

新疆石油地质 ›› 2023, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (4): 411-420.doi: 10.7657/XJPG20230404
周新锐1,2,3( ), 王喜鑫1,2,3(
), 王喜鑫1,2,3( ), 李少华1, 张昌民1, 胡凯4, 严春景1, 倪雪儿1
), 李少华1, 张昌民1, 胡凯4, 严春景1, 倪雪儿1
收稿日期:2022-11-12
修回日期:2022-11-25
出版日期:2023-08-01
发布日期:2023-08-01
通讯作者:
王喜鑫(1986-),男,黑龙江佳木斯人,副教授,博士,地质资源与地质工程,(Tel)18632713360(E-mail)作者简介:周新锐(1998-),男,湖北宜昌人,硕士研究生,地质资源与地质工程,(Tel)13872528939(E-mail)基金资助:
ZHOU Xinrui1,2,3( ), WANG Xixin1,2,3(
), WANG Xixin1,2,3( ), LI Shaohua1, ZHANG Changmin1, HU Kai4, YAN Chunjing1, NI Xueer1
), LI Shaohua1, ZHANG Changmin1, HU Kai4, YAN Chunjing1, NI Xueer1
Received:2022-11-12
Revised:2022-11-25
Online:2023-08-01
Published:2023-08-01
摘要:
陆相混合沉积岩岩性复杂,储集层物性差异大,其孔隙结构及其主控因素,是揭示陆相混积型页岩储集层物性的关键。通过岩石薄片、铸体薄片、扫描电镜、高压压汞、恒速压汞、X射线衍射等,识别了吉木萨尔凹陷二叠系芦草沟组页岩储集层岩性,分析了不同岩性的孔隙结构特征及其与成岩作用的关系。芦草沟组页岩储集层主要发育泥晶白云岩、粉砂质砂屑白云岩、石灰质粉砂岩、石灰质泥岩、粉砂质凝灰岩和石灰质凝灰岩6种岩性。粉砂质砂屑白云岩、石灰质粉砂岩和粉砂质凝灰岩压实程度中等,溶蚀孔发育,孔喉半径大,孔隙连通性及孔喉分选好,储集层物性好;石灰质凝灰岩压实作用中等,主要以方解石、自生石英及方沸石胶结为主,储集层物性中等;泥晶白云岩和石灰质泥岩成分单一,压实作用较强,溶蚀作用弱,孔喉半径小,物性差。
中图分类号:
周新锐, 王喜鑫, 李少华, 张昌民, 胡凯, 严春景, 倪雪儿. 陆相混积型页岩储集层孔隙结构特征及其控制因素[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2023, 44(4): 411-420.
ZHOU Xinrui, WANG Xixin, LI Shaohua, ZHANG Changmin, HU Kai, YAN Chunjing, NI Xueer. Pore Structure Characteristics and Controlling Factors of Continental Mixed Shale Reservoirs[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2023, 44(4): 411-420.
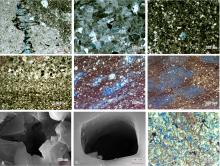
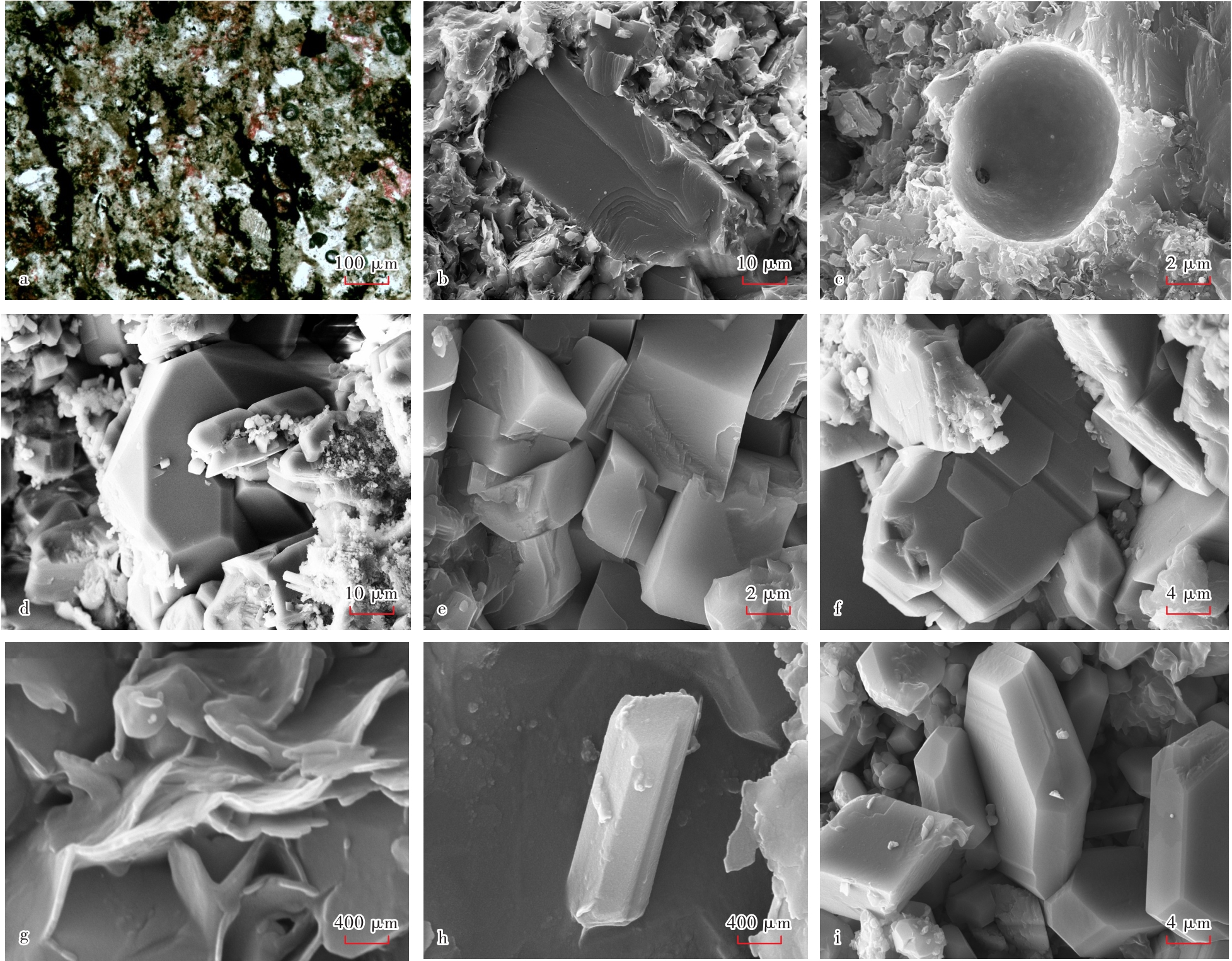
图4
吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组页岩储集层压实及溶蚀作用特征 a—强压实作用,泥晶白云岩,缝合线,J30井,4 041.01 m,单偏光;b—中等压实作用,粉砂质砂屑白云岩,线接触,J31井,4 048.67 m,单偏光;c—强压实作用,石灰质泥岩,J31井,2 712.15 m,铸体薄片;d—中等—强压实作用,石灰质粉砂岩,颗粒定向排列,J31井,2 715.00 m,单偏光;e—条带状溶蚀孔,粉砂质凝灰岩,J174井,3 280.74 m,铸体薄片;f—团块状溶蚀孔,石灰质凝灰岩,J174井,3 230.93 m,铸体薄片;g—晶间孔,粉砂质砂屑白云岩,J174井,3 100.08 m,扫描电镜;h—粒内溶蚀孔,石灰质粉砂岩,J174井,3 329.68 m,扫描电镜;i—溶蚀孔,石灰质粉砂岩,J174井,3 267.19 m,铸体薄片"

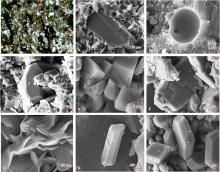
图5
吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组页岩储集层胶结作用特征 a—方解石胶结,粉砂质砂屑白云岩,J31井,2 859.79 m,单偏光;b—方解石胶结,粉砂质砂屑白云岩,J174井,3 307.28 m,扫描电镜;c—黄铁矿胶结,粉砂质砂屑白云岩,J174井,3 264.65 m,扫描电镜;d—硅质胶结,石灰质粉砂岩,J174井,3 146.13 m,扫描电镜;e白云石胶结,石灰质粉砂岩,J174井,3 114.86 m,扫描电镜;f—方解石胶结,石灰质粉砂岩,J174井,3 155.05 m,扫描电镜;g—绿泥石充填,石灰质粉砂岩,J174井,3 142.13 m,扫描电镜;h—沸石充填,粉砂质凝灰岩,J174井,3 268.81 m,扫描电镜;i—伴生的白云石和沸石,石灰质凝灰岩,J174井,3 142.13 m,扫描电镜"

| [1] | 马远, 张瑞. 美欧俄石油供应贸易网络对中国石油进口效率的影响研究[J]. 大连理工大学学报(社会科学版), 2022, 43(4):8-19. |
| MA Yuan, ZHANG Rui. The impact of oil supply and trade network of the US-OPEC-Russia on China’s oil import efficiency[J]. Journal of Dalian University of Technology(Social Science), 2022, 43(4):8-19. | |
