

新疆石油地质 ›› 2021, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (4): 399-409.doi: 10.7657/XJPG20210402
宁超众1( ), 李勇1, 邓晓娟1, 陈家恒1, 王孝明2, 孙昭3, 韩永泉4
), 李勇1, 邓晓娟1, 陈家恒1, 王孝明2, 孙昭3, 韩永泉4
收稿日期:2020-09-23
修回日期:2021-01-19
出版日期:2021-08-01
发布日期:2021-08-09
作者简介:宁超众(1988-),男,山东济南人,工程师,博士,油气田开发地质,(Tel)18811386627(E-mail) 基金资助:
NING Chaozhong1( ), LI Yong1, DENG Xiaojuan1, CHEN Jiaheng1, WANG Xiaoming2, SUN Zhao3, HAN Yongquan4
), LI Yong1, DENG Xiaojuan1, CHEN Jiaheng1, WANG Xiaoming2, SUN Zhao3, HAN Yongquan4
Received:2020-09-23
Revised:2021-01-19
Online:2021-08-01
Published:2021-08-09
摘要:
哈拉哈塘油田奥陶系碳酸盐岩油藏为塔里木油田高产稳产的主力油藏,其缝洞型储集层成因机理、形成时期和油气分布一直是研究难点。基于地球物理资料,结合岩心和薄片观察、地球化学分析、生产特征分析等手段,研究了哈拉哈塘地区热液岩溶的特征,厘定了热液岩溶时期,明确了海西运动期活动断裂与加里东运动期走滑断裂对热液岩溶和油气分布的控制。研究认为,岩浆活动、海西运动期活动断裂形成、热液岩溶和油气成藏均主要发生在二叠纪,时间相近并具有成因上的继承性。海西运动期活动断裂与加里东运动期走滑断裂在力学性质、产状、规模、分布以及对热液岩溶的发育和控制方面存在差异。加里东运动期走滑断裂上热液岩溶体可以有效成藏,而海西运动期活动断裂由于在油气成藏期存在开启和间歇活动,导致热液岩溶体不能成藏或成藏能力差,从而造成哈拉哈塘地区奥陶系东西部油气分布差异巨大。在进行油气勘探和井位部署时应区分海西运动期活动断裂和加里东运动期走滑断裂,以寻找加里东运动期走滑断裂上热液岩溶体作为勘探目标。
中图分类号:
宁超众, 李勇, 邓晓娟, 陈家恒, 王孝明, 孙昭, 韩永泉. 哈拉哈塘地区热液岩溶形成演化与油气分布[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2021, 42(4): 399-409.
NING Chaozhong, LI Yong, DENG Xiaojuan, CHEN Jiaheng, WANG Xiaoming, SUN Zhao, HAN Yongquan. Formation and Evolution of Hydrothermal Karst and Hydrocarbon Distribution in Halahatang Area[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2021, 42(4): 399-409.
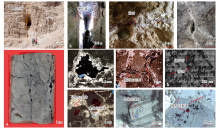
图3
塔里木盆地西北缘一间房地区野外露头及哈拉哈塘地区岩心和显微镜下热液特征 a—溶洞发育在2条断裂的交会处,鹰山组;b—a图洞穴内部,洞穴为竖型洞,内壁附有硬石膏;c—萤石洞内萤石;d—沿裂缝发育的溶蚀孔洞,缝壁充填热液方解石;e—裂缝扩溶,缝壁附着热液方解石,储集空间为小型孔洞以及热液方解石之间的微孔,孔洞内充填沥青,X38井,一间房组,7 216.0 m;f—晶洞,洞壁充填热液方解石,洞内充填沥青,X10井,一间房组,单偏光,6 591.0 m;g—沿裂缝的白云石化,白云石小晶体间充填沥青,X39井,良里塔格组,单偏光,6 728.9 m;h—裂缝内部的地开石和方解石溶蚀,X22井,一间房组,扫描电镜;i—早期和晚期方解石充填晶洞,早期方解石呈半自形粒状,晚期方解石呈他形,X40井,一间房组,单偏光;j—早期包裹体,包裹体为原生气液两相包裹体,均一温度125.0~135.0 ℃,i图中红框内;k—晚期包裹体,原生气液两相包裹体与固体沥青包裹体共存,均一温度93.8~122.0 ℃"

表2
哈拉哈塘地区2种断裂特征对比"
| 断裂类型 | 位置 | 断裂性质 | 力学机制 | 发育时期 | 走向 | 单段平面延伸 距离 | 层位 | 剖面识别 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 海西运动期活动断裂 | 靠近东河塘断隆的哈拉哈塘北部齐古和新垦区,分布密集 | 张性断裂 | 张扭 | 海西运动期二叠纪,与奥陶系油气成藏近同期 | 北西60°为主 | 1.5~6.0 km | 上奥陶统—二叠系 | 在地震剖面上难识别,依据伴生岩溶和热液排泄通道确定其分布和走向 |
| 加里东运动期走滑断裂 | 哈拉哈塘全区分布,北部相对密集,向南密度减小 | 走滑断裂 | 压扭 | 加里东运动期奥陶纪末 | 北东30°和北西20°为主 | 一般大于3.0 km,可达几十千米 | 基底—志留系 | 在地震剖面上较难识别,垂向断距小,奥陶系上部被岩溶复杂化 |
| [1] | 焦方正. 塔里木盆地顺托果勒地区北东向走滑断裂带的油气勘探意义[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2017, 38(5):831-839. |
| JIAO Fangzheng. Significance of oil and gas exploration in NE strike-slip fault belts in Shuntuoguole area of Tarim basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2017, 38(5):831-839. | |
| [2] | 宁超众, 胡素云, 李勇, 等. 深层与露头碳酸盐岩岩溶洞穴对比及类比:以塔里木盆地哈拉哈塘油田奥陶系良里塔格组古岩溶洞穴与美国德克萨斯州 Longhorn 近现代岩溶洞穴为例[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2020, 31(12):1 700-1 716. |
| NING Chaozhong, HU Suyun, LI Yong, et al. Comparison and analog of the deep-buried and outcrop carbonate karst cave systems:case study of the Lianglitage formation karst cave system,Halahatang oilfield,Tarim basin,China and the Longhorn modern karst cave system,Texas,USA[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2020, 31(12):1 700-1 716. | |
