

新疆石油地质 ›› 2025, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (6): 712-722.doi: 10.7657/XJPG20250607
李庆1a( ), 罗刚1b, 李映艳1b, 邓远1b, 肖佃师2(
), 罗刚1b, 李映艳1b, 邓远1b, 肖佃师2( ), 谢潇权2
), 谢潇权2
收稿日期:2025-04-30
修回日期:2025-07-12
出版日期:2025-12-01
发布日期:2025-12-05
通讯作者:
肖佃师
E-mail:liqing688@petrochina.com.cn;xiaods@upc.edu.cn
作者简介:李庆(1975-),男,四川资阳人,高级工程师,油气田开发,(Email)基金资助:
LI Qing1a( ), LUO Gang1b, LI Yingyan1b, DENG Yuan1b, XIAO Dianshi2(
), LUO Gang1b, LI Yingyan1b, DENG Yuan1b, XIAO Dianshi2( ), XIE Xiaoquan2
), XIE Xiaoquan2
Received:2025-04-30
Revised:2025-07-12
Online:2025-12-01
Published:2025-12-05
Contact:
XIAO Dianshi
E-mail:liqing688@petrochina.com.cn;xiaods@upc.edu.cn
摘要: 吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组页岩油接替区页岩油资源量大,但该区储集层厚度较小,甜点分布非均质性强。通过有机地球化学、岩石学、微观孔隙结构、油气赋存与可动性等实验测试,对接替区烃源岩、原油性质、储集层岩性、孔隙类型、页岩油赋存特征及可动性开展系统评价。结果表明:接替区烃源岩条件优良,相较于主力区普遍经历2期生烃高峰,原油密度与黏度显著降低,轻质组分占比提高;接替区储集层厚度小、粒度细,粒间孔不发育,溶蚀孔与晶间孔更发育,孔隙直径分布范围与主力区相近,但孔喉半径较主力区小;接替区与主力区均表现为多类型孔隙含油特征,页岩油赋存方式相似,接替区游离烃赋存的孔隙直径下限为40~60 nm,小于主力区;原油黏度对页岩油可动性具有显著控制作用,低黏度条件下接替区可动性较强,核磁共振可动性解释截止值较主力区小;可动油量、含油饱和度、孔隙压力及脆性是影响接替区产能的关键因素。在此基础上,提出了四因素权重组合的甜点评价技术,接替区甜点识别精度大于80%,研究成果为芦草沟组页岩油的稳产提供了理论支撑。
中图分类号:
李庆, 罗刚, 李映艳, 邓远, 肖佃师, 谢潇权. 吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组页岩油接替区开发潜力[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(6): 712-722.
LI Qing, LUO Gang, LI Yingyan, DENG Yuan, XIAO Dianshi, XIE Xiaoquan. Potential of Replacement Areas for Shale Oil Development in the Lucaogou Formation, Jimsar Sag[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2025, 46(6): 712-722.