| [2] | 张祺. 中国石油进口依存度问题研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2013. |
| ZHANG Qi. A study on oil import dependency of China[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University, 2013. | |
| [3] | 邹才能, 董大忠, 王社教, 等. 中国页岩气形成机理、地质特征及资源潜力[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2010, 37(6):641-653. |
|
ZOU Caineng, DONG Dazhong, WANG Shejiao, et al. Geological characteristics,formation mechanism and resource potential of shale gas in China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2010, 37(6):641-653.
doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(11)60001-3 |
|
| [4] | 邹才能, 杨智, 崔景伟, 等. 页岩油形成机制、地质特征及发展对策[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2013, 40(1):14-26. |
| ZOU Caineng, YANG Zhi, CUI Jingwei, et al. Formation mechanism,geological characteristics and development strategy of nonmarine shale oil in China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2013, 40(1):14-26. | |
| [5] | 邹才能, 杨智, 朱如凯, 等. 中国非常规油气勘探开发与理论技术进展[J]. 地质学报, 2015, 89(6):979-1 007. |
| ZOU Caineng, YANG Zhi, ZHU Rukai, et al. Progress in China’s unconventional oil & gas exploration and development and theoretical technologies[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2015, 89(6):979-1 007. | |
| [6] | 王剑, 周路, 靳军, 等. 准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组页岩油储层孔隙结构、烃类赋存及其与可动性关系[J]. 石油实验地质, 2021, 43(6):941-948. |
| WANG Jian, ZHOU Lu, JIN Jun, et al. Pore structure, hydrocarbon occurrence and their relationship with shale oil production in Lucaogou formation of Jimsar sag, Junggar basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2021, 43(6):941-948. | |
| [7] | 卢双舫, 黄文彪, 陈方文, 等. 页岩油气资源分级评价标准探讨[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2012, 39(2):249-256. |
| LU Shuangfang, HUANG Wenbiao, CHEN Fangwen, et al. Classification and evaluation criteria of shale oil and gas resources:Discussion and application[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2012, 39(2):249-256. | |
| [8] | 匡立春, 唐勇, 雷德文, 等. 准噶尔盆地二叠系咸化湖相云质岩致密油形成条件与勘探潜力[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2012, 39(6):657-667. |
| KUANG Lichun, TANG Yong, LEI Dewen, et al. Formation conditions and exploration potential of tight oil in the Permian saline lacustrine dolomitic rock,Junggar basin,NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2012, 39(6):657-667. | |
| [9] | 匡立春, 王霞田, 郭旭光, 等. 吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组致密油地质特征与勘探实践[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2015, 36(6):629-634. |
