

新疆石油地质 ›› 2025, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (1): 13-21.doi: 10.7657/XJPG20250102
收稿日期:2024-07-25
修回日期:2024-08-17
出版日期:2025-02-01
发布日期:2025-01-24
通讯作者:
梁飞(1992-),男,安徽亳州人,讲师,博士,油气地质与沉积地质,(Tel)18611286346(Email)作者简介:牛君(1986-),女,新疆克拉玛依人,副教授,博士,储集层地质学和沉积学,(Tel)18892982076(Email)基金资助:
NIU Jun( ), WANG Cong, LIANG Fei(
), WANG Cong, LIANG Fei( )
)
Received:2024-07-25
Revised:2024-08-17
Online:2025-02-01
Published:2025-01-24
摘要:
为增强对准噶尔盆地陆梁隆起西部二叠系下乌尔禾组绿泥石和浊沸石矿物特征的认识,利用岩石薄片、电子探针、X射线衍射等,对其化学成分、产出状态及其对储集层物性的影响进行了研究。研究区下乌尔禾组绿泥石矿物晶体结构为三八面体,具孔隙衬里式、颗粒包膜式和孔隙充填式3种产出状态,属于铁镁过渡型偏富镁绿泥石,其八面体位置主要为Fe对Mg的置换,Al/(Al+Mg+Fe)为0.25~0.37,发育泥质岩石蚀变和镁铁质岩石转化形成的绿泥石,凝灰质等火山物质的水解溶蚀、黏土矿物之间的相互转化为其形成提供了大量的物质基础。浊沸石具连晶状、充填状和交代状3种产出状态,连晶状浊沸石周围发育大量岩屑,促进了浊沸石的形成;充填状浊沸石与绿泥石、方解石等矿物共生,在物质来源上相互竞争,在一定程度上抑制了浊沸石的形成;交代状浊沸石主要由交代长石和岩屑生成,导致Si/Al较高,耐酸性较强,不易被溶蚀。绿泥石与浊沸石对储集层物性均具有双重影响,绿泥石对储集层物性的改善作用较为明显,有利于形成优质储集层,浊沸石对改善储集层的作用较为有限。研究区下乌尔禾组随着埋藏深度增大,存在从碱性到弱酸性、再到碱性的成岩环境变化,其成岩系统较为封闭。
中图分类号:
牛君, 王聪, 梁飞. 绿泥石与浊沸石矿物特征及其对储集层物性的影响——以准噶尔盆地陆梁隆起西部下乌尔禾组为例[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(1): 13-21.
NIU Jun, WANG Cong, LIANG Fei. Mineral Features of Chlorite and Laumontite and Their Impacts on Reservoir Physical Properties: A Case Study of Lower Wuerhe Formation in Western Luliang Uplift, Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2025, 46(1): 13-21.
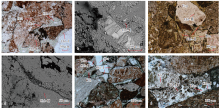
图3
研究区下乌尔禾组绿泥石产出状态 a—孔隙衬里式绿泥石(连片状)和颗粒包膜式绿泥石,XY2井,4 620.10 m,单偏光;b—孔隙衬里式绿泥石,YB4井,3 913.67 m,扫描电镜;c—颗粒包膜式绿泥石和孔隙充填式绿泥石,XY2井,4 854.67 m,单偏光;d—孔隙充填式绿泥石,XY2井,3 868.50 m,扫描电镜;e—孔隙衬里式绿泥石(栉壳状、竹叶状)绿泥石和孔隙充填式绿泥石,XY2井,4 718.56 m,单偏光;f—孔隙衬里式绿泥石(栉壳状)和浊沸石,YB4井,3 869.37 m,单偏光;Chl-Ⅰ—孔隙衬里式绿泥石;Chl-Ⅱ——颗粒包膜式绿泥石;Chl-Ⅲ—孔隙充填式绿泥石;Fsp—长石;Hul—片沸石;Ilm—钛铁质薄膜;Kfs—钾长石;Lmt—浊沸石;Qtz—石英。"