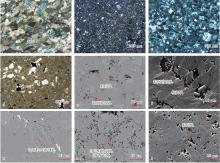
图4
吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组储集层岩性及孔隙特征 a—粉砂质页岩,J414井,4 122.3 m,铸体薄片;b—含白云粉砂质页岩,J412井,4 386.8 m,铸体薄片;c—含白云屑粉砂质页岩,J412井,4 387.2 m,铸体薄片;d—含粉砂白云质页岩,J412井,4 399.9 m,铸体薄片;e—含白云屑粉砂质页岩,J412井,4 249.9 m,扫描电镜;f—含白云粉砂质页岩,J31井,2 715.2 m,扫描电镜;g—粉砂质页岩,J412井,4 378.7 m,扫描电镜;h—含白云屑粉砂质页岩,J412井,4 399.9 m,扫描电镜;i—粉砂质页岩,J32井,3 570.7 m,扫描电镜。"

表2
吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组接替区页岩油甜点评价标准"
| 甜点类型 | 综合评价因子 | 可动油孔隙度/% | 含油饱和度/% | 孔隙压力/MPa | 脆性指数 | 归一化产能强度 | 油层类型 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ类 | >0.350 | >1.85 | >72.2 | >60.0 | >0.38 | >0.58 | Ⅰ |
| Ⅱ类 | 0.295~0.350 | 1.45~1.85 | 71.5~72.2 | 49.9~60.0 | 0.33~0.38 | 0.30~0.58 | Ⅱ |
| Ⅲ类 | 0.180~0.295 | 0.55~1.45 | 62.2~71.5 | 47.3~49.9 | 0.30~0.33 | 0.10~0.30 | Ⅲ |
| 无效 | <0.180 | <0.55 | <62.2 | <47.3 | <0.30 | <0.10 | 无效 |
| [1] | 魏登峰. 新疆地区页岩油气资源潜力及勘探方向[J]. 石油物探, 2024, 63(6):1087-1099. |
| WEI Dengfeng. Potential resources and exploration direction of shale oil and gas in Xinjiang[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2024, 63(6):1087-1099. | |
| [2] | 贾承造, 郑民, 张永峰. 中国非常规油气资源与勘探开发前景[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2012, 39(2):129-136. |
| JIA Chengzao, ZHENG Min, ZHANG Yongfeng. Unconventional hydrocarbon resources in China and the prospect of exploration and development[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2012, 39(2):129-136. | |
| [3] | 邹才能, 董大忠, 王社教, 等. 中国页岩气形成机理、地质特征及资源潜力[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2010, 37(6):641-653. |
|
ZOU Caineng, DONG Dazhong, WANG Shejiao, et al. Geological characteristics,formation mechanism and resource potential of shale gas in China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2010, 37(6):641-653.
doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(11)60001-3 |
|
| [4] |
赵文智, 朱如凯, 张婧雅, 等. 中国陆相页岩油类型、勘探开发现状与发展趋势[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2023, 28(4):1-13.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2023.04.001 |
|
ZHAO Wenzhi, ZHU Rukai, ZHANG Jingya, et al. Classification, exploration and development status and development trend of continental shale oil in China[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2023, 28(4):1-13.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2023.04.001 |
|
| [5] | 贾承造, 王祖纲, 姜林, 等. 中国页岩油勘探开发研究进展与科学技术问题[J]. 世界石油工业, 2024, 31(4):1-11. |
| JIA Chengzao, WANG Zugang, JIANG Lin, et al. Progress and key scientific and technological problems of shale oil exploration and development in China[J]. World Petroleum Industry, 2024, 31(4):1-11. | |
| [6] | 齐洪岩, 吴承美, 胡可, 等. 准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷页岩油效益开发关键技术与实践[J]. 新疆石油天然气, 2024, 20(3):15-22. |
| QI Hongyan, WU Chengmei, HU Ke, et al. Key technologies and practice of shale oil cost-effective development in Jimsar sag,Junggar Basin[J]. Xingjiang Oil & Gas, 2024, 20(3):15-22. | |
| [7] | 孙志刚, 于春磊, 陈辉, 等. 陆相页岩油开发实验技术现状与展望[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2024, 31(5):186-198. |
| SUN Zhigang, YU Chunlei, CHEN Hui, et al. Progress and prospect of experimental technologies for continental shale oil development[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2024, 31(5):186-198. | |
| [8] | 汪海阁, 常龙, 卓鲁斌, 等. 中国石油陆相页岩油钻井技术现状与发展建议[J]. 新疆石油天然气, 2024, 20(3):1-14. |
| WANG Haige, CHANG Long, ZHUO Lubin, et al. Current status and suggestions for drilling technology of CNPC continental shale oil reservoirs[J]. Xingjiang Oil & Gas, 2024, 20(3):1-14. | |
| [9] |
邓远, 陈轩, 覃建华, 等. 吉木萨尔凹陷二叠系芦草沟组一段沉积期古地貌特征及有利储层分布[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2024, 36(1):136-144.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20240113 |
|
DENG Yuan, CHEN Xuan, QIN Jianhua, et al. Paleogeomorphology and favorable reservior distribution of the first member of Permian Lucaogou formation in Jimsar sag[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2024, 36(1):136-144.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20240113 |
|
| [10] |
吴宝成, 吴承美, 谭强, 等. 准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷昌吉页岩油成藏条件及勘探开发关键技术[J]. 石油学报, 2024, 45(2):437-460.