| KUANG Lichun, WANG Xiatian, GUO Xuguang, et al. Geological characteristics and exploration practice of tight oil of Lucaogou formation in Jimsar sag[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2015, 36(6):629-634. | |
| [10] | 邵雨, 杨勇强, 万敏, 等. 吉木萨尔凹陷二叠系芦草沟组沉积特征及沉积相演化[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2015, 36(6):635-641. |
| SHAO Yu, YANG Yongqiang, WAN Min, et al. Sedimentary characteristic and facies evolution of Permian Lucaogou formation in Jimsar sag,Junggar basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2015, 36(6):635-641. | |
| [11] | 斯春松, 陈能贵, 余朝丰, 等. 吉木萨尔凹陷二叠系芦草沟组致密油储层沉积特征[J]. 石油实验地质, 2013, 35(5):528-533. |
| SI Chunsong, CHEN Nenggui, YU Chaofeng, et al. Sedimentary characteristics of tight oil reservoir in Permian Lucaogou formation,Jimsar sag[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2013, 35(5):528-533. | |
| [12] |
杨智, 付金华, 郭秋麟, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组陆相致密油发现、特征及潜力[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2017, 22(6):9-15.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2017.06.002 |
| YANG Zhi, FU Jinhua, GUO Qiulin, et al. Discovery,characteristics and resource potential of continental tight oil in Triassic Yanchang formation,Ordos basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2017, 22(6):9-15. | |
| [13] |
付金华, 牛小兵, 淡卫东, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地中生界延长组长7段页岩油地质特征及勘探开发进展[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2019, 24(5):601-614.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2019.05.007 |
|
FU Jinhua, NIU Xiaobing, DAN Weidong, et al. The geological characteristics and the progress on exploration and development of shale oil in Chang 7 member of Mesozoic Yanchang formation,Ordos basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2019, 24(5):601-614.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2019.05.007 |
|
| [14] | 罗安湘, 喻建, 刘显阳, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地中生界石油勘探实践及主要认识[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2022, 43(3):253-260. |
| LUO Anxiang, YU Jian, LIU Xianyang, et al. Practice and cognitions of petroleum exploration in Mesozoic,Ordos basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2022, 43 (3):253-260. | |
| [15] |
吴宝成, 李建民, 邬元月, 等. 准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组页岩油上甜点地质工程一体化开发实践[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2019, 24(5):679-690.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2019.05.014 |
|
WU Baocheng, LI Jianmin, WU Yuanyue, et al. Development practices of geology-engineering integration on upper sweet spots of Lucaogou formation shale oil in Jimsar sag,Junggar basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2019, 24(5):679-690.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2019.05.014 |