| [3] | 鲁新便, 胡文革, 汪彦, 等. 塔河地区碳酸盐岩断溶体油藏特征与开发实践[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2015, 36(3):347-355. |
| LU Xinbian, HU Wen’ge, WANG Yan, et al. Characteristics and development practice of fault-karst carbonate reservoirs in Tahe area,Tarim basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2015, 36(3):347-355. | |
| [4] | 李曰俊, 杨海军, 张光亚, 等. 重新划分塔里木盆地塔北隆起的次级构造单元[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(8):2 466-2 478. |
| LI Yuejun, YANG Haijun, ZHANG Guangya, et al. Redivision of the tectonic units of Tabei rise in Tarim basin,NW China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2012, 28(8):2 466-2 478. | |
| [5] | 俞仁连, 傅恒. 构造运动对塔河油田奥陶系碳酸盐岩的影响[J]. 天然气勘探与开发, 2006, 29(2):1-5. |
| YU Renlian, FU Heng. Influence of tectonic movement on Ordovician carbonates of Tahe oilfield[J]. Natural Gas Exploration and Development, 2006, 29(2):1-5. | |
| [6] | 朱光有, 杨海军, 朱永峰, 等. 塔里木盆地哈拉哈塘地区碳酸盐岩油气地质特征与富集成藏研究[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(3):827-844. |
| ZHU Guangyou, YANG Haijun, ZHU Yongfeng, et al. Study on petroleum geological characteristics and accumulation of carbonate reservoirs in Hanilcatam area,Tarim basin[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2011, 27(3):827-844. | |
| [7] | 安海亭, 李海银, 王建忠, 等. 塔北地区构造和演化特征及其对油气成藏的控制[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2009, 33(1):142-147. |
| AN Haiting, LI Haiyin, WANG Jianzhong, et al. Tectonic evolution and its controlling on oil and gas accumulation in the northern Tarim basin[J]. Geotectonica Et Metallogenia, 2009, 33(1):142-147. | |
| [8] | 程海艳, 李江海, 赵星. 塔北隆起古生代构造样式和构造反演[J]. 中国地质, 2009, 36(2):314-321. |
| CHENG Haiyan, LI Jianghai, ZHAO Xing. Paleozoic structural styles and evolution of the north Tarim uplift[J]. Geology in China, 2009, 36(2):314-321. | |
| [9] | 李彬, 贺凯, 吕海涛, 等. 塔北地区二叠系火山岩岩性特征及油气勘探前景[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2011, 32(6):851-858. |
| LI Bin, HE Kai, LYU Haitao, et al. Lithologic characteristics and petroleum exploration potential of the Permian volcanic rocks in northern Tarim basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2011, 32(6):851-858. | |
| [10] | 张巍, 关平, 简星. 塔里木盆地二叠纪火山—岩浆活动对古生界生储条件的影响:以塔中47井区为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2014, 32(1):148-158. |
| ZHANG Wei, GUAN Ping, JIAN Xing. Effects of Permian volcanic-magmatic activity on the Paleozoic oil and gas generating and storing conditions in the Tarim basin:a case study of Tazhong-47 well area[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2014, 32(1):148-158. | |
| [11] | 陈汉林, 杨树锋, 董传万, 等. 塔里木盆地地质热事件研究[J]. 科学通报, 1997, 42(10):1 096-1 099. |
| CHEN Hanlin, YANG Shufeng, DONG Chuanwan, et al. The geothermal events in the Tarim basin[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1997, 42(10):1 096-1 099. | |
| [12] | 潘文庆, 刘永福, D DICKSON J A, 等. 塔里木盆地下古生界碳酸盐岩热液岩溶的特征及地质模型[J]. 沉积学报, 2009, 27(5):983-994. |
| PAN Wenqing, LIU Yongfu, D DICKSON J A, et al. The geological model of hydrothermal activity in outcrop and the characteristics of carbonate hydrothermal karst of Lower Paleozoic in Tarim basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2009, 27(5):983-994. | |