doi: 10.7623/syxb202402009 |
|
WU Baocheng, WU Chengmei, TAN Qiang, et al. Accumulation conditions and key technologies for exploration and development of Changji shale oil in Jimusar sag of Junggar Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2024, 45(2):437-460.
doi: 10.7623/syxb202402009 |
|
| [11] |
熊雄, 肖佃师, 雷祥辉, 等. 吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组页岩油录井响应及“甜点”快速评价技术[J]. 特种油气藏, 2023, 30(4):35-43.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2023.04.005 |
| XIONG Xiong, XIAO Dianshi, LEI Xianghui, et al. Response of well logging and “sweet spot” rapid evaluation technology for shale oil in the Lucaogou formation of Jimsar sag[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2023, 30(4):35-43. | |
| [12] |
蒋中发, 丁修建, 王忠泉, 等. 吉木萨尔凹陷二叠系芦草沟组烃源岩沉积古环境[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2020, 32(6):109-119.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20200610 |
|
JIANG Zhongfa, DING Xiujian, WANG Zhongquan, et al. Sedimentary paleoenvironment of source rocks of Permian Lucaogou formation in Jimsar sag[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2020, 32(6):109-119.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20200610 |
|
| [13] | 陈轩, 陶鑫, 覃建华, 等. 准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷及周缘二叠系芦草沟组异重流沉积[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2023, 44(6):1530-1545. |
| CHEN Xuan, TAO Xin, QIN Jianhua, et al. Hyperpycnal flow deposits of the Permian Lucaogou formation in the Jimusaer sag and its peripheries,Junggar Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2023, 44(6):1530-1545. | |
| [14] | ZENG Wenren, ZHANG Zhihuan, WANG Boran, et al. Formation mechanism of organic-rich mixed sedimentary rocks in saline lacustrine basin,Permian Lucaogou formation,Jimsar sag,Junggar Basin,northwest China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2023,156:106452. |
| [15] | 曹志锋, 蔺敬旗, 凌亮, 等. 吉木萨尔凹陷页岩油超压成因及其对产能的影响[J]. 测井技术, 2025, 49(2):298-309. |
| CAO Zhifeng, LIN Jingqi, LING Liang, et al. The cause of shale oil overpressure and its influence on productivity in Jimsar sag[J]. Well Logging Technology, 2025, 49(2):298-309. | |
| [16] |
张文文, 韩长城, 田继军, 等. 吉木萨尔凹陷二叠系芦草沟组层序地层划分及演化特征[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2021, 33(5):45-58.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20210505 |
|
ZHANG Wenwen, HAN Changcheng, TIAN Jijun, et al. Sequence stratigraphy division and evolutionary features of Permian Lucaogou formation in Jimsar sag[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2021, 33(5):45-58.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20210505 |
|
| [17] | 何晋译, 冷筠滢, 何文军, 等. 准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷二叠系芦草沟组不同岩相泥质烃源岩品质与含油性特征:以J10025井为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2025, 47(3):606-620. |
| HE Jinyi, LENG Yunying, HE Wenjun, et al. Quality and oil-bearing properties of argillaceous hydrocarbon source rocks across different lithofacies of Permian Lucaogou formation in Jimsar sag,Junggar Basin:A case study of Well J10025[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2025, 47(3):606-620. | |
| [18] | 刘金, 王剑, 张宝真, 等. 准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷二叠系芦草沟组微—纳米孔隙页岩油原位赋存特征[J]. 石油实验地质, 2022, 44(2):270-278. |
| LIU Jin, WANG Jian, ZHANG Baozhen, et al. In situ occurrence of shale oil in micro-nano pores in Permian Lucaogou formation in Jimsar sag,Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2022, 44(2):270-278. | |
| [19] | 周新锐, 王喜鑫, 李少华, 等. 陆相混积型页岩储集层孔隙结构特征及其控制因素[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2023, 44(4):411-420. |
| ZHOU Xinrui, WANG Xixin, LI Shaohua, et al. Pore structure characteristics and controlling factors of continental mixed shale reservoirs[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2023, 44(4):411-420. | |
| [20] | 齐洪岩, 王振林, 张艳宁, 等. 吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组页岩油藏甜点分类[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(2):127-135. |
| QI Hongyan, WANG Zhenlin, ZHANG Yanning, et al. Classification of sweet spots in shale oil reservoir of Lucaogou formation in Jimsar sag,Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2025, 46(2):127-135. | |
| [21] |
龚德瑜, 苗一豪, 陈旋, 等. 准噶尔盆地东部中二叠统芦草沟组烃源岩生烃潜力评价[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2024, 35(5):823-837.
doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2024.03.011 |
|
GONG Deyu, MIAO Yihao, CHEN Xuan, et al. Hydrocarbon-generating potential of the Middle Permian Lucaogou source rock in the eastern Junggar Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2024, 35(5):823-837.
doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2024.03.011 |
|
| [22] |
刘胜男, 朱如凯, 靳军, 等. 油气运移约束陆相页岩油富集:以准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组为例[J]. 石油学报, 2024, 45(6):932-946.
doi: 10.7623/syxb202406004 |
|
LIU Shengnan, ZHU Rukai, JIN Jun, et al. Hydrocarbon migration constraints on continental shale oil enrichment:A case study of Lucaogou formation in Jimusaer sag,Junggar Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2024, 45(6):932-946.
doi: 10.7623/syxb202406004 |
|
| [23] | 李映艳, 邓远, 何吉祥, 等. 吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组页岩油有效储层物性下限研究[J]. 断块油气田, 2025, 32(1):20-26. |
| LI Yingyan, DENG Yuan, HE Jixiang, et al. Study on lower limit of physical properties of effective shale oil reservoirs of Lucaogou formation,Jimsar sag[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2025, 32(1):20-26. | |
| [24] | 刘金, 王剑, 张晓刚, 等. 准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组甜点页岩油微观赋存特征及成因机制[J]. 地质论评, 2022, 68(3):907-920. |
| LIU Jin, WANG Jian, ZHANG Xiaogang, et al. Microscopic occurrence characteristics and genetic mechanism of shale oil in sweet spot reservoir of the Lucaogou formation in Jimsar sag[J]. Geological Review, 2022, 68(3):907-920. | |
| [25] | GAO Zhiye, DUAN Longfei, JIANG Zhenxue, et al. Using laser scanning confocal microscopy combined with saturated oil experiment to investigate the pseudo in-situ occurrence mechanism of light and heavy components of shale oil in sub-micron scale[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2023,220:111234. |
| [26] |
陈旋, 苟红光, 张有锦, 等. 准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷北部芦草沟组高产页岩油特征及地质意义:以奇探1井为例[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2025, 36(1):1-12.
doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2024.05.015 |
|
CHEN Xuan, GOU Hongguang, ZHANG Youjin, et al. Characteristics and geological significance of high-yield shale oil from the Lucaogou formation in the northern Jimsar sag of Junggar Basin:A case study of Well Qitan 1[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2025, 36(1):1-12.
doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2024.05.015 |
|
| [27] | 周源. 吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组页岩油赋存特征及可动性评价[D]. 山东青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2022. |
| ZHOU Yuan. Occurrence characteristics and mobility evaluation of shale oil in Lucaogou formation,Jimsar[D]. Qingdao, Shandong: China University of Petroleum(East China), 2022. | |
| [28] | 覃建华, 李映艳, 杜戈峰, 等. 基于核磁共振测井的页岩油产能分析及甜点评价[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2024, 45(3):317-326. |
| QIN Jianhua, LI Yingyan, DU Gefeng, et al. NMR logging-based productivity analysis and sweet spot evaluation for shale oil[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2024, 45(3):317-326. | |
| [29] | 李玉丹. 页岩气藏多尺度渗流规律研究及产能评价[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2020. |
| LI Yudan. Multi-scale flow mechanism analysis and productivity evaluation of shale gas[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum(Beijing), 2020. | |
| [30] | 谭成仟, 宋子齐, 吴少波. 灰色关联分析在辽河小洼油田储层油气产能评价中的应用[J]. 测井技术, 2001, 25(2):119-122. |
| TAN Chengqian, SONG Ziqi, WU Shaobo. Application of grey correlation analysis in predicting reservoir production capacity in Liaohe Xiaowa oilfield[J]. Well Logging Technology, 2001, 25(2):119-122. |
| [1] | 金之钧, 曹琰, 张虹, 唐勇, 秦志军, 刘扣其, 梁成钢, 李关访, 何文军. 吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组页岩油甜点主控因素研究与实践[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(6): 647-658. |
| [2] | 毛新军, 王然, 郑孟林, 李菁, 潘进, 王韬, 黄立良, 常秋生. 吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组页岩油甜点储集层孔隙成因及成岩演化[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(6): 659-667. |
| [3] | 曹剑, 秦志军, 魏超, 向宝力, 刘金. 陆相纹层型页岩油源储耦合与甜点形成机理——以准噶尔盆地风城组为例[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(6): 668-683. |
| [4] | 刘金, 白雷, 张宝真, 魏超, 雷海艳, 邓远, 曹剑. 吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组页岩油微观赋存特征与开采动态响应[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(6): 684-692. |
| [5] | 邹阳, 陈文顺, 罗刚, 陈绍蓉, 陈方文, 何文军, 刘新龙, 朱涛. 玛湖凹陷风城组碱湖页岩油富集和高产主控因素[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(6): 693-702. |
| [6] | 魏兆胜, 齐洪岩, 赵建飞, 何吉祥, 刘可成, 王俊超. 准噶尔盆地页岩油开发进展及效益建产关键技术[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(6): 703-711. |
| [7] | 刘向君, 甘仁忠, 熊健, 汤诗棋, 万有维, 周鑫, 梁利喜, 张淼. 吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组页岩油储层体积改造主控地质力学因素[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(6): 723-733. |
| [8] | 齐洪岩, 王振林, 郑国庆, 余佩蓉, 杨旺旺. 页岩油储集层水平井密切割压裂裂缝非均衡扩展机理[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(6): 734-741. |
| [9] | 李映艳, 丁艺, 罗刚, 丁怀宇, 唐慧莹, 贺戈. 基于地质工程一体化的井网-缝网协同优化——以准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷页岩油为例[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(6): 742-753. |
| [10] | 吝佳莹, 齐洪岩, 常婷, 张韵洁, 张浩, 陈刚, 梁成钢, 魏晓琛. 走滑断裂滑移诱发套管变形数值模拟及压裂方案优化——以吉木萨尔凹陷页岩油为例[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(6): 754-761. |
| [11] | 杜雪彪, 张金风, 肖佃师, 冉阳, 刘英杰, 秦嘉敏, 王良哲. 基于ReliefF和LSBoost集成树核磁有效孔隙度频谱预测及分辨率匹配研究[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(6): 762-772. |
| [12] | 姚菊琴, 陈刚, 唐廷明, 赵春雪, 李维, 余雪峰, 于江龙. 点复数谱提频方法在吉木萨尔页岩油甜点预测中的应用[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(6): 773-778. |
| [13] | 毛锐, 尉珈敏, 王盼, 李晴晴, 赵磊. 玛湖凹陷风城组页岩油储集层关键参数测井评价方法[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(6): 779-789. |
| [14] | 李杨虎, 王振林, 邵欢欢, 陈山河, 汤富康, 刘财广, 王伟, 张浩. 基于黏土矿物含量的页岩油水平井声波各向异性校正方法及应用[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(6): 790-799. |
| [15] | 吴勃翰, 李芳, 汤翟, 吴一雄, 骆玉虎, 肖大志, 张顺超. 基于双驱动模型的低渗气藏测井渗透率预测方法——以莺歌海盆地东方气田为例[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(5): 622-629. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||