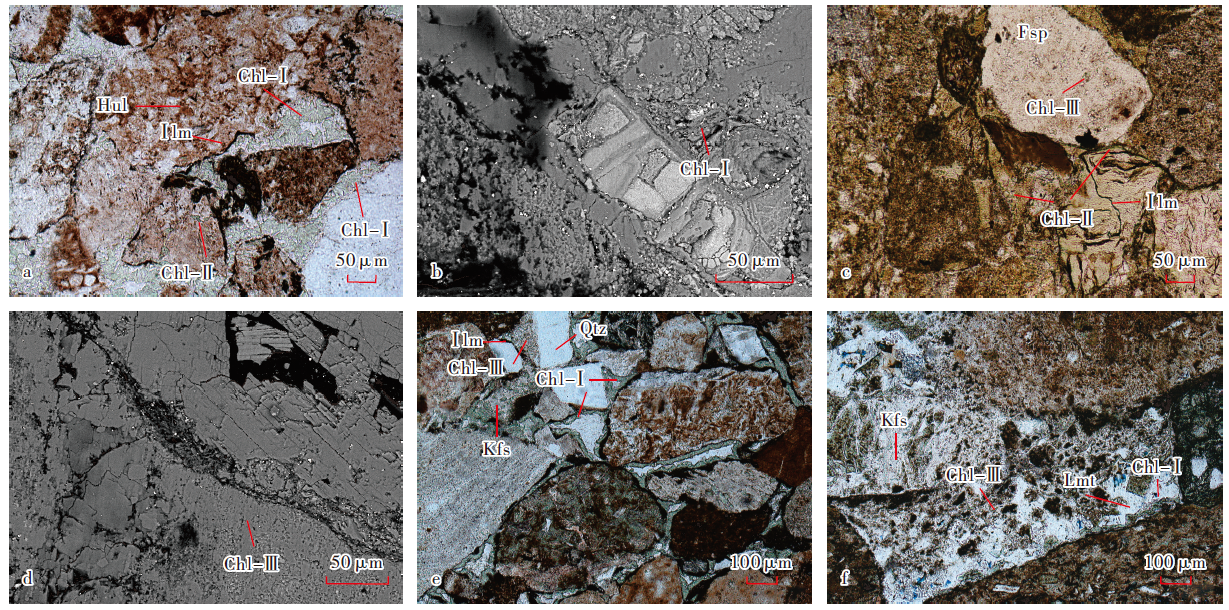
表1
研究区下乌尔禾组绿泥石矿物中部分氧化物含量"
| 井名 | 测点 | 产状 | 含量测试结果/% | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | MgO | FeO | Na2O | CaO | K2O | MnO | TiO2 | NiO | 合计 | |||
| XY2井 | 18-1 | 孔隙充填式 | 31.04 | 16.37 | 20.55 | 18.16 | 0.03 | 0.40 | 0.02 | 0.61 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 87.27 |
| 18-7 | 孔隙充填式 | 30.84 | 15.42 | 20.69 | 17.56 | 0.03 | 0.42 | 0.03 | 0.58 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 85.68 | |
| YB4井 | 61-3 | 颗粒包膜式 | 30.57 | 18.04 | 18.98 | 18.10 | 0.01 | 0.47 | 0.01 | 0.27 | 0.05 | 0 | 86.50 |
| 61-9 | 孔隙衬里式 | 30.15 | 12.72 | 17.67 | 23.52 | 0.09 | 0.29 | 0 | 0.42 | 0.05 | 0.16 | 85.07 | |
| 61-11 | 颗粒包膜式 | 33.87 | 14.29 | 31.31 | 6.42 | 0.05 | 0.42 | 0.03 | 0.12 | 0 | 0.04 | 86.55 | |
| 61-12 | 颗粒包膜式 | 32.23 | 20.84 | 18.10 | 17.54 | 0.06 | 0.40 | 0.04 | 0.25 | 0.05 | 0 | 89.51 | |
| M218井 | 59-3 | 孔隙衬里式 | 29.82 | 19.39 | 14.82 | 21.36 | 0.03 | 0.40 | 0.06 | 0.25 | 0 | 0.03 | 86.16 |
| Y001井 | 21-3 | 孔隙衬里式 | 29.56 | 15.48 | 23.28 | 19.55 | 0 | 0.45 | 0.04 | 0.52 | 0 | 0.04 | 88.92 |
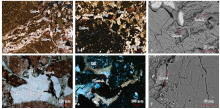
图6
研究区下乌尔禾组浊沸石产状特征 a—连晶状浊沸石和交代状浊沸石(交代岩屑),YB4井,3 913.67 m,单偏光;b—连晶状浊沸石和交代状浊沸石(交代岩屑),YB4井,3 915.00 m,单偏光;c—连晶状浊沸石和充填状浊沸石,YB4井,3 915.00 m,扫描电镜;d—充填状浊沸石和交代状浊沸石(交代长石),XY2井,4 717.76 m,单偏光;e—充填状浊沸石,XY2井,4 850.75 m,正交偏光;f—交代状浊沸石,YB4井,3 868.50 m,扫描电镜;Cal—方解石;Chl—绿泥石;Fsp—长石;Ilm—钛铁质薄膜;Lmt-a—连晶状浊沸石;Lmt-b—充填状浊沸石;Lmt-c—交代状浊沸石。"

表2
研究区下乌尔禾组浊沸石矿物中的主要氧化物含量"
| 井名 | 测点 | 产状 | 含量测试结果/% | Si/Al | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | MgO | FeO | Na2O | CaO | K2O | TiO2 | NiO | MnO | 合计 | ||||
| YB4井 | 61-1 | 连晶状 | 57.48 | 21.20 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.29 | 10.25 | 0.06 | 0.02 | — | — | 89.38 | 2.16 |
