

新疆石油地质 ›› 2023, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (3): 289-298.doi: 10.7657/XJPG20230304
周港1( ), 程甜2a, 李杰2b, 陈安清1, 李富祥1, 徐慧1, 徐胜林1(
), 程甜2a, 李杰2b, 陈安清1, 李富祥1, 徐慧1, 徐胜林1( )
)
收稿日期:2022-09-15
修回日期:2022-11-30
出版日期:2023-06-01
发布日期:2023-05-19
通讯作者:
徐胜林(1981-),男,安徽望江人,副教授,博士,沉积学和层序地层学,(Tel)18980689965(E-mail)作者简介:周港(1997-),男,四川都江堰人,硕士研究生,沉积学,(Tel)13438834730(E-mail)基金资助:
ZHOU Gang1( ), CHENG Tian2a, LI Jie2b, CHEN Anqing1, LI Fuxiang1, XU Hui1, XU Shenglin1(
), CHENG Tian2a, LI Jie2b, CHEN Anqing1, LI Fuxiang1, XU Hui1, XU Shenglin1( )
)
Received:2022-09-15
Revised:2022-11-30
Online:2023-06-01
Published:2023-05-19
摘要:
吐哈盆地台北凹陷胜北洼陷中侏罗统三间房组油气资源丰富,但该组储集砂体致密,非均质性较强,制约了油气的勘探开发。以胜北洼陷中侏统三间房组砂岩储集层为研究对象,在岩心观察的基础上,结合薄片观察、电镜扫描、高压压汞测试等,研究致密砂岩储集层成岩作用和孔隙演化规律。结果表明,胜北洼陷三间房组储集层以长石岩屑砂岩为主,其次为岩屑砂岩,孔隙类型以次生孔隙为主,平均孔隙度为6.44%,平均渗透率为0.18 mD,属于低孔低渗储集层;成岩演化过程为压实—自生黏土矿物胶结、绿泥石环边胶结—石英Ⅰ期次生加大、长石溶解—钠长石化—绿泥石环边胶结—碳酸盐岩胶结—长石溶解—高岭石伊利石化,目前处于中成岩阶段B期。胜北洼陷三间房组储集砂岩平均初始孔隙度为34.66%,早成岩阶段A期压实作用平均减孔14.05%,胶结作用平均减孔0.50%;早成岩阶段B期压实作用平均减孔3.21%,胶结作用平均减孔0.75%;中成岩阶段A期压实作用平均减孔7.02%,胶结作用平均减孔4.26%;中成岩阶段B期压实作用平均减孔1.08%,胶结作用平均减孔0.75%。中成岩阶段A期溶蚀作用是研究区增孔的关键,平均增孔量为3.38%。
中图分类号:
周港, 程甜, 李杰, 陈安清, 李富祥, 徐慧, 徐胜林. 胜北洼陷三间房组致密储集层成岩作用及孔隙演化[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2023, 44(3): 289-298.
ZHOU Gang, CHENG Tian, LI Jie, CHEN Anqing, LI Fuxiang, XU Hui, XU Shenglin. Diagenesis and Pore Evolution of Tight Reservoirs of Sanjianfang Formation in Shengbei Subsag[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2023, 44(3): 289-298.