| [13] | 张兴阳, 顾家裕, 罗平, 等. 塔里木盆地奥陶系萤石成因及其油气地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(8):2 220-2 228. |
| ZHANG Xingyang, GU Jiayu, LUO Ping, et al. Genesis of the fluorite in the Ordovician and its significance to the petroleum geology of Tarim basin[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2006, 22(8):2 220-2 228. | |
| [14] | 陈红汉, 吴悠, 朱红涛, 等. 塔中地区北坡中—下奥陶统早成岩岩溶作用及储层形成模式[J]. 石油学报, 2016, 37(10):1 231-1 246. |
| CHEN Honghan, WU You, ZHU Hongtao, et al. Eogenetic karstification and reservoir formation model of the Middle-Lower Ordovician in the northeast slope of Tazhong uplift,Tarim basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2016, 37(10):1 231-1 246. | |
| [15] | 傅恒, 韩建辉, 孟万斌, 等. 塔里木盆地塔中北坡奥陶系碳酸盐岩岩溶储层的形成机理[J]. 天然气工业, 2017, 37(3):25-36. |
| FU Heng, HAN Jianhui, MENG Wanbin, et al. Forming mechanism of the Ordovician karst carbonate reservoirs on the northern slope of central Tarim basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2017, 37(3):25-36. | |
| [16] | 李坤白, 云露, 蒲仁海, 等. 塔东顺南1井区火山活动与断裂及热液作用关系[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2016,(5):1 934-1 946. |
| LI Kunbai, YUN Lu, PU Renhai, et al. Relationship between volcanic activity and fault,hydrothermalism in Shunnan-1 3D well zone in Tadong area,Tarim basin[J]. Progress in Geophysics(in Chinese), 2016, 31(5):1 934-1 946. | |
| [17] | 倪新锋, 王招明, 杨海军, 等. 塔北地区奥陶系碳酸盐岩储层岩溶作用[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2010, 17(5):11-16. |
| NI Xinfeng, WANG Zhaoming, YANG Haijun. Formation mechanism of Ordovician carbonate karst reservoir in the northern Tarim basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2010, 17(5):11-16. | |
| [18] | 陈兰朴, 李国蓉, 吴章志, 等. 塔里木盆地塔河油田东南斜坡海西晚期奥陶系热液作用[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2017, 28(3):410-419. |
| CHEN Lanpu, LI Guorong, WU Zhangzhi, et al. Study on the Ordovician hydrothermal action at Late Hercynian in the southeast slope of Tahe oilfield,Tarim basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2017, 28(3):410-419. | |
| [19] | 斯春松, 乔占峰, 沈安江, 等. 塔北南缘奥陶系层序地层对岩溶储层的控制作用[J]. 石油学报, 2012, 33(增刊2):135-144. |
| SI Chunsong, QIAO Zhanfeng, SHEN Anjiang, et al. The controlling effect of sequence stratigraphy on karst reservoirs of Ordovician in the south margin of northern Tarim basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(Supp.2):135-144. | |
| [20] | 孙东, 杨丽莎, 王宏斌, 等. 塔里木盆地哈拉哈塘地区走滑断裂体系对奥陶系海相碳酸盐岩储层的控制作用[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2015, 26(增刊1):80-87. |
| SUN Dong, YANG Lisha, WANG Hongbin, et al. Strike-slip fault system in Halahatang area of Tarim basin and its control on reservoirs of Ordovician marine carbonate rock[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2015, 26(Supp.1):80-87. | |
| [21] | 孙崇浩, 朱光有, 郑多明, 等. 塔里木盆地哈拉哈塘地区超深碳酸盐岩缝洞型储集层特征与控制因素[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2016, 35(5):1 028-1 036. |
| SUN Chonghao, ZHU Guangyou, ZHENG Duoming, et al. Characteristics and controlling factors of fracture-cavity carbonate reservoirs in the Halahatang area,Tarim basin[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy,Petrology and Geochemistry, 2016, 35(5):1 028-1 036. | |