| 61-2 | 连晶状 | 53.56 | 20.56 | — | 0.04 | 0.17 | 11.09 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 85.50 | 2.08 | |
| 61-4 | 连晶状 | 53.91 | 20.64 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.24 | 10.81 | 0.07 | 0.03 | — | — | 85.80 | 2.08 | |
| 65-5 | 连晶状 | 53.61 | 20.37 | — | — | 0.05 | 10.43 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.04 | — | 84.57 | 2.10 | |
| 65-7 | 连晶状 | 52.58 | 20.52 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 10.85 | 0.03 | — | — | 0.02 | 84.16 | 2.04 | |
| 65-4 | 充填状 | 52.06 | 20.63 | — | 0.07 | — | 11.30 | — | 0.03 | — | — | 84.09 | 2.01 | |
| 65-6 | 充填状 | 56.44 | 20.72 | 0.05 | 0.14 | 0.21 | 10.38 | 0.06 | — | — | 0.02 | 88.02 | 2.17 | |
| 68-2 | 充填状 | 54.32 | 20.19 | — | 0.12 | 0.28 | 10.49 | 0.08 | — | — | — | 85.48 | 2.14 | |
| 68-6 | 充填状 | 53.77 | 20.98 | 0.06 | 0.12 | 0.02 | 11.21 | — | — | — | — | 86.16 | 2.04 | |
| XY2井 | 18-4 | 交代状 | 53.10 | 20.23 | — | 0.13 | 0.25 | 10.38 | 0.10 | 0.03 | — | — | 84.22 | 2.09 |
| 18-5 | 交代状 | 53.20 | 19.39 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.52 | 10.11 | 0.14 | — | 0.02 | — | 83.43 | 2.19 | |
| Y001井 | 21-1 | 交代状 | 54.10 | 20.03 | 0.05 | — | 0.30 | 10.27 | 0.17 | — | 0.04 | — | 84.96 | 2.15 |
| 21-2 | 交代状 | 53.32 | 19.53 | — | 0.08 | 0.32 | 10.43 | 0.12 | — | 0.02 | — | 83.82 | 2.17 | |
| [1] |
李峰, 姜振学, 肖中尧, 等. 塔里木盆地满东1致密气藏成因机制[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2014, 25(10):1568-1576.
doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2014.10.1568 |
|
LI Feng, JIANG Zhenxue, XIAO Zhongyao, et al. Genetic mechanism of Mandong 1 tight gas reservoir in Tarim Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2014, 25(10):1568-1576.
doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2014.10.1568 |
|
| [2] | 卞保力, 吴和源, 李娜, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷东斜坡中二叠统扇三角洲储层特征与成因[J]. 新疆地质, 2017, 35(3):306-312. |
| BIAN Baoli, WU Heyuan, LI Na, et al. Characteristics and origin of the middle Permian fan-delta reservoir in eastern slope area of Mahu sag,Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 2017, 35(3):306-312. | |
| [3] | 瞿建华, 钱海涛, 李鹏, 等. 玛湖凹陷百口泉组砾岩自生绿泥石成因及其对储集层物性的影响[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2017, 38(5):519-523. |
| QU Jianhua, QIAN Haitao, LI Peng, et al. Genesis of authigenic chlorite and its influence on reservoir physical properties in conglomerates of Baikouquan formation,Mahu sag[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2017, 38(5):519-523. | |
| [4] | 雷海艳, 樊顺, 鲜本忠, 等. 玛湖凹陷二叠系下乌尔禾组沸石成因及溶蚀机制[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2020, 32(5):102-112. |
| LEI Haiyan, FAN Shun, XIAN Benzhong, et al. Genesis and corrosion mechanism of zeolite of lower Wuerhe formation of Permian in Mahu sag[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2020, 32(5):102-112. | |
| [5] | 乔江华. 碎屑岩中的自生绿泥石及其对储层影响研究[J]. 辽宁化工, 2019, 48(2):143-147. |
| QIAO Jianghua. Chlorite in clastic rocks and its influence on reservoirs[J]. Liaoning Chemical Industry, 2019, 48 (2):143-147. | |
| [6] |
郭晖, 纪宝强, 杨森, 等. 准噶尔盆地环玛湖凹陷二叠系砂砾岩储层沸石类胶结物的形成及石油地质意义[J]. 石油学报, 2022, 43(3):341-354.
doi: 10.7623/syxb202203002 |
| GUO Hui, JI Baoqiang, YANG Sen, et al. Formation of zeolite cement in Permian sandy conglomerate reservoir in the circum-Mahu sag,Junggar Basin and its petroleum geological significance[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2022, 43(3):341-354. | |
| [7] | 何登发, 张磊, 吴松涛, 等. 准噶尔盆地构造演化阶段及其特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2018, 39(5):845-861. |
| HE Dengfa, ZHANG Lei, WU Songtao, et al. Tectonic evolution stages and features of the Junggar Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2018, 39(5):845-861. | |
| [8] | 钱海涛, 尤新才, 魏云, 等. 玛东地区百口泉组地层新认识及油气勘探意义[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 42(2):27-36. |
| QIAN Haitao, YOU Xincai, WEI Yun, et al. The new understanding and exploration significance in Triassic Baikouquan formation of eastern Mahu sag[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University (Science & Technology Edition), 2020, 42(2):27-36. | |
| [9] | 邹妞妞, 张大权, 姜杨, 等. 准噶尔玛东地区下乌尔禾组储层成岩作用与孔隙演化[J]. 地质科技情报, 2015, 34(1):42-48. |
| ZOU Niuniu, ZHANG Daquan, JIANG Yang, et al. Diagenesis and porosity evolution of Permian lower Urho formation reservoir in the Madong area,Junggar Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2015, 34(1):42-48. | |
| [10] | 王剑, 靳军, 张宝真, 等. 玛湖凹陷东斜坡区下乌尔禾组砂砾岩储层孔隙形成机理及优势储层成因分析[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2015, 15(23):136-142. |
| WANG Jian, JIN Jun, ZHANG Baozhen, et al. Pore formation mechanism and genesis of advantage reservoir of Permian lower Urho formation glutenite reservoir in the Madong area,Junggar Basin[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2015, 15(23):136-142. | |
| [11] | 张永波, 佟莹, 王东学, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷东斜坡夏子街组油气成藏条件及下步勘探方向[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 2022, 41(4):12-19. |
| ZHANG Yongbo, TONG Ying, WANG Dongxue, et al. Hydrocarbon accumulation conditions and future exploration direction of Xiazijie formation in east slope of Mahu sag in Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Development in Daqing, 2022, 41(4):12-19. | |
| [12] | 曾淑明, 张艳, 韩润生, 等. 滇西南翁孔坝铜多金属矿床绿泥石特征及其地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2023, 42(4):828-844. |