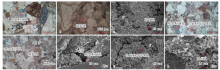
图3
研究区三间房组储集空间类型 a—残余粒间孔,岩屑粒内溶蚀孔,胜北6井,4 296.00 m,铸体薄片,单偏光;b—石英粒内溶蚀孔,胜北506H井,4 236.30 m,铸体薄片,单偏光;c—长石沿节理面溶蚀形成次生孔隙和微裂缝,胜北506H井,4 262.07 m,扫描电镜;d—长石粒内溶蚀孔,岩屑颗粒见残余粒间孔,台参2井,4 227.95 m,铸体薄片,单偏光;e—碎屑颗粒见残余粒间孔,发育微裂缝,胜深3井,4 452.80 m,铸体薄片,单偏光;f—残余粒间孔,粒间孔被叶片状绿泥石和石英充填,台参2井,4 427.95 m,扫描电镜;g—长石粒内溶蚀孔,胜北506H井,4 238.45 m,扫描电镜;h—高岭石晶间孔,胜深3井,4 452.80 m,扫描电镜;Chl—绿泥石;I—伊利石;K—高岭石;F—长石;Qtz—石英"


图7
研究区三间房组砂岩储集层胶结特征 a—方解石胶结在长石颗粒周围,胜北506H井,4 363.56 m,正交偏光;b—书页状高岭石和叶片状绿泥石充填粒间孔,胜北506H井,4 139.83 m,扫描电镜;c—球粒状黄铁矿与绿泥石伴生,胜北10井,3 898.10 m,扫描电镜;d—毛发状伊利石和石英充填粒间孔,胜北506H井,4 261.12 m,扫描电镜;e—石英次生加大边,伊利石附着在石英颗粒表面,胜深3井,4 454.90 m,扫描电镜;f—石英次生加大边,台参2井,4 161.50 m,正交偏光;Ca—方解石胶结;Chl—绿泥石;F—长石;I—伊利石;K—高岭石;Py—黄铁矿;Qtz—石英"

| [1] | 邹才能, 陶士振, 杨智, 等. 中国非常规油气勘探与研究新进展[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2012, 31(4):312-322. |
| ZOU Caineng, TAO Shizhen, YANG Zhi, et al. New advance in unconventional petroleum exploration and research in China[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy,Petrology and Geochemistry, 2012, 31(4):312-322. | |
| [2] | 李国欣, 雷征东, 董伟宏, 等. 中国石油非常规油气开发进展、挑战与展望[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2022, 27(1):1-11. |
| LI Guoxin, LEI Zhengdong, DONG Weihong, et al. Progress,challenges and prospects of unconventional oil and gas development of CNPC[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2022, 27(1):1-11. | |
| [3] | 邹才能, 杨智, 张国生, 等. 常规-非常规油气“有序聚集”理论认识及实践意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2014, 41(1):14-27. |
|
ZOU Caineng, YANG Zhi, ZHANG Guosheng, et al. Conventional and unconventional petroleum “orderly accumulation”:Concept and practical significance[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2014, 41(1):14-27.
doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(14)60002-1 |
|
| [4] | 邹才能, 赵群, 王红岩, 等. 非常规油气勘探开发理论技术助力我国油气增储上产[J]. 石油科技论坛, 2021, 40(3):72-79. |
| ZOU Caineng, ZHAO Qun, WANG Hongyan, et al. Theory and technology of unconventional oil and gas exploration and development helps China increase oil and gas reserves and production[J]. Petroleum Science and Technology Forum, 2021, 40(3):72-79. | |
| [5] | 张哨楠. 致密天然气砂岩储层:成因和讨论[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2008, 29(1):1-10. |
| ZHANG Shaonan. Tight sandstone gas reservoirs:Their origin and discussion[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2008, 29(1):1-10. | |
| [6] | YANG Peng, ZHANG Likuan, LIU Keyu, et al. Diagenetic history and reservoir evolution of tight sandstones in the second member of the Upper Triassic Xujiahe formation,western Sichuan basin,China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2021, 201:108 451. |
| [7] | 罗静兰, 刘新社, 付晓燕, 等. 岩石学组成及其成岩演化过程对致密砂岩储集质量与产能的影响:以鄂尔多斯盆地上古生界盒8天然气储层为例[J]. 地球科学—中国地质大学学报, 2014, 39(5):537-545. |