| [22] | 金之钧, 朱东亚, 胡文瑄, 等. 塔里木盆地热液活动地质地球化学特征及其对储层影响[J]. 地质学报, 2006, 80(2):245-253. |
| JIN Zhijun, ZHU Dongya, HU Wenxuan, et al. Geological and geochemical signatures of hydrothermal activity and their influence on carbonate reservoir beds in the Tarim basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2006, 80(2):245-253. | |
| [23] | 丁茜, 何治亮, 沃玉进, 等. 高温高压条件下碳酸盐岩溶蚀过程控制因素[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2017, 38(4):784-791. |
| DING Qian, HE Zhiliang, WO Yujin, et al. Factors controlling carbonate rock dissolution under high temperature and pressure[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2017, 38(4):784-791. | |
| [24] | 邹高峰, 郭肖, 朱争, 等. 高含硫气藏海相碳酸盐岩高温高压水岩反应实验[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 2019, 38(1):34-41. |
| ZOU Gaofeng, GUO Xiao, ZHU Zheng, et al. Experiment of the water-rock reaction for the marine carbonate under high temperature and high pressure in high-sulfur gas reservoir[J]. Petroleum Geology and Oilfield Development in Daqing, 2019, 38(1):34-41. | |
| [25] | 潘文庆, 胡秀芳, 刘亚雷, 等. 塔里木盆地西北缘奥陶系碳酸盐岩中两种来源热流体的地质与地球化学证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(8):2 515-2 524. |
| PAN Wenqing, HU Xiufang, LIU Yalei, et al. Geological and geochemical evidences for two sources of hydrothermal fluids found in Ordovician carbonate rocks in northwestern Tarim basin[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2012, 28(8):2 515-2 524. | |
| [26] | KLIMCHOUK A B. Hypogene speleogenesis:karst geomorphology[J]. Treatise on Geomorphology, 2013, 6:220-240. |
| [27] | 宁超众, 孙龙德, 胡素云, 等. 塔里木盆地哈拉哈塘油田奥陶系缝洞型碳酸盐岩储层岩溶类型及特征[J]. 石油学报, 2021, 42(1):15-32. |
| NING Chaozhong, SUN Longde, HU Suyun, et al. Karst types and characteristics of the Ordovician fracture-cavity type carbonate reservoirs in Halahatang oilfield,Tarim basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2021, 42(1):15-32. | |
| [28] | ARK E M V, DETRICK R S, CANALES J P, et al. Seismic structure of the Endeavour segment,Juan de Fuca ridge:correlations with seismicity and hydrothermal activity[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2007, 112:1-22. |
| [29] | 张宝民, 刘静江. 中国岩溶储集层分类与特征及相关的理论问题[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2009, 36(1):12-29. |
| ZHANG Baomin, LIU Jingjiang. Classification and characteristics of karst reservoirs in China and related theories[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2009, 36(1):12-29. | |
| [30] | 杨树锋, 厉子龙, 陈汉林, 等. 塔里木二叠纪石英正长斑岩岩墙的发现及其构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(5):1 405-1 412. |
| YANG Shufeng, LI Zilong, CHEN Hanlin, et al. Discovery of a Permian quartz syenitic prophyritic dyke from the Tarim basin and its tectoic implications[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2006, 22(5):1 405-1 412. | |
| [31] |
WEI Tian, CAMPBELL I H, ALLEN C M. The Tarim picrate-basalt-rhyolite suite,a Permian flood basalt from northwest China with contrasting rhyolites produced by fractional crystallization and anatexis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2010, 160(3):407-425.