|
| [16] | WANG Song, WANG Guiwen, HUANG Liliang, et al. Logging evaluation of lamina structure and reservoir quality in shale oil reservoir of Fengcheng formation in Mahu sag,China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2021, 133:1-16. |
| [17] | SHARMA V, SIRCAR A. Multi-technique characterization of shale reservoir quality parameters[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2019, 75:1-17. |
| [18] | 操应长, 朱宁, 张少敏, 等. 准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷二叠系芦草沟组致密油储层成岩作用与储集空间特征[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2019, 41(3):253-266. |
| CAO Yingchang, ZHU Ning, ZHANG Shaomin, et al. Diagenesis and reserving space characteristics of tight oil reservoirs of Permian Lucaogou formation in Jimusaer sag of Junggar basin,China[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2019, 41(3):253-266. | |
| [19] | 王越, 熊伟, 于洪州, 等. 准噶尔盆地东部芦草沟组层序地层格架与沉积充填模式[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2022, 29(4):12-24. |
| WANG Yue, XIONG Wei, YU Hongzhou, et al. Sequence stratigraphic framework and sedimentary filling model of Lucaogou formation in eastern Junggar basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2022, 29(4):12-24. | |
| [20] | 罗锦昌, 田继军, 马静辉, 等. 吉木萨尔凹陷吉页1井区二叠系芦草沟组沉积环境及有机质富集机理[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2022, 34(5):73-85. |
| LUO Jinchang, TIAN Jijun, MA Jinghui, et al. Sedimentary environment and organic matter enrichment mechanism of Permian Lucaogou formation in Jiye-1 well area,Jimsar sag[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2022, 34(5):73-85. | |
| [21] | 刘金, 王剑, 张晓刚, 等. 准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组甜点页岩油微观赋存特征及成因机制[J]. 地质论评, 2022, 68(3):907-920. |
| LIU Jin, WANG Jian, ZHANG Xiaogang, et al. Microscopic occurrence characteristics and genetic mechanism of shale oil in sweet spot reservoir of the Lucaogou formation in Jimusaer sag[J]. Geological Review, 2022, 68(3):907-920. | |
| [22] | 支东明, 唐勇, 杨智峰, 等. 准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷陆相页岩油地质特征与聚集机理[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2019, 40(3):524-534. |
| ZHI Dongming, TANG Yong, YANG Zhifeng, et al. Geological characteristics and accumulation mechanism of continental shale oil in Jimusaer sag,Junggar basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2019, 40(3):524-534. | |
| [23] |
彭寿昌, 查小军, 雷祥辉, 等. 吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组上“甜点”段页岩油储层演化特征及差异性评价[J]. 特种油气藏, 2021, 28(4):30-38.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2021.04.005 |