| ZENG Shuming, ZHANG Yan, HAN Runsheng, et al. Characteristics and geological significance of chlorite in the Wengkongba copper polymetallic deposit,southwest Yunnan[J]. Mineral Deposit, 2023, 42(4):828-844. | |
| [13] | 刘强, 赵葵东, 刘国奇, 等. 赣南草桃背铀矿床中绿泥石地球化学特征及成矿指示意义[J]. 高校地质学报, 2022, 28(6):874-893. |
| LIU Qiang, ZHAO Kuidong, LIU Guoqi, et al. Geochemical characteristics and metallogenic indications of chlorite in Caotaobei uranium deposit in southern Jiangxi province[J]. Journal of Geology of China Universities, 2022, 28(6):874-893. | |
| [14] | ZANG W, FYFE W S. Chloritization of the hydrothermally altered bedrock at the Igarape Bahia gold deposite,Carajas,Brazil[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 1995, 30(1):30-38. |
| [15] | XIE Xiaogong, BYERLY G R, FERRELL R E. Ⅱb trioctahedral chlorite from the Barberton greenstone belt:Crystal structure and rock composition constraints with implications to geothermometry[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1997, 126(3):275-291. |
| [16] | 潘春蓉, 牟平, 钟福军, 等. 南岭中段黄沙铀矿区绿泥石成因及其与铀成矿关系[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(2):348-361. |
| PAN Chunrong, MOU Ping, ZHONG Fujun, et al. Genesis of chlorite in the Huangsha uranium deposit,middle part of Nanling and relationship with uranium mineralization[J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(2):348-361. | |
| [17] | 刘松岩, 张达, 杨明建, 等. 熊耳山矿集区蒿坪沟Ag-Au多金属矿床绿泥石特征及其找矿意义[J]. 地质力学学报, 2024, 30(1):129-146. |
| LIU Songyan, ZHANG Da, YANG Mingjian, et al. Characteristics of chlorite from the Haopinggou Ag-Au polymetallic deposit in the Xiong’ershan ore concentration area and its exploration implications[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2018, 30(1):129-146. | |
| [18] | 张伟, 张寿庭, 曹华文, 等. 滇西小龙河锡矿床中绿泥石矿物特征及其指示意义[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 41(3):318-328. |
| ZHANG Wei, ZHANG Shouting, CAO Huawen, et al. Characteristics of chlorite minerals from Xiaolonghe tin deposit in west Yunnan,China and their geological implications[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology(Science & Technology Edition), 2014, 41(3):318-328. | |
| [19] | 张霞, 林春明, 陈召佑. 鄂尔多斯盆地镇泾区块上三叠统延长组砂岩中绿泥石矿物特征[J]. 地质学报, 2011, 85(10):1659-1671. |
| ZHANG Xia, LIN Chunming, CHEN Zhaoyou. Characteristics of chlorite minerals from Upper Triassic Yanchang formation in the Zhenjing area,Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2011, 85 (10):1659-1671. | |
| [20] | 祁利祺, 张晓童, 张浩宇, 等. 阜东斜坡区齐古组自生绿泥石的赋存状态与影响因素[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2023, 42(6):826-837. |
| QI Liqi, ZHANG Xiaotong, ZHANG Haoyu, et al. The occurrence status and influencing factors of autogenic chlorite in the Qigu formation of the Fudong slope area[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2023, 42(6):826-837. | |
| [21] | 田建锋, 高永利, 张蓬勃, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地合水地区长7致密油储层伊利石成因[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2013, 34(5):700-707. |
| TIAN Jianfeng, GAO Yongli, ZHANG Pengbo, et al. Genesis of illite in Chang 7 tight oil reservoir in Heshui area,Ordos Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2013, 34(5):700-707. | |
| [22] | 田建锋, 喻建, 张志国. 砂岩中碱性溶蚀研究进展[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(5):83-93. |
| TIAN Jianfeng, YU Jian, ZHANG Zhiguo. Advance in alkaline dissolution of sandstone[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(5):83-93. | |
| [23] |
郭沫贞, 寿建峰, 徐洋, 等. 准噶尔盆地中拐—西北缘地区二叠系沸石胶结物分布与控制因素[J]. 石油学报, 2016, 37(6):695-705.
doi: 10.7623/syxb201606001 |
|
GUO Mozhen, SHOU Jianfeng, XU Yang, et al. Distribution and controlling factors of Permian zeolite cement in Zhongguai-northwest margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2016, 37(6):695-705.