| LUO Jinglan, LIU Xinshe, FU Xiaoyan, et al. Impact of petrologic components and their diagenetic evolution on tight sandstone reservoir quality and gas yield:A case study from He 8 gas-bearing reservoir of Upper Paleozoic in northern Ordos basin[J]. Earth Science—Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2014, 39(5):537-545. | |
| [8] | ZHU Peng, MENG Xianghao, WANG Xin, et al. Geochemical characteristics of diagenetic fluid and densification model of tight gas sandstone reservoirs in Linxing area,eastern margin of Ordos basin,China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2022, 138:105 496. |
| [9] | 张满郎, 谷江锐, 孔凡志, 等. 川中合川气田须二段致密砂岩储层甜点研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2019, 48(4):806-818. |
| ZHANG Manlang, GU Jiangrui, KONG Fanzhi, et al. Research on tight sandstone reservoir sweet spots of the second member of Xujiahe formation of Upper Triassic in Hechuan gas field,central Sichuan basin[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2019, 48(4):806-818. | |
| [10] | 张考文, 王天鹏, 苟红光, 等. 吐哈盆地胜北地区中下侏罗统储层特征及有利勘探方向[J]. 石油天然气学报, 2008, 30(2):43-46. |
| ZHANG Kaowen, WANG Tianpeng, GOU Hongguang, et al. Mid-Lower Jurassic reservoir characteristics and its beneficial exploration directions in Shengbei region of Tuha basin[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 2008, 30(2):43-46. | |
| [11] | 肖冬生, 陈旋, 文川江, 等. 吐哈盆地台北凹陷胜北构造带油气成藏新认识[J]. 特种油气藏, 2016, 23(3):21-24. |
| XIAO Dongsheng, CHEN Xuan, WEN Chuanjiang, et al. New lnsights into hydrocarbon accumulation of Shengbei structural zone in Taibei depression of Tuha basin[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2016, 23(3):21-24. | |
| [12] | 李延钧, 陈义才, 张艳云, 等. 吐哈盆地胜北凹陷浅层油气源与成藏研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2007, 29(4):405-410. |
| LI Yanjun, CHEN Yicai, ZHANG Yanyun, et al. Research of the oil-gas source and formation of the pools in the shallow bed of the Shengbei sag,the Tuha basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2007, 29(4):405-410. | |
| [13] | 吴青鹏, 杨占龙, 李红哲, 等. 吐哈盆地台北凹陷西缘侏罗系层序划分及沉积体系演化[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2009, 20(3):348-355. |
| WU Qingpeng, YANG Zhanlong, LI Hongzhe, et al. Sequence division,distribution and evolution of sedimentary facies of Jurassic system,western Taibei sag,Turpan-Hami basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2009, 20(3):348-355. | |
| [14] | 徐论勋, 李建民, 李景义. 吐哈盆地台北凹陷侏罗系烃源岩特征[J]. 江汉石油学院学报, 2004, 26(2):13-14. |
| XU Lunxun, LI Jianmin, LI Jingyi, et al. Characteristics of Jurassic source rock in Taibei sag of Tuha basin[J]. Journal of Jianghan Petroleum Institute, 2004, 26(2):13-14. | |
| [15] |
王彤, 朱筱敏, 张自力, 等. 莱州湾凹陷北洼沙河街组三段砂岩储层孔隙定量演化模式[J]. 石油学报, 2020, 41(6):671-690.