| PENG Shouchang, ZHA Xiaojun, LEI Xianghui, et al. Evolution characteristics and difference evaluation of shale oil reservoirs in the upper sweet spot interval of Lucaogou formation in Jimusaer sag[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2021, 28(4):30-38. | |
| [24] | 王剑, 袁波, 刘金, 等. 准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷二叠系芦草沟组混积岩成因及其孔隙发育特征[J]. 石油实验地质, 2022, 44(3):413-424. |
| WANG Jian, YUAN Bo, LIU Jin, et al. Genesis and pore development characteristics of Permian Lucaogou migmatites,Jimsar sag, Junggar basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2022, 44(3):413-424. | |
| [25] |
肖佃师, 高阳, 彭寿昌, 等. 准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷混积岩孔喉系统分类及控制因素[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2021, 48(4):719-731.
doi: 10.11698/PED.2021.04.05 |
| XIAO Dianshi, GAO Yang, PENG Shouchang, et al. Classification and control factors of pore-throat systems in hybrid sedimentary rocks of Jimusar sag,Junggar basin,NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2021, 48(4):719-731. | |
| [26] | WANG Xixin, HOU Jiagen, LI Shaohua, et al. Insight into the nanoscale pore structure of organic-rich shales in the Bakken formation,USA[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science & Engineering, 2020, 191:1-13. |
| [27] | WANG Xixin, HOU Jiagen, SONG Suihong, et al. Combining pressure-controlled porosimetry and rate-controlled porosimetry to investigate the fractal characteristics of full-range pores in tight oil reservoirs[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science & Engineering, 2018, 171:353-361. |
| [28] | 马克, 刘钰铭, 侯加根, 等. 陆相咸化湖混合沉积致密储集层致密化机理:以吉木萨尔凹陷二叠系芦草沟组为例[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2019, 40(3):253-261. |
| MA Ke, LIU Yuming, HOU Jiagen, et al. Densification mechanism of tight reservoirs from mixed sedimentation in saline lacustrine environment:A case study of Permian Lucaogou formation,Jimsar sag[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2019, 40(3):253-261. | |
| [29] | 蒋宜勤, 柳益群, 杨召, 等. 准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷凝灰岩型致密油特征与成因[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2015, 42(6):741-749. |
| JIANG Yiqin, LIU Yiqun, YANG Zhao, et al. Characteristics and origin of tuff-type tight oil in Jimusar depression,Junggar basin,NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2015, 42(6):741-749. | |
| [30] |
王剑, 周路, 刘金, 等. 准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷二叠系芦草沟组酸碱交替成岩作用特征及对页岩储集层的影响[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2020, 47(5):898-912.