doi: 10.7623/syxb201606001 |
|
| [24] | 况昊, 周元东, 刘豪, 等. 沙湾凹陷砂砾岩沸石胶结物与碎屑颗粒粘结差异成因分析[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2024, 45(2):163-171. |
| KUANG Hao, ZHOU Yuandong, LIU Hao, et al. Genesis of differential bonding between zeolite cements and clastic particles in sandy conglomerates in Shawan sag,Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2024, 45(2):163-171. | |
| [25] | 张雪花, 黄思静, 兰叶芳, 等. 浊沸石溶解过程的热力学计算及地质意义[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2011, 23(2):64-69. |
| ZHANG Xuehua, HUANG Sijing, LAN Yefang, et al. Thermodynamic calculation of laumontite dissolution and its geological significance[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2011, 23(2):64-69. | |
| [26] | 丁波, 刘红旭, 李平, 等. 伊犁蒙其古尔铀矿床含矿层砂岩中高岭石形成机制及与铀成矿关系[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(8):2020-2036. |
| DING Bo, LIU Hongxu, LI Ping, et al. The genetic mechanism of kaolinite in ore-bearing sandstone in the Mengqigur uranium deposit,Yili,and its relation with uranium mineralization[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2019, 93(8):2020-2036. | |
| [27] | 况昊, 周润驰, 王钧民, 等. 玛湖凹陷与沙湾凹陷上乌尔禾组储集层差异及成因[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2023, 44(1):18-24. |
| KUANG Hao, ZHOU Runchi, WANG Junmin, et al. Differences and genesis of upper Wuerhe formation reservoirs in Mahu sag and Shawan sag[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2023, 44(1):18-24. | |
| [28] | 王涛, 张生银, 魏璞, 等. 沸石类矿物成因及其对储层储集性能的影响[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2022, 34(1):175-186. |
| WANG Tao, ZHANG Shengyin, WEI Pu, et al. Genesis of zeolite minerals and its influences on reservoir performances[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2022, 34(1):175-186. |
| [1] | 王春伟, 杨俊, 赵东睿, 杜焕福, 孙鑫, 王晔磊, 孟方华. 准噶尔盆地永进—征沙村地区侏罗系超深层致密砂岩储集层分级评价[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(1): 48-56. |
| [2] | 何昌松, 王秉乾, 魏双宝, 蒲振山, 王力龙, 马强, 张伟. 准噶尔盆地石钱滩凹陷石钱滩组地质特征及油气勘探[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2024, 45(6): 642-649. |
| [3] | 李枫凌, 方鑫鑫, 张镇, 马思洁, 刘荣军. 中拐凸起南斜坡八道湾组油层低阻成因及识别[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2024, 45(5): 541-551. |
| [4] | 王剑, 刘金, 潘晓慧, 张宝真, 李二庭, 周新艳. 吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组页岩油生烃母质及其生烃机理[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2024, 45(3): 253-261. |
| [5] | 李娜, 李卉, 刘鸿, 陈方文, 杨森, 邹阳. 玛湖凹陷玛页1井风城组页岩油地质甜点优选[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2024, 45(3): 271-278. |
| [6] | 毛锐, 白雨, 王盼, 黄志强. 玛西斜坡区风城组高含盐致密储集层流体识别[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2024, 45(3): 279-285. |
| [7] | 卞保力, 苏东旭, 蒋文龙, 王学勇, 潘进, 刘龙松, 蒋中发. 玛湖凹陷及周缘白碱滩组勘探突破与新认识[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2024, 45(3): 296-305. |
| [8] | 盖姗姗, 王子振, 刘浩杰, 张文盛, 于文政, 杨崇翔, 王玉萍. 永进油田致密储集层岩石力学参数剖面构建及应用[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2024, 45(3): 362-370. |
| [9] | 支东明, 陈旋, 杨润泽, 刘俊田, 于海跃, 马强. 准噶尔盆地东部残留海相凹陷勘探实践及全油气系统[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2024, 45(2): 127-138. |
| [10] | 刘超威, 李辉, 王泽胜, 王秋玉, 谢知益, 黄志强, 张蓉. 准噶尔盆地阜康凹陷二叠系上乌尔禾组油气勘探突破与启示[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2024, 45(2): 139-150. |
| [11] | 熊婷, 刘宇, 陈文利, 仲伟军, 贾春明, 姜涛, 尚春. 准噶尔盆地沙湾凹陷西斜坡上乌尔禾组油藏成藏模式新认识[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2024, 45(2): 151-162. |
| [12] | 张德尧. 春风油田沙湾组稠油油藏倾斜油水界面成因[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2024, 45(2): 205-212. |
| [13] | 方正, 陈勉, 王溯, 李嘉成, 吕嘉昕, 余延波, 焦冀博. 准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷页岩水平井水力压裂裂缝形态[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2024, 45(1): 72-80. |
| [14] | 甘仁忠, 熊健, 彭妙, 刘向君, 梁利喜, 丁乙. 陆相页岩储集层岩石力学特性及能量演化特征[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2023, 44(4): 472-478. |
| [15] | 支东明, 李建忠, 陈旋, 杨帆, 刘俊田, 林霖. 吐哈探区深层油气勘探进展及潜力评价[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2023, 44(3): 253-264. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||