doi: 10.7623/syxb202006003 |
| WANG Tong, ZHU Xiaomin, ZHANG Zili, et al. Quantitative pore evolution model of sandstone reservoirs for Member 3 of Shahejie formation in the northern subsag of Laizhouwan sag[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2020, 41(6):671-690. | |
| [16] | 苟红光, 张品, 佘家朝, 等. 吐哈盆地石油地质条件、资源潜力及勘探方向[J]. 海相油气地质, 2019, 24(2):85-96. |
| GOU Hongguang, ZHANG Pin, SHE Jiachao, et al. Petroleum geological conditions,resource potential and exploration direction in Turpan-Hami basin[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2019, 24(2):85-96. | |
| [17] | 李红哲, 杨占龙, 吴青鹏, 等. 沉积相分析在岩性油气藏勘探中的应用:以吐哈盆地胜北洼陷中侏罗统—白垩系为例[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2006, 17(5):698-702. |
| LI Hongzhe, YANG Zhanlong, WU Qingpeng, et al. The application of sedimentary facies analyses in lithologic pool:Taking Turpan-Hami basin Jurassic serious and Cretaceous serious as examples[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2006, 17(5):698-702. | |
| [18] | 柳波, 黄志龙, 王玫玫, 等. 吐哈盆地胜北构造带油气成藏过程[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2011, 41(4):1006-1 012. |
| LIU Bo, HUANG Zhilong, WANG Meimei, et al. Restoration of hydrocarbon accumulation history in Shengbei structure belt,Tuha basin[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 2011, 41(4):1006-1 012. | |
| [19] | 刘一杉, 东晓虎, 闫林, 等. 吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组孔隙结构定量表征[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2019, 40(3):284-289. |
| LIU Yishan, DONG Xiaohu, YAN Lin, et al. Quantitative characterization of pore structure of Lucaogou formation in Jimsar sag[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2019, 40(3):284-289. | |
| [20] | 丁强, 成健, 杨博, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地胡154区块长4+5段孔隙结构定量表征及分类[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2021, 42(4):410-417. |
| DING Qiang, CHENG Jian, YANG Bo, et al. Quantitative characterization and classification of pore structures in Chang 4+5 member in Block Hu-154,Ordos basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2021, 42(4):410-417. | |
| [21] | 任新成. 准噶尔盆地永进油田西山窑组油藏成岩演化及成藏史[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2021, 42(1):21-28. |
| REN Xincheng. Diagenetic evolution and hydrocarbon accumulation history in reservoirs of Xishanyao formation in Yongjin oilfield,Junggar basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2021, 42(1):21-28. | |
| [22] | 吴小斌, 侯加根, 孙卫. 特低渗砂岩储层微观结构及孔隙演化定量分析[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 42(11):3438-3 446. |
| WU Xiaobin, HOU Jiagen, SUN Wei, et al. Microstructure characteristics and quantitative analysis on porosity evolution of ultra-low sandstone reservoir[J]. Journal of Central South University(Science and Technology), 2011, 42(11):3438-3 446. | |
| [23] | 钟大康. 致密油储层微观特征及其形成机理:以鄂尔多斯盆地长6—长7段为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2017, 38(1):49-61. |
| ZHONG Dakang. Micro-petrology,pore throat characteristics and genetic mechanism of tight oil reservoirs:A case from the 6th and 7th members of Triassic Yanchang formation in the Ordos basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2017, 38(1):49-61. | |
| [24] | 张青青, 刘可禹, 刘太勋, 等. 碎屑岩储层碳酸盐胶结物成因研究进展[J]. 海相油气地质, 2021, 26(3):231-244. |