doi: 10.11698/PED.2020.05.05 |
| WANG Jian, ZHOU Lu, LIU Jin, et al. Acid-base alternation diagenesis and its influence on shale reservoirs in the Permian Lucaogou formation,Jimusar sag,Junggar basin,NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2020, 47(5):898-912. | |
| [31] | 王子强, 李春涛, 张代燕, 等. 吉木萨尔凹陷页岩油储集层渗流机理[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2019, 40(6):695-700. |
| WANG Ziqiang, LI Chuntao, ZHANG Daiyan, et al. Flow mechanism of shale oil reservoir in Jimusar sag[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2019, 40 (6):695-700. | |
| [32] | 曲长胜, 邱隆伟, 杨勇强, 等. 吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组碳酸盐岩碳氧同位素特征及其古湖泊学意义[J]. 地质学报, 2017, 91(3):605-616. |
| QU Changsheng, QIU Longwei, YANG Yongqiang, et al. Carbon and oxygen isotope compositions of carbonatic rock from Permian Lucaogou formation in the Jimsar sag,NW China and their paleolimnological significance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2017, 91(3):605-616. | |
| [33] |
CAO Zhe, LIU Guangdi, ZHAN Hongbin, et al. Geological roles of the siltstones in tight oil play of Permian Lucaogou formation in Jimusar sag,Junggar basin[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2017, 83:333-344.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2017.02.020 |
| [34] | 葸克来, 操应长, 朱如凯, 等. 吉木萨尔凹陷二叠系芦草沟组致密油储层岩石类型及特征[J]. 石油学报, 2015, 36(12):1 495-1 507. |
| XI Kelai, CAO Yingchang, ZHU Rukai, et al. Rock types and characteristics of tight oil reservoir in Permian Lucaogou formation,Jimusaer sag[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2015, 36(12):1 495-1 507. | |
| [35] | 宋永, 周路, 郭旭光, 等. 准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组湖相云质致密油储层特征与分布规律[J]. 岩石学报, 2017, 33(4):1 159-1 170. |
| SONG Yong, ZHOU Lu, GUO Xuguang, et al. Characteristics and occurrence of lacustrine dolomitic tight-oil reservoir in the Middle Permian Lucaogou formation,Jimusaer sag,southeastern Junggar basin[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2017, 33(4):1 159-1 170. | |
| [36] | 王小军, 杨智峰, 郭旭光, 等. 准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷页岩油勘探实践与展望[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2019, 40(4):402-413. |
| WANG Xiaojun, YANG Zhifeng, GUO Xuguang, et al. Practices and prospects of shale oil exploration in Jimsar sag of Junggar basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2019, 40(4):402-413. | |
| [37] | 马明伟, 祝健, 李嘉成, 等. 吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组页岩油储集层渗吸规律[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2021, 42(6):702-708. |
| MA Mingwei, ZHU Jian, LI Jiacheng, et al. Imbibition law of shale oil reservoirs in the Lucaogou formation in Jimsar sag[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2021, 42(6):702-708. | |
| [38] |
HACKLEY P C, FISHMAN N, WU Tao, et al. Organic petrology and geochemistry of mudrocks from the lacustrine Lucaogou formation,Santanghu basin,northwest China:Application to lake basin evolution[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2016, 168:20-34.
doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2016.05.011 |
| [39] |
LUO Qingyong, GONG Lei, QU Yansheng, et al. The tight oil potential of the Lucaogou formation from the southern Junggar basin,China[J]. Fuel, 2018, 234:858-871.
doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2018.07.002 |
| [40] |
HU Tao, PANG Xiongqi, WANG Qifeng, et al. Geochemical and geological characteristics of Permian Lucaogou formation shale of the Well Ji174,Jimusar sag,Junggar basin,China:Implications for shale oil exploration[J]. Geological Journal, 2018, 53(5):2 371-2 385.
doi: 10.1002/gj.v53.5 |
| [41] |
CHEN Qiang, KANG Yili, YOU Lijun, et al. Change in composition and pore structure of Longmaxi black shale during oxidative dissolution[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2017, 172:95-111.
doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2017.01.011 |
| [42] |
GHANIZADEH A, CLARKSON C R, AQUINO S, et al. Petrophysical and geomechemical characteristics of Canadian tight oil and liquid-rich gas reservoirs:Ⅰ Pore network and permeability characterization[J]. Fuel, 2015, 153:664-681.
doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2015.03.020 |
| [43] | MA Ke, HOU Jiagen, YAN Lin, et al. Pore-throat structures and their control of terrestrial lacustrine tight reservoir quality:The Permian Lucaogou formation,Jimsar sag,northwestern China[J]. Interpretation, 2018, 6(4):889-906. |
| [44] | WANG Xiaojun, SONG Yong, GUO Xuguang, et al. Pore-throat structure characteristics of tight reservoirs of the Middle Permian Lucaogou formation in the Jimsar sag,Junggar basin,northwest China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2022, 208:1-15. |
| [45] |
ZHANG Mingming, LI Zhao. The lithofacies and reservoir characteristics of the fine-grained sedimentary rocks of the Permian Lucaogou formation at the northern foot of Bogda mountains,Junggar basin (NW China)[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2018, 170:21-39.
doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2018.06.007 |
| [46] |
ZHAO Peiqiang, WANG Zhenlin, SUN Zhongchun, et al. Investigation on the pore structure and multifractal characteristics of tight oil reservoirs using NMR measurements:Permian Lucaogou formation in Jimusaer sag,Junggar basin[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2017, 86:1 067-1 081.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2017.07.011 |
| [47] | SU Yang, ZHA Ming, LIU Keyu, et al. Characterization of pore structures and implications for flow transport property of tight reservoirs:A case study of the Lucaogou formation,Jimsar sag,Junggar basin,northwestern China[J]. Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute, 2021, 14:1-20. |
| [48] |
SU Yang, ZHA Ming, DING Xiujian, et al. Pore type and pore size distribution of tight reservoirs in the Permian Lucaogou formation of the Jimsar sag,Junggar basin,NW China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2018, 89(3):761-774.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2017.11.014 |
| [49] | 邱振, 施振生, 董大忠, 等. 致密油源储特征与聚集机理:以准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷二叠系芦草沟组为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2016, 43(6):928-939. |
| QIU Zhen, SHI Zhensheng, DONG Dazhong, et al. Geological characteristics of source rock and reservoir of tight oil and its accumulation mechanism:A case study of Permian Lucaogou formation in Jimusar sag,Junggar basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2016, 43(6):928-939. |
| [1] | 孔祥晔, 曾溅辉, 罗群, 谭杰, 张芮, 王鑫, 王乾右. 川中地区大安寨段陆相页岩岩相对孔隙结构的控制作用[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2023, 44(4): 392-403. |
| [2] | 甘仁忠, 熊健, 彭妙, 刘向君, 梁利喜, 丁乙. 陆相页岩储集层岩石力学特性及能量演化特征[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2023, 44(4): 472-478. |
| [3] | 秦恩鹏, 张君莹, 张生兵, 刘俊田, 张小芹, 陈永慧. 三塘湖盆地芦草沟组细粒岩储集层微观特征[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2023, 44(3): 299-306. |
| [4] | 周云秋, 贺锡雷, 林凯, 秦思萍, 张陈强, 刘宗杰. 基于动态有效应力系数的地层压力估算方法[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2023, 44(2): 245-251. |
| [5] | 张德梅, 段朝伟, 李高仁, 李永胜, 陆敬武, 林伟川. 华池—南梁油田长8油藏高阻水层解释方法[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2023, 44(1): 105-111. |
| [6] | 白振强, 王清华, 宋文波. 基于核磁共振的天然气驱储集层孔喉动用下限[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2023, 44(1): 58-63. |
| [7] | 郭海平, 吴承美, 张金风, 徐田录, 肖佃师, 郭雪燚. 吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组混积型页岩油可动性实验[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2023, 44(1): 76-83. |
| [8] | 于淑艳, 汪洋, 冯宏业, 朱洪建. 川东北城口地区筇竹寺组页岩流变对孔隙结构的影响[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2022, 43(5): 513-518. |
| [9] | 段文刚, 吝文, 田继军, 马静辉, 杜猛, 罗锦昌. 川南罗布向斜五峰组—龙马溪组页岩孔隙分形特征与主控因素[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2022, 43(2): 153-159. |
| [10] | 石善志, 邹雨时, 王俊超, 张士诚, 李建民, 张啸寰. 吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组储集层脆性特征[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2022, 43(2): 169-176. |
| [11] | 姚振华, 覃建华, 高阳, 陈超, 刘振平, 张效恭. 吉木萨尔凹陷页岩油物性变化规律[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2022, 43(1): 72-78. |
| [12] | 卢婷, 王鸣川, 马文礼, 彭泽阳, 田玲钰, 李王鹏. 考虑多重应力敏感效应的页岩气藏压裂水平井试井模型[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2021, 42(6): 741-748. |
| [13] | 马明伟, 祝健, 李嘉成, 廖凯, 王俊超, 王飞. 吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组页岩油储集层渗吸规律[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2021, 42(6): 702-708. |
| [14] | 梁成钢, 谢建勇, 陈依伟, 刘娟丽, 何永清, 赵军, 王伟, 王良哲. 吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组页岩储集层裂缝成因及耦合关系[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2021, 42(5): 521-528. |
| [15] | 李晶晶, 孙国翔, 刘琦, 刘淼. 吉木萨尔凹陷芦一段页岩储集层孔隙结构及敏感性[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2021, 42(5): 541-547. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||