doi: 10.1007/s00410-009-0485-3 |
| [32] | 徐汉林, 方乐华, 张昕, 等. 塔里木盆地早二叠世岩浆特征及其对油气成藏关系初探[J]. 地球学报, 2006, 27(3):235-240. |
| XU Hanlin, FANG Lehua, ZHANG Xin, et al. Characteristics of Early Permian magmatic rocks and their impact on hydrocarbon accumulation in Tarim basin[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2006, 27(3):235-240. | |
| [33] | 江同文, 肖阳, 刘子龙, 等. 哈拉哈塘油田缝洞型油藏自流注水耦合计算模型[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2019, 40(1):74-78. |
| JIANG Tongwen, XIAO Yang, LIU Zilong, et al. A dumpflood coupling calculation model of fractured-vuggy reservoirs in Halahatang oilfield[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2019, 40(1):74-78. | |
| [34] | 郑晓丽, 安海亭, 王祖君, 等. 哈拉哈塘地区走滑断裂与断溶体油藏特征[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2019, 40(4):449-455. |
| ZHENG Xiaoli, AN Haiting, WANG Zujun, et al. Characteristics of strike-slip faults and fault-karst carbonate reservoirs in Halahatang area,Tarim basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2019, 40(4):449-455. |
| [1] | 李海英, 韩俊, 陈平, 李媛, 卜旭强. 塔里木盆地顺北4号走滑断裂带变形特征及有利区评价[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2023, 44(2): 127-135. |
| [2] | 陈平, 能源, 吴鲜, 黄诚, 王来源, 郭曼. 塔里木盆地顺北5号走滑断裂带分层分段特征及构造演化[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2023, 44(1): 33-42. |
| [3] | 代兰, 邬光辉, 陈鑫, 朱永峰, 陈思锜, 罗鑫, 胡明. 共轭走滑断裂形成演化的控制因素及物理模拟实验[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2023, 44(1): 43-50. |
| [4] | 张长建, 吕艳萍, 马海陇, 耿甜, 张晓. 塔河油田岩溶峡谷区伏流坍塌型古暗河缝洞系统[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2023, 44(1): 9-17. |
| [5] | 白晓飞, 周博, 董长银, 王方智, 刘霄, 甘凌云, 任今明. 哈拉哈塘油田奥陶系碳酸盐岩油藏储集层泥砂产出机理[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2022, 43(4): 456-462. |
| [6] | 张长建, 吕艳萍, 文欢, 王震, 马海陇. 塔河油田西部斜坡区加里东运动中期Ⅱ幕水文地貌特征及其对洞穴发育的控制[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2022, 43(2): 135-144. |
| [7] | 雷昇, 周玉辉, 王宁, 赛尔江·阿哈提, 郑强, 盛广龙. 基于井间连通性的碳酸盐岩油藏注采关系优化[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2021, 42(5): 584-591. |
| [8] | 郝婧, 张厚和, 李春荣, 张文昭, 李凡异, 严寒, 徐庆梅. 渤海海域油气勘探历程与启示[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2021, 42(3): 328-336. |
| [9] | 方俊伟, 董晓强, 李雄, 张国, 吴雄军. 顺北油田断溶体储集层特征及损害预防[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2021, 42(2): 201-205. |
| [10] | 刘军, 李伟, 龚伟, 黄超. 顺北地区超深断控储集体地震识别与描述[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2021, 42(2): 238-245. |
| [11] | 杨威, 周刚, 李海英, 马学军. 碳酸盐岩深层走滑断裂成像技术[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2021, 42(2): 246-252. |
| [12] | 张三, 金强, 赵深圳, 孙建芳, 李永强, 张旭栋, 程付启. 塔河油田海西运动早期奥陶系岩溶地貌[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2020, 41(5): 527-534. |
| [13] | 杨柳, 臧殿光, 徐宝亮, 邓绍强, 陈虹帆, 杨荣荣, 陈伟. 川东北开江地区茅口组凹陷异常体分布特征及成因[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2020, 41(5): 542-549. |
| [14] | 李红波, 王翠丽, 牛阁, 梁洪涛, 补璐璐, 顾俊颖. 有封闭水体的缝洞型油藏动态储量评价——以塔里木盆地哈拉哈塘油田为例[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2020, 41(3): 321-325. |
| [15] | 李振华,顾乔元,张大鹏,仝可佳,魏华,皮秋梅. 塔里木油田碳酸盐岩油藏产量预测方法[J]. , 2019, 40(5): 1-1. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||