| ZHANG Qingqing, LIU Keyu, LIU Taixun, et al. Research status of the genesis of carbonate cementation in clastic reservoirs[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2021, 26(3):231-244. | |
| [25] | 王代富, 罗静兰, 陈淑慧, 等. 珠江口盆地白云凹陷深层砂岩储层中碳酸盐胶结作用及成因探讨[J]. 地质学报, 2017, 91(9):2079-2 090. |
| WANG Daifu, LUO Jinglan, CHEN Shuhui, et al. Carbonate cementation and origin analysis of deep sandstone reservoirs in the Baiyun sag,Pearl River Mouth basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2017, 91(9):2079-2 090. | |
| [26] | 张杰, 夏维民, 徐丽, 等. 柴北缘九龙山地区侏罗系致密砂岩储层成因分析[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2014, 25(增刊1):71-78. |
| ZHANG Jie, XIA Weimin, XU Li, et al. Genesis of Jurassic tight sandstone reservoirs of Jiulongshan region in the northern Qaidam basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2014,25 (Supp.1):71-78. | |
| [27] | 黄思静, 黄可可, 冯文立, 等. 成岩过程中长石、高岭石、伊利石之间的物质交换与次生孔隙的形成:来自鄂尔多斯盆地上古生界和川西凹陷三叠系须家河组的研究[J]. 地球化学, 2009, 38(5):498-506. |
| HUANG Sijing, HUANG Keke, FENG Wenli, et al. Mass exchanges among feldspar,kaolinite and illite and their influences on secondary porosity formation in clastic diagenesis:A case study on the Upper Paleozoic,Ordos basin and Xujiahe formation,Western Sichuan depression[J]. Geochimica, 2009, 38(5):498-506. | |
| [28] | 黄可可, 黄思静, 佟宏鹏, 等. 长石溶解过程的热力学计算及其在碎屑岩储层研究中的意义[J]. 地质通报, 2009, 28(4):474-482. |
| HUANG Keke, HUANG Sijing, TONG Hongpeng, et al. Thermodynamic calculation of feldspar dissolution and its significance on research of clastic reservoir[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2009, 28(4):474-482. | |
| [29] | 秦晓艳, 林进, 武富礼. 鄂尔多斯盆地东南部本溪组致密石英砂岩成岩作用与孔隙演化[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 46(4):579-584. |
| QIN Xiaoyan, LIN Jin, WU Fuli, et al. Diagenesis and porosity evolution of tight quartz sandstones in Benxi formation,southeast Ordos basin[J]. Journal of Northwest University(Natural Science Edition), 2016, 46(4):579-584. | |
| [30] | 郑锐, 刘林玉, 李南星, 等. 陕北子长长4+5砂岩储层成岩作用及孔隙演化[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 41(5):848-852. |
| ZHENG Rui, LIU Linyu, LI Nanxing, et al. Reservoir diagenesis and pore evolution of Chang 4+5 of Yanchang formation in Shaanbei Zichang area[J]. Journal of Northwest University(Natural Science Edition), 2011, 41(5):848-852. | |
| [31] | 胡江柰, 张哨楠, 李德敏. 鄂尔多斯盆地北部下石盒子组—山西组成岩作用与储层的关系[J]. 成都理工学院学报, 2001, 28(2):169-173. |
| HU Jiangnai, ZHANG Shaonan, LI Demin. The influence of diagenesis on reservoir quality in Shihezi-Shanxi formation in northern Ordos basin[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology, 2001, 28(2):169-173. | |
| [32] | 张悦, 张翔, 田景春, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地杭锦旗地区山西组储层成岩作用及孔隙演化[J]. 矿物岩石, 2021, 41(2):118-128. |
| ZHANG Yue, ZHANG Xiang, TIAN Jingchun, et al. Reservoir diagenesis and pore evolution of Shanxi formation in Hangjinqi area,Ordos basin[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 2021, 41(2):118-128. | |
| [33] | 朱如凯, 赵霞, 刘柳红, 等. 四川盆地须家河组沉积体系与有利储集层分布[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2009, 36(1):46-55. |
|
ZHU Rukai, ZHAO Xia, LIU Liuhong, et al. Depositional system and favorable reservoir distribution of Xujiahe formation in Sichuan basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2009, 36(1):46-55.
doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(09)60110-5 |
|
| [34] | 刘锐娥, 孙粉锦, 拜文华, 等. 苏里格庙盒8气层次生孔隙成因及孔隙演化模式探讨[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2002, 29(4):47-49. |
| LIU Ruie, SUN Fenjin, BAI Wenhua, et al. An approach to the generating mechanism of secondary pores and pore evolution model of He 8 gas layer in Suligemiao gas field[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2002, 29(4):47-49. | |
| [35] | 冯旭, 刘洛夫, 李朝玮, 等. 碎屑岩孔隙演化定量计算方法的改进和应用[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2017, 38(6):1198-1 207. |
| FENG Xu, LIU Luofu, LI Chaowei, et al. Improvement and application of quantitative calculation of porosity evolution of clastic rock[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2017, 38(6):1198-1 207. | |
| [36] | 陈旋, 王居峰, 肖冬生, 等. 台北凹陷下侏罗统致密砂岩气成藏条件与勘探方向[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2022, 43(5):505-512. |
| CHEN Xuan, WANG Jufeng, XIAO Dongsheng, et al. Accumulation conditions and exploration direction of Lower Jurassic tight sandstone gas reservoirs in Taibei sag[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2022, 43(5):505-512. | |
| [37] |
刘俊田, 谢佃和, 彭亚中, 等. 胜北构造带致密气成藏机理及富集规律[J]. 特种油气藏, 2022, 29(5):18-27.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2022.05.003 |
| LIU Juntian, XIE Dianhe, PENG Yazhong, et al. Accumulation mechanism and enrichment law of tight gas in Shengbei structural zone[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2022, 29(5):18-27. |
| [1] | 支东明, 李建忠, 陈旋, 杨帆, 刘俊田, 林霖. 吐哈探区深层油气勘探进展及潜力评价[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2023, 44(3): 253-264. |
| [2] | 刘锋, 赵红静, 金颖, 甘应星, 曾雁, 温旺彪, 徐桂芳. 吐哈盆地胜北洼陷中—下侏罗统致密油烃源岩评价及油源对比[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2023, 44(3): 277-288. |
| [3] | 司宝, 闫茜, 刘强, 张彦斌, 付春苗, 齐桓. 油藏型储气库与天然气驱油协同建设实验——以葡北油田三间房组油藏为例[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2023, 44(3): 321-326. |
| [4] | 肖志朋, 齐桓, 张艺桢, 李宜强, 姚帅旗, 刘通. 葡北油田三间房组油藏天然气重力驱特征及影响因素[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2023, 44(3): 334-340. |
| [5] | 万海乔, 王盛, 刘学良. 低孔低渗稠油油藏注水增能效果影响因素[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2023, 44(3): 347-351. |
| [6] | 朱永贤, 姚帅旗, 张彦斌, 韩继凡, 赵瑞明. 稀油油藏密闭取心流体饱和度校正方法[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2023, 44(3): 359-364. |
| [7] | 石楠, 刘源, 冷玥, 文一华, 潘海峰, 孙博, 王兵. 基于低频模型优化的相控地质统计学反演方法及应用[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2023, 44(3): 375-382. |
| [8] | 崔耀科, 杜贵超, 王凤琴, 王聪娥, 陈奕阳, 王颖, 黄杏雨. 甘泉油田长8油藏水下分流河道砂体钙质夹层特征及成因[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2023, 44(2): 161-168. |
| [9] | 况昊, 周润驰, 王钧民, 刘豪, 谭先锋, 蔡鑫勇, 肖振兴. 玛湖凹陷与沙湾凹陷上乌尔禾组储集层差异及成因[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2023, 44(1): 18-24. |
| [10] | 陈旋, 王居峰, 肖冬生, 刘俊田, 苟红光, 张华, 林霖, 李宏伟. 台北凹陷下侏罗统致密砂岩气成藏条件与勘探方向[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2022, 43(5): 505-512. |
| [11] | 吕焕泽, 邹妞妞, 蔡宁宁, 黄永志, 宁诗坦, 朱彪. 玛湖凹陷北斜坡百口泉组碳酸盐胶结物形成机理及其地质意义[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2022, 43(5): 554-562. |
| [12] | 白慧, 杨特波, 侯科锋, 马志欣, 冯敏. 苏里格气田东区马五5气藏主控因素及富集区优选[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2022, 43(3): 271-277. |
| [13] | 王晔磊, 邱隆伟, 杨勇强, 吴宛秋, 杨保良, 乔雨鹏. 济阳坳陷义和庄—大王庄地区二叠系储集层成岩作用及孔隙演化[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2021, 42(6): 676-682. |
| [14] | 陈超峰, 王佳, 俞天喜, 李轶, 邹雨时, 马新仿, 刘立. 玛湖凹陷乌尔禾组砾岩储集层裂缝支撑剂运移规律[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2021, 42(5): 559-564. |
| [15] | 梁世君. 吐哈探区油气勘探成果及潜力[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2020, 41(6): 631-641. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||