例[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2022, 43(5):526-536. |
| DAI Jianwen, ZHANG Wei, WANG Hua, et al. Architecture and prediction of clastic reservoirs in offshore oilfields with sparse well pattern:A case study on L14 oilfield in Lufeng sag in Pearl River Mouth basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2022, 43(5):526-536. | |
| [22] | 彭光荣, 温华华, 刘从印, 等. 珠江口盆地珠一坳陷浅层油气勘探实践及潜力探讨:以番禺4洼为例[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2013, 29(3):22-28. |
| PENG Guangrong, WEN Huahua, LIU Congyin, et al. Practice of shallow oil and gas exploration in Zhu Ⅰ depression of the Pearl River Mouth basin:A case from Panyu 4 sag[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2013, 29(3):22-28. | |
| [23] | 李瑞彪, 陈兆明, 石宁, 等. 高分辨率FMI成像测井在珠江口盆地番禺B洼勘探中的应用及其指示意义[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2020, 36(5):64-72. |
| LI Ruibiao, CHEN Zhaoming, SHI Ning, et al. Applications of high-resolution formation microscanner image logs(FMI) to hydrocarbon exploration in Panyu B sub-sag,Pearl River Mouth basin and its implications[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2020, 36(5):64-72. | |
| [24] | 张青青, 刘可禹, 衡立群, 等. 珠江口盆地番禺A油田珠江组“顶钙”发育特征、成因与分布模式[J]. 地球科学, 2021, 46(5):1783-1796. |
| ZHANG Qingqing, LIU Keyu, HENG Liqun, et al. Characteristics and genetic distribution model of top calcareous cementation layers within Zhujiang formation in Panyu A oilfield,Pearl River Mouth basin[J]. Earth Science, 2021, 46(5):1783-1796. | |
| [25] | 朱筱敏, 陈贺贺, 葛家旺, 等. 陆相断陷湖盆层序构型与砂体发育分布特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2022, 43(4):746-762. |
| ZHU Xiaomin, CHEN Hehe, GE Jiawang, et al. Characterization of sequence architectures and sandbody distribution in continental rift basins[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2022, 43(4):746-762. |
| [1] | BAO Dian, HU Wenge, CAO Fei, PENG Xiaoping, LIAO Shixi, PAN Lin, WANG Xiao. Development Characteristics and Main Controlling Factors of Reservoir Space in Northern Yujiang Strike-Slip Fault Zone [J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2024, 45(2): 172-180. |
| [2] | DING Shuaiwei, ZHANG Meng, LI Yuanduo, XU Chuan, ZHOU Yipeng, GAO Qun, YU Hongyan. Sensitivity Analysis of Injection-Production Parameters for CO2 Huff-n-Puff Flooding and Storage in Tight Oil Reservoirs:A Case From Typical Tight Reservoirs of Chang 7 Member,Ordos Basin [J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2024, 45(2): 181-188. |
| [3] | WANG Jie, LI Hongyu, LYU Dongliang, QIAN Chuanchuan, ZHOU Qunmao. Optimized Laboratory Experiment on Interlayer Interference in Heterogeneous Reservoirs [J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2024, 45(2): 199-204. |
| [4] | ZHANG Deyao. Genesis of Tilted Oil-Water Contact of Heavy Oil Reservoir in Shawan Formation, Chunfeng Oilfield, Junggar Basin [J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2024, 45(2): 205-212. |
| [5] | LIANG Yu, YANG Huidong, FU Xiandi, CAI Dongmei, WANG Yanhui, SUN Yanmin. Comprehensive Determination of Oil-Water Boundary in Eastern Transitional Zone of Daqing SN Oilfield [J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2024, 45(2): 213-220. |
| [6] | WEI Hongkun, WANG Jian, XU Tianhan, LU Yuhao, ZHOU Yaqin, WANG Junheng. Regulation of CO2 on Physical Properties of Heavy Oil Reservoir and EOR of CO2-Assisted Steam Flooding [J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2024, 45(2): 221-227. |
| [7] | MA Zhaojun, HU Zhiquan, ZHANG Jianfei. High-Resolution Processing Technology for Restoring Weak Signals Based on Harmonic Decomposition [J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2024, 45(2): 235-243. |
| [8] | LUO Danting, LUO Jinglan, DENG Chao, NIAN Tao, HAN Jianfa, CHENG Daojie, YUAN Long. Distribution Patterns and Significance of Salt in Deep Cretaceous Subsalt Reservoirs in Kuqa Depression,Tarim Basin [J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2024, 45(1): 1-12. |
| [9] | CHEN Keyang, ZHOU Hui, YANG Wei, WANG Cheng. Application of Scattered Wave Field in Identifying Fractured Reservoirs [J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2024, 45(1): 109-117. |
| [10] | ZUO Yi, SONG Jing, SHI Zhuoli, QIAO Jingxuan, ZU Xiuran, ZHENG Jie. Layered Modeling Algorithms and Cases for Different Reservoir Development Stages [J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2024, 45(1): 118-125. |
| [11] | LIU Honglin, WANG Huaichang, LI Xiaobo. Shale Gas Accumulation Characteristics of Wufeng Formation-Longmaxi Formation in Luzhou Area [J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2024, 45(1): 19-26. |
| [12] | SONG Haiqiang, LIU Huiqing, WANG Jing, SI Shanghua, YANG Xiao. Main Controlling Factors of Shale Oil and Gas Enrichment in Chang 7 Member, Southeastern Ordos Basin [J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2024, 45(1): 27-34. |
| [13] | CHU Fujian, GOU Tuobin, HAN Yuetao, GAO Wenjun. Establishment and Application of Type Ⅱ Generalized Gas-Water Miscible Flooding Characteristic Curve [J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2024, 45(1): 47-52. |
| [14] | ZHANG Rujie, YUE Ping, ZHANG Ying, LI Xiaobo, HUANG Nan, ZHAO Liming, FAN Qingzhen. Numerical Simulation of Grid-Like Fragmented Structure of Fault-Karst Reservoirs in Southern Tuoputai Block [J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2024, 45(1): 58-64. |
| [15] | LYU Xiaoguang, LI Wei. Thermally Recovered Reservoir Management and EOR for a Multi-Layered Sandstone Oilfield [J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2024, 45(1): 65-